Abstract
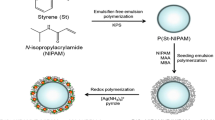
Environmentally sensitive polymer microgels are increasingly being used to enhance the catalytic activity of supported metal nanoparticles. Herein, we synthesized composite polymer microgels composed of the core–shell structure poly(styrene-N-isopropylacrylamide)/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) (P(St-NIPAM)/P(NIPAM-co-MAA)). Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) were loaded onto/into the network chains of the polymer microgels through a facile method. The prepared composite microgels were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy. The catalytic selectivity of P(St-NIPAM)/P(NIPAM-co-MAA)–Ag composite microgels for the reduction of hydrophilic 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) and hydrophobic nitrobenzene (NB) by NaBH4 was investigated. The results indicated that the introduction of PMAA segments into the microgel networks caused the poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) chains to separate into a shell layer and prevented the aggregation of AgNPs. The separated PNIPAM segments not only favor the mass transfer, but also possess thermosensitive function to modulate the catalytic activity of AgNPs. These structural features of the prepared composite microgels could enhance the selectivity and mass transfer of the reactants for catalytic reduction of 4-NP and NB through temperature modulation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Králik M, Biffis A (2001) Catalysis by metal nanoparticles supported on functional organic polymers. J Mol Catal A Chem 177:113–138
Welsch N, Ballauff M, Lu Y (2011) Microgels as nanoreactors: applications in catalysis. Adv Polym Sci 234:129–163
Li XH, Wang XC, Antonietti M (2012) Mesoporous g-C3N4 nanorods as multifunctional supports of ultrafine metal nanoparticles: hydrogen generation from water and reduction of nitrophenol with tandem catalysis in one step. Chem Sci 3:2170–2174
Gardella L, Basso A, Prato M, Monticelli O (2013) PLA/POSS nanofibers: a novel system for the immobilization of metal nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:7688–7692
Qiu LH, Peng YJ, Liu BQ, Lin BC, Peng Y, Malik MJ, Yan F (2012) Polypyrrole nanotube-supported gold nanoparticles: an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Appl Catal A Gen 413–414:230–237
Sahiner N (2013) Soft and flexible hydrogel templates of different sizes and various functionalities for metal nanoparticle preparation and their use in catalysis. Prog Polym Sci 38:1329–1356
Cheng JL, Wang Y, Teng C, Shang YY, Ren LB, Jiang BW (2014) Preparation and characterization of monodisperse, micrometer-sized, hierarchically porous carbon spheres as catalyst support. Chem Eng J 242:285–293
Lu JN, Toy PH (2009) Organic polymer supports for synthesis and for reagent and catalyst immobilization. Chem Rev 109:815–838
Hu YG, Zhao T, Zhu PL, Sun R (2012) Preparation of monodisperse polystyrene/silver composite microspheres and their catalytic properties. Colloid Polym Sci 290:401–409
Buitrago-Sierra R, García-Fernández MJ, Pastor-Blas MM, Sepúlveda-Escribano A (2013) Environmentally friendly reduction of a platinum catalyst precursor supported on polypyrrole. Green Chem 15:1981–1990
Hu HW, Xin JH, Hu H (2014) PAM/graphene/Ag ternary hydrogel: synthesis, characterization and catalytic application. J Mater Chem A 2:11319–11333
Qi JJ, Lv WP, Zhang GH, Li Y, Zhang GL, Zhang FB, Fan XB (2013) A graphene-based smart catalytic system with superior catalytic performances and temperature responsive catalytic behaviors. Nanoscale 5:6275–6279
Zhang JL, Zhang MX, Tang KJ, Verpoort F, Sun TL (2014) Polymer-based stimuli-responsive recyclable catalytic systems for organic synthesis. Small 10:32–46
Li DJ, Dunlap JR, Zhao B (2008) Thermosensitive water-dispersible hairy particle-supported Pd nanoparticles for catalysis of hydrogenation in an aqueous/organic biphasic system. Langmuir 24:5911–5918
Geng QR, Du JZ (2014) Reduction of 4-nitrophenol catalyzed by silver nanoparticles supported on polymer micelles and vesicles. RSC Adv 4:16425–16428
Thorne JB, Vine GJ, Snowden MJ (2011) Microgel applications and commercial considerations. Colloid Polym Sci 289:625–646
Zhang YM, Quek XY, Wu LL, Guan YJ, Hensen EJ (2013) Palladium nanoparticles entrapped in polymeric ionic liquid microgels as recyclable hydrogenation catalysts. J Mol Catal A Chem 379:53–58
Bergbreiter DE (2002) Using soluble polymers to recover catalysts and ligands. Chem Rev 102:3345–3384
Karg M (2012) Multifunctional inorganic/organic hybrid microgels. Colloid Polym Sci 290:673–688
Lu Y, Ballauff M (2011) Thermosensitive core-shell microgels: from colloidal model systems to nanoreactors. Prog Polym Sci 36:767–792
Hervés P, Pérez-Lorenzo M, Liz-Marzán LM, Dzubiella J, Lu Y, Ballauff M (2012) Catalysis by metallic nanoparticles in aqueous solution: model reactions. Chem Soc Rev 41:5577–5587
Lu A, Moatsou D, Longbottom DA, O’Reilly RK (2013) Tuning the catalytic activity of L-proline functionalized hydrophobic nanogel particles in water. Chem Sci 4:965–969
Döring A, Birnbaum W, Kuckling D (2013) Responsive hydrogels—structurally and dimensionally optimized smart frameworks for applications in catalysis, micro-system technology and material science. Chem Soc Rev 42:7391–7420
Mei Y, Lu Y, Polzer F, Ballauff M (2007) Catalytic activity of palladium nanoparticles encapsulated in spherical polyelectrolyte brushes and core-shell microgels. Chem Mater 19:1062–1069
Lu Y, Proch S, Schrinner M, Drechsler M, Kempe R, Ballauff M (2009) Thermosensitive core-shell microgel as a “nanoreactor” for catalytic active metal nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 19:3955–3961
Agrawal G, Schürings MP, Rijn PV, Pich A (2013) Formation of catalytically active gold–polymer microgel hybrids via a controlled in situ reductive process. J Mater Chem A 1:13244–13251
Pérez-Juste J, Pastoriza-Santos I, Liz-Marzán LM (2013) Multifunctionality in metal@microgel colloidal nanocomposites. J Mater Chem A 1:20–26
Shi S, Zhang L, Wang T, Wang QM, Gao Y, Wang N (2013) Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)–Au hybrid microgels: synthesis, characterization, thermally tunable optical and catalytic properties. Soft Matter 9:10966–10970
Crassous JJ, Mihut AM, Dietsch H, Pravaz O, Ackermann-Hirschi L, Hirt AM, Schurtenberger P (2014) Advanced multiresponsive comploids: from design to possible applications. Nanoscale 6:8726–8735
Füllbrandt M, Klitzing RV, Schönhals A (2013) The dielectric signature of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels at the volume phase transition: dependence on the crosslinking density. Soft Matter 9:4464–4471
Scherzinger C, Schwarz A, Bardow A, Leonhard K, Richtering W (2014) Cononsolvency of poly-N-isopropyl acrylamide (PNIPAM): microgels versus linear chains and macrogels. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 19:84–94
Carregal-Romero S, Buurma NJ, Pérez-Juste J, Liz-Marzán LM, Hervés P (2010) Catalysis by Au@pNIPAM nanocomposites: effect of the cross-linking density. Chem Mater 22:3051–3059
Lu Y, Mei Y, Ballauff M (2006) Thermosensitive core-shell particles as carrier systems for metallic nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 110:3930–3937
Lu Y, Yuan JY, Polzer F, Drechsler M, Preussner J (2010) In situ growth of catalytic active Au–Pt bimetallic nanorods in thermoresponsive core–shell microgels. ACS Nano 4:7078–7086
Zhang CX, Li C, Chen YY, Zhang Y (2014) Synthesis and catalysis of Ag nanoparticles trapped into temperature-sensitive and conductive polymers. J Mater Sci 49:6872–6882
Wu S, Dzubiella J, Kaiser J, Drechsler M, Guo XH, Ballauff M, Lu Y (2012) Thermosensitive Au-PNIPA yolk–shell nanoparticles with tunable selectivity for catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:2229–2233
Peng MF, Gao J, Zhang PP, Li Y, Sun XH, Lee ST (2011) Reductive self-assembling of Ag nanoparticles on germanium nanowires and their application in ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem Mater 23:3296–3301
Zhan F, Wang CC (2008) Preparation of thermoresponsive core–shell polymeric microspheres and hollow PNIPAM microgels. Colloid Polym Sci 286:889–895
Chang BS, Sha XY, Guo J, Jiao YF, Wang CC, Yang WL (2011) Thermo and pH dual responsive, polymer shell coated, magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug release. J Mater Chem 21:9239–9247
Teng W, Li XY, Zhao QD, Chen GH (2013) Fabrication of Ag/Ag3PO4/TiO2 heterostructure photoelectrodes for efficient decomposition of 2-chlorophenol under visible light irradiation. J Mater Chem A 1:9060–9068
Yin PG, Chen Y, Jiang L, You TT, Lu XY, Guo L, Yang SH (2011) Controlled dispersion of silver nanoparticles into the bulk of thermosensitive polymer microspheres: tunable plasmonic coupling by temperature detected by surface enhanced Raman scattering. Macromol Rapid Commun 32:1000–1006
Liu YY, Liu XY, Yang JM, Lin DL, Chen X, Zha LS (2012) Investigation of Ag nanoparticles loading temperature responsive hybrid microgels and their temperature controlled catalytic activity. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 393:105–110
Zhou DS, Xu N, Li L, Ji GD, Xue G (2003) Surface reactions on polymer thin films studied by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Phys Chem B 107:2748–2751
Wunder S, Lu Y, Albrecht M, Ballauff M (2011) Catalytic activity of faceted gold nanoparticles studied by a model reaction: evidence for substrate-induced surface restructuring. ACS Catal 1:908–916
Xu WY, Fan JB, Gao TY (2006) Electrochemical reduction characteristics and mechanism of nitrobenzene compounds in the catalyzed Fe-Cu process. J Environ Sci 18:379–387
Mu Y, Yu HQ, Zheng JC, Zhang SJ, Sheng GP (2004) Reductive degradation of nitrobenzene in aqueous solution by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 54:789–794
Kumar VV, Anthony SP (2014) AuNP based selective colorimetric sensor for cysteine at a wide pH range: investigation of capping molecule structure on the colorimetric sensing and catalytic properties. RSC Adv 4:18467–18472
Wunder S, Polzer F, Lu Y, Mei Y, Ballauff M (2010) Kinetic analysis of catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by metallic nanoparticles immobilized in spherical polyelectrolyte brushes. J Phys Chem C 114:8814–8820
Zhu CH, Hai ZB, Cui CH, Li HH, Chen JF, Yu SH (2012) In situ controlled synthesis of thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/Au nanocomposite hydrogels by gamma radiation for catalytic application. Small 8:930–936
Hoare T, Pelton R (2004) Highly pH and temperature responsive microgels functionalized with vinylacetic acid. Macromolecules 37:2544–2550
Gao J, Frisken BJ (2005) Influence of secondary components on the synthesis of self-cross-linked N-isopropylacrylamide microgels. Langmuir 21:545–551
Burmistrova A, Richter M, Eisele M, Üzüm C, Klitzing RV (2011) The effect of co-monomer content on the swelling/shrinking and mechanical behaviour of individually adsorbed PNIPAM microgel particles. Polymers 3:1575–1590
Lu Y, Mei Y, Drechsler M, Ballauff M (2006) Thermosensitive core–shell particles as carriers for Ag nanoparticles: modulating the catalytic activity by a phase transition in networks. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:813–816
Sun S, Hu J, Tang H, Wu PY (2011) Spectral interpretation of thermally irreversible recovery of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogel. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:5061–5067
Kratz K, Hellweg T, Eimer W (2000) Influence of charge density on the swelling of colloidal poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) microgels. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 170:137–149
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Daodao Hu for intensive and illuminating discussions. Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21173141), Key Industry Project of Shaanxi Province of China (2011K08-14), National 111 Project of China (B14041), and the Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University of China (IRT-14R33) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: TEM images of the prepared microgels at different initial concentration of [Ag(NH3)2]+ (Fig. S1), UV–Vis spectra of 4-NP (Fig. S2) and NB (Fig. S3) at different reaction temperatures, and the dependences of the hydrodynamic diameters of the composite microgels on temperature and pH value (Fig. S4).
ESM 1
(PDF 425 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, LQ., Hao, MM., Wang, HY. et al. Amphiphilic polymer-Ag composite microgels with tunable catalytic activity and selectivity. Colloid Polym Sci 293, 2405–2417 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3642-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3642-4