Abstract
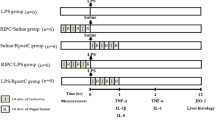
Remote ischemic conditioning (RIC) is acutely cardioprotective in ischemia–reperfusion injury. We aimed to evaluate the effect of RIC on septic cardiomyopathy and associated multi-organ failure in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sepsis mouse model. Balb/c mice were divided into sham, LPS, and LPS + RIC groups. LPS 10 mg/kg or saline control was injected intraperitoneally. RIC was performed by four cycles of 5 min ischemia and 5 min reperfusion of the left lower limb just before the LPS injection. Cardiac function on echocardiography, circulating mediators, blood biochemistry, and MAPK signalling was assessed. Survival 7 days after LPS injection was evaluated in sham-treated, RIC, and daily repeated RIC groups. An LPS-induced decrease in cardiac output was ameliorated by RIC with preserved left ventricular systolic function. LPS-induced increases in TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and high-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) were significantly suppressed by RIC. RIC also suppressed increases in plasma cardiac troponin I, aspartate transaminase, alanine transaminase, blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine with suppressed ERK and JNK phosphorylation in heart, liver, and kidney tissue. RIC significantly improved survival rate (p = 0.0037). Survival rate in the daily repeated RIC group was 100%, and it was higher than that in the RIC group (p = 0.0088). In summary, RIC reduced circulating and myocardial inflammatory mediators associated with septic cardiomyopathy, and led to improved ventricular function, cardiac output, and survival. Our data also revealed that chronic RIC has additional benefit in terms of mortality in sepsis. While further studies are required, RIC may be a clinically useful tool to ameliorate sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basalay MV, Davidson SM, Gourine AV, Yellon DM (2018) Neural mechanisms in remote ischaemic conditioning in the heart and brain: mechanistic and translational aspects. Basic Res Cardiol 113:25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0684-z
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW, Tracey KJ (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405:458–462 https://doi.org/10.1038/35013070
Bøtker HE, Kharbanda R, Schmidt MR, Bøttcher M, Kaltoft AK, Terkelsen CJ, Munk K, Andersen NH, Hansen TM, Trautner S, Lassen JF, Christiansen EH, Krusell LR, Kristensen SD, Thuesen L, Nielsen SS, Rehling M, Sørensen HT, Redington AN, Nielsen TT (2010) Remote ischaemic conditioning before hospital admission, as a complement to angioplasty, and effect on myocardial salvage in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a randomised trial. Lancet 375:727–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)62001-8
Donato M, Buchholz B, Rodriguez M, Pérez V, Inserte J, García-Dorado D, Gelpi RJ (2013) Role of the parasympathetic nervous system in cardioprotection by remote hindlimb ischaemic preconditioning. Exp Physiol 98:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2012.066217
Dumitru CD, Ceci JD, Tsatsanis C, Kontoyiannis D, Stamatakis K, Lin JH, Patriotis C, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Kollias G, Tsichlis PN (2000) TNF-α induction by LPS is regulated posttranscriptionally via a Tpl2/ERK-dependent pathway. Cell 103:1071–1083. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00210-5
Gedik N, Kottenberg E, Thielmann M, Frey UH, Jakob H, Peters J, Heusch G, Kleinbongard P (2017) Potential humoral mediators of remote ischemic preconditioning in patients undergoing surgical coronary revascularization. Sci Rep 7:12660 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12833-2
Hausenloy DJ, Bøtker HE, Ferdinandy P, Heusch G, Ng GA, Redington A, Garcia-Dorado D (2019) Cardiac innervation in acute myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Cardiovasc Res (in press). https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvz053
Heusch G (2019) The spleen in myocardial infarction. Circ Res 124:26–28. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314331
Heusch G, Bøtker HE, Przyklenk Redington A, Yellon D (2015) Remote ischemic conditioning. J Am Coll Cardiol 65:177–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.10.031
Huston JM, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ochani M, Ochani K, Yuan R, Rosas-Ballina M, Ashok M, Goldstein RS, Chavan S, Pavlov VA, Metz CN, Yang H, Czura CJ, Wang H, Tracey KJ (2007) Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation reduces serum high mobility group box 1 levels and improves survival in murine sepsis. Crit Care Med 35:2762–2768. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000288102.15975.BA
Huston JM, Ochani M, Rosas-Ballina M, Liao H, Ochani K, Pavlov VA, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ashok M, Czura CJ, Foxwell B, Tracey KJ, Ulloa L (2006) Splenectomy inactivates the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway during lethal endotoxemia and polymicrobial sepsis. J Exp Med 203:1623–1628. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20052362
Joseph B, Khalil M, Hashmi A, Hecker L, Kulvatunyou N, Tang A, Friese RS, Rhee P (2017) Survival benefits of remote ischemic conditioning in sepsis. J Surg Res 213:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.01.033
Kakihana Y, Ito T, Nakahara M, Yamaguchi K, Yasuda T (2016) Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction: pathophysiology and management. J Intensive Care 4:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40560-016-0148-1
Kharbanda RK, Mortensen UM, White PA, Kristiansen SB, Schmidt MR, Hoschtitzky JA, Vogel M, Sorensen K, Redington AN, MacAllister R (2002) Transient limb ischemia induces remote ischemic preconditioning in vivo. Circulation 106:2881–2883. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.87.3.893
Kim YH, Yoon DW, Kim JH, Lee JH, Lim CH (2014) Effect of remote ischemic post-conditioning on systemic inflammatory response and survival rate in lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation model. J Inflamm (Lond) 11:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-9255-11-16
Kleinbongard P, Skyschally A, Heusch G (2016) Cardioprotection by remote ischemic conditioning and its signal transduction. Pflugers Arch 469:159–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1922-6
Konstantinov IE, Arab S, Kharbanda RK, Li J, Cheung MM, Cherepanov V, Downey GP, Liu PP, Cukerman E, Coles JG, Redington AN (2004) The remote ischemic preconditioning stimulus modifies inflammatory gene expression in humans. Physiol Genomics 19:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00046.2004
Li J, Rohailla S, Gelber N, Rutka J, Sabah N, Gladstone RA, Wei C, Hu P, Kharbanda RK, Redington AN (2014) MicroRNA-144 is a circulating effector of remote ischemic preconditioning. Basic Res Cardiol 109:423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-014-0423-z
Lieder HR, Kleinbongard P, Skyschally A, Hagelschuer H, Chilian WM, Heusch G (2018) Vago-splenic axis in signal transduction of remote ischemic preconditioning in pigs and rats. Circ Res 123:1152–1163. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313859
McLeod SL, Iansavichene A, Cheskes S (2017) Remote ischemic perconditioning to reduce reperfusion injury during acute ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc 17:6. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.005522
Niu J, Azfer A, Kolattukudy PE (2008) Protection against lipopolysacharide-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of soluble Fas. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.09.016
Orbegozo Cortés D, Su F, Santacruz C, Hosokawa K, Donadello K, Creteur J, De Backer D, Vincent JL (2016) Ischemic conditioning protects the microcirculation, preserves organ function, and prolongs survival in sepsis. Shock 45:419–427. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000526
Pavlov VA, Ochani M, Yang LH, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ochani K, Lin X, Levi J, Parrish WR, Rosas-Ballina M, Czura CJ, Larosa GJ, Miller EJ, Tracey KJ, Al-Abed Y (2007) Selective α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 improves survival in murine endotoxemia and severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 35:1139–1144. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000259381.56526.96
Pryds K, Kristiansen J, Neergaard-Petersen S, Nielsen RR, Schmidt MR, Refsgaard J, Kristensen SD, Bøtker HE, Hvas AM, Grove EL (2017) Effect of long-term remote ischaemic conditioning on platelet function and fibrinolysis in patients with chronic ischaemic heart failure. Thromb Res 153:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2017.03.008
Pryds K, Nielsen RR, Jorsal A, Hansen MS, Ringgaard S, Refsgaard J, Kim WY, Petersen AK, Bøtker HE, Schmidt MR (2017) Effect of long-term remote ischemic conditioning in patients with chronic ischemic heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol 112:67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0658-6
Przyklenk K, Bauer B, Ovize M, Kloner RA, Whittaker P (1993) Regional ischemic ‘preconditioning’ protects remote virgin myocardium from subsequent sustained coronary occlusion. Circulation 87:893–899. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.87.3.893
Rohailla S, Clarizia N, Sourour M, Sourour W, Gelber N, Wei C, Li J, Redington AN (2014) Acute, delayed and chronic remote ischemic conditioning is associated with downregulation of mTOR and enhanced autophagy signaling. PLoS ONE 9:e111291. (https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111291)
Sabio G, Davis RJ (2014) TNF and MAP kinase signaling pathways. Semin Immunol 26:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2014.02.009
Shimizu M, Saxena P, Konstantinov IE, Cherepanov V, Cheung MM, Wearden P, Zhangdong H, Schmidt M, Downey GP, Redington AN (2010) Remote ischemic preconditioning decreases adhesion and selectively modifies functional responses of human neutrophils. J Surg Res 158:155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2008.08.010
Shimizu M, Tropak M, Diaz RJ, Suto F, Surendra H, Kuzmin E, Li J, Gross G, Wilson GJ, Callahan J, Redington AN (2009) Transient limb ischaemia remotely preconditions through a humoral mechanism acting directly on the myocardium: evidence suggesting cross-species protection. Clin Sci (Lond) 117:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20080523
Thielmann M, Kottenberg E, Kleinbongard P, Wendt D, Gedik N, Pasa S, Price V, Tsagakis K, Neuhäuser M, Peters J, Jakob H, Heusch G (2013) Cardioprotective and prognostic effects of remote ischaemic preconditioning in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery: a single-centre randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet 382:597–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61450-6
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM, Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, Manogue KR, Faist E, Abraham E, Andersson J, Andersson U, Molina PE, Abumrad NN, Sama A, Tracey KJ (1999) HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 285:248–251. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.285.5425.248
Wang Q, Liu GP, Xue FS, Wang SY, Cui XL, Li RP, Yang GZ, Sun C, Liao X (2015) Combined vagal stimulation and limb remote ischemic perconditioning enhances cardioprotection via an anti-inflammatory pathway. Inflammation 38:1748–1760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0152-y
Wei M, Xin P, Li S, Tao J, Li Y, Li J, Liu M, Li J, Zhu W, Redington AN (2011) Repeated remote ischemic postconditioning protects against adverse left ventricular remodeling and improves survival in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Circ Res 108:1220–1225. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.236190
Xu H, Su Z, Wu J, Yang M, Penninger JM, Martin CM, Kvietys PR, Rui T (2010) The alarmin cytokine, high mobility group box 1, is produced by viable cardiomyocytes and mediates the lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial dysfunction via a TLR4/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase γ pathway. J Immunol 184:1492–1498. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0902660
Yang H, Ochani M, Li J, Qiang X, Tanovic M, Harris HE, Susarla SM, Ulloa L, Wang H, DiRaimo R, Czura CJ, Wang H, Roth J, Warren HS, Fink MP, Fenton MJ, Andersson U, Tracey KJ (2004) Reversing established sepsis with antagonists of endogenous high-mobility group box 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:296–301. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2434651100
Zhang J, Zhang J, Yu P, Chen M, Peng Q, Wang Z, Dong N (2017) Remote ischaemic preconditioning and sevoflurane postconditioning synergistically protect rats from myocardial injury induced by ischemia and reperfusion partly via inhibition TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 41:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1159/000455815
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflict of interests to report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honda, T., He, Q., Wang, F. et al. Acute and chronic remote ischemic conditioning attenuate septic cardiomyopathy, improve cardiac output, protect systemic organs, and improve mortality in a lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis model. Basic Res Cardiol 114, 15 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-019-0724-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-019-0724-3