Abstract
Purpose
We evaluated the effect of low-calorie mediterranean (MD) and vegetarian (VD) diets on gut microbiome (GM) composition and short-chain-fatty acids (SCFA) production.
Methods
We performed next generation sequencing (NGS) of 16S rRNA and SCFA analysis on fecal samples of 23 overweight omnivores (16 F; 7 M) with low-to-moderate cardiovascular risk. They were randomly assigned to a VD or MD, each lasting 3 months, with a crossover study design.
Results
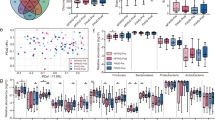
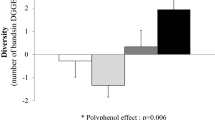
Dietary interventions did not produce significant diversity in the GM composition at higher ranks (family and above), neither between nor within MD and VD, but they did it at genus level. MD significantly changed the abundance of Enterorhabdus, Lachnoclostridium and Parabacteroides, while VD significantly affected the abundance of Anaerostipes, Streptococcus, Clostridium sensu stricto, and Odoribacter. Comparison of the mean variation of each SCFA between MD and VD showed an opposite and statistically significant trend for propionic acid (+ 10% vs − 28%, respectively, p = 0.034). In addition, variations of SCFA were negatively correlated with changes of some inflammatory cytokines such as VEGF, MCP-1, IL-17, IP-10 and IL-12, only after MD. Finally, correlation analyses showed a potential relationship—modulated by the two diets—between changes of genera and changes of clinical and biochemical parameters.
Conclusions
A short-term dietary intervention with MD or VD does not induce major change in the GM, suggesting that a diet should last longer than 3 months for scratching the microbial resilience. Changes in SCFA production support their role in modulating the inflammatory response, thus mediating the anti-inflammatory and protective properties of MD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Sequence data sets from 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing supporting the conclusion of this article are available in GenBank with study accession number: PRJNA510080
References
Sommer F, Bäckhed F (2013) The gut microbiota—masters of host development and physiology. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:227–238
Russell WR, Hoyles L, Flint HJ, Dumas ME (2013) Colonic bacterial metabolites and human health. Curr Opin Micr 16:246–254
Salonen A, Lahti L, Salojärvim J, Holtrop G, Korpelam K, Duncan SH, Date P, Farquharson F, Johnstone AJ, Lobley GE, Louis P, Flint HJ, de Vos WM (2014) Impact of diet and individual variation on intestinal microbiota composition and fermentation products in obese men. ISME J 8:2218–2230
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444:1027–1031
Cerf-Bensussan N, Gaboriau-Routhiau V (2010) The immune system and the gut microbiota: friends or foes? Nat Rev Immunol 10:735–744
Burcelin R, Garidou L, Pomié C (2012) Immuno-microbiota cross and talk: the new paradigm of metabolic diseases. Sem Immunol 24:67–74
Everard A, Cani PD (2013) Diabetes, obesity and gut microbiota. Best Prac Res Clin Gastroenterol 27:73–83
De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Di Paola M, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P (2010) Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:14691–14696
Dinu M, Abbate R, Gensini GF, Casini A, Sofi F (2017) Vegetarian, vegan diets and multiple health outcomes: a systematic review with meta-analysis of observational studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57:3640–3649
Dinu M, Pagliai G, Casini A, Sofi F (2018) Mediterranean diet and multiple health outcomes: an umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies and randomised trials. Eur J Clin Nutr 72:30–43
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R, Sinha R, Gilroy E, Gupta K, Baldassano R, Nessel L, Li H, Bushman FD, Lewis JD (2011) Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 334:105–108
De Filippis F, Pellegrini N, Vannini L, Jeffery IB, La Storia A, Laghi L, Serrazanetti DI, Di Cagno R, Ferrocino I, Lazzi C, Turroni S, Cocolin L, Brigidi P, Neviani E, Gobbetti M, O’Toole PW, Ercolini D (2016) High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut 65:1812–1821
Wu GD, Compher C, Chen EZ, Smith SA, Shah RD, Bittinger K, Chehoud C, Albenberg LG, Nessel L, Gilroy E, Star J, Weljie AM, Flint HJ, Metz DC, Bennett MJ, Li H, Bushman FD, Lewis JD (2014) Comparative metabolomics in vegans and omnivores reveal constraints on diet-dependent gut microbiota metabolite production. Gut 65:63–72
Shankar V, Gouda M, Moncivaiz J, Gordon A, Reo NV, Hussein L, Paliy O (2017) Differences in gut metabolites and microbial composition and functions between Egyptian and U.S. children are consistent with their diets. Systems 2:e00169-16
Sofi F, Dinu M, Pagliai G, Cesari F, Gori AM, Sereni A, Becatti M, Fiorillo C, Marcucci R, Casini A (2018) Low-calorie vegetarian vs. Mediterranean diets for reducing body weight and improving cardiovascular risk profile: the CARDIVEG study. Circulation 137:1103–1113
Sofi F, Dinu M, Pagliai G, Cesari F, Marcucci R, Casini A (2016) Mediterranean vs. vegetarian diet for cardiovascular prevention (the CARDIVEG study): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 17:233
Russo E, Bacci G, Chiellini C, Fagorzi C, Niccolai E, Taddei E, Ricci F, Ringressi MN, Borrelli R, Melli F, Miloeva M, Bechi P, Mengoni A, Fani R, Amedei A (2018) Preliminary comparison of oral and intestinal human microbiota in patients with colorectal cancer: a pilot study. Front Microbiol 8:2699
Zhang J, Kobert K, Flouri T, Stamatakis A (2014) PEAR: a fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 30:614–620
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DA, Caporaso JG (2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 10:57–59
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D590–D596
Langille MG, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Vega Thurber RL, Knight R, Beiko RG, Huttenhower C (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31:814–821
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12:R60
Zapala MA, Schork NJ (2006) Multivariate regression analysis of distance matrices for testing associations between gene expression patterns and related variables. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:19430–19435
Fagan A, Culhane AC, Higgins DG (2007) A multivariate analysis approach to the integration of proteomic and gene expression data. Proteomics 7:2162–2171
Cho I, Blaser MJ (2012) The human microbiome: at the interface of health and disease. Nat Rev Genet 13:260–270
Zhang C, Björkman A, Cai K, Liu G, Wang C, Li Y, Xia H, Sun L, Kristiansen K, Wang J, Han J, Hammarström L, Pan-Hammarström Q (2018) Impact of a 3-months vegetarian diet on the gut microbiota and immune repertoire. Front Immunol 9:908
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444:1022–1023
Duncan SH, Belenguer A, Holtrop G, Johnstone AM, Flint HJ, Lobley GE (2007) Reduced dietary intake of carbohydrates by obese subjects results in decreased concentrations of butyrate and butyrate-producing bacteria in feces. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1073–1078
Walker AW, Ince J, Duncan SH, Webster LM, Holtrop G, Ze X, Brown D, Stares MD, Scott P, Bergerat A, Louis P, McIntosh F, Johnstone AM, Lobley GE, Parkhill J, Flint HJ (2011) Dominant and diet-responsive groups of bacteria within the human colonic microbiota. ISME J 5:220–230
Mariat D, Firmesse O, Levenez F, Guimarăes V, Sokol H, Doré J, Corthier G, Furet JP (2009) The firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiol 9:123
Hollister EB, Riehle K, Luna RA, Weidler EM, Rubio-Gonzales M, Mistretta TA, Doddapaneni HR, Metcalf GA, Muzny DM, Gibbs RA, Petrosino JF, Shulman RJ, Versalovic J (2015) Structure and function of the healthy pre-adolescent pediatric gut microbiome. Microbiome 3:36
Geurts L, Lazarevic V, Derrien M, Everard A, Van Roye M, Knauf C, Valet P, Girard M, Muccioli GG, François P, de Vos WM, Schrenzel J, Delzenne NM, Cani PD (2011) Altered gut microbiota and endocannabinoid system tone in obese and diabetic leptin-resistant mice: impact on apelin regulation in adipose tissue. Front Microbiol 2:149
Yan O, Gu Y, Li X, Yang W, Jia L, Chen C, Han X, Huang Y, Zhao L, Li P, Fang Z, Zhou J, Guan X, Ding Y, Wang S, Khan M, Xin Y, Li S, Ma Y (2017) Alterations of the Gut Microbiome in Hypertension. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:381
Velasquez-Manoff M (2015) Gut microbiome: the peacekeepers. Nature 518:S3–S11
Rajilić-Stojanović M, de Vos WM (2014) The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38:996–1047
Lakshminarayanan B, Harris HM, Coakley M, O’Sullivan O, Stanton C, Pruteanu M, Shanahan F, O’Toole PW, Ross RP, ELDERMET consortium (2013) Prevalence and characterization of Clostridium perfringens from the faecal microbiota of elderly Irish subjects. J Med Microbiol 62:457–466
Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Shima T, Imaoka A, Kuwahara T, Momose Y, Cheng G, Yamasaki S, Saito T, Ohba Y, Taniguchi T, Takeda K, Hori S, Ivanov II, Umesaki Y et al (2011) Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 331:337–341
Kosiewicz MM, Dryden GW, Chhabra A, Alard P (2014) Relationship between gut microbiota and development of T cell associated disease. FEBS Lett 588:4195–4206
Kim CH, Park J, Kim M (2014) Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids, T cells, and inflammation. Immune Net 14:277–288
Meddah AT, Yazourh A, Desmet I, Risbourg B, Verstraete W, Romond MB (2001) The regulatory effects of whey retentate from bifidobacteria fermented milk on the microbiota of the simulator of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem (SHIME). J Appl Microbiol 6:1110–1117
Scott KP, Martin JC, Campbell G, Mayer CD, Flint HJ (2006) Whole-genome transcription profiling reveals genes up-regulated by growth on fucose in the human gut bacterium “Roseburia inulinivorans”. J Bacteriol 188:4340434–4340439
Mortensen PB, Clausen MR (1996) Short-chain fatty acids in the human colon: relation to gastrointestinal health and disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 216(s):132–148
Sakurazawa T, Ohkusa T (2005) Cytotoxicity of organic acids produced by anaerobic intestinal bacteria on cultured epithelial cells. J Gastroenterol 40(6):600–609
Yang J, Rose DJ (2016) The impact of long-term dietary pattern of fecal donor on in vitro fecal fermentation properties of inulin. Food Funct 7(4):1805–1813
Richards LB, Li M, van Esch BCAM, Garssen J, Folkerts G (2016) The effects of short-chain fatty acids on the cardiovascular system. PharmaNutrition 4:68–111
Casas R, Urpi-Sardà M, Sacanella E, Arranz S, Corella D, Castañer O, Lamuela-Raventós RM, Salas-Salvadó J, Lapetra J, Portillo MP, Estruch R (2017) Anti-inflammatory effects of the mediterranean diet in the early and late stages of atheroma plaque development. Med Inflamm 1:1–12
Acknowledgements
The research was founded with a grant from the regional contribution of “The Programma Attuativo Regionale (Toscana) funded by FAS (now FSC), Grant number 4042.16092014.066000029, the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MIUR) and the Foundation ‘Ente Cassa di Risparmio di Firenze’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AA and FS conceived the study, participated in the design of the study, wrote the study protocol, and prepared the final version of the manuscript. FS has been responsible for recruitment and clinical evaluations. GP, ER and MD, participated in the design of the study. ER and SB conducted microbiota experiments. GB, SB and MM performed SCFA analysis. AM, EN and VP performed the statistical analysis. RM participated in the writing of the study protocol. AC, GMR and BG participated in the design of the study and critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. EN, GP, ER wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors read and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pagliai, G., Russo, E., Niccolai, E. et al. Influence of a 3-month low-calorie Mediterranean diet compared to the vegetarian diet on human gut microbiota and SCFA: the CARDIVEG Study. Eur J Nutr 59, 2011–2024 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02050-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02050-0