Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to evaluate the swallowing problems by fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) study in both short- and long-gap patients after esophageal atresia (EA) repair.
Methods
Hospital records of patients who had undergone surgery for EA were reviewed retrospectively. Patients were divided into two groups as short-gap (SG) group (n:16) and long-gap (LG) group (n:10) to compare the swallowing problems. FEES study was performed, and the results were discussed in detail.
Results
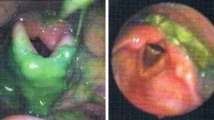
There were twenty-six (16 M/10 F) patients with a mean age at evaluation was 7.52 ∓ 3.68 years. Mean follow-up period was 75.35 ∓ 44.48 months. In FEES study, pharyngeal phase abnormalities were detected in 10 patients (38.4%). Pharyngeal phase abnormalities were detected significantly higher in LG group (p:0.015). Laryngeal penetration/aspiration was seen in four patients on FEES study (15.3%). All of them was in LG group (40%). Laryngeal penetration/aspiration was seen significantly higher in LG group (p:0.014).
Conclusion
This is the first study to conduct FEES study in children after esophageal atresia repair to evaluate their swallowing conditions. Even though our sample is small, swallowing problems are more common than expected in the cases of LG when compared to SG.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EA:
-
Esophageal atresia
- FEES:
-
Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing
- FOIS:
-
Functional oral intake scale
- GER:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux
- PAS:
-
Penetration–aspiration scale
- VFSS:
-
Videofluoroscopy swallowing study
References
Rintala RJ, Pakarinen MP (2013) Long-term outcome of esophageal anastomosis. Eur J Pediatr Surg 23:2019–2025. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1347912
Tuğcu GD, Soyer T, Polat SE et al (2021) Evaluation of pulmonary complications and affecting factors in children for repaired esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula. Respir Med 181:106376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106376
Rayyan M, Allegaert K, Omari T et al (2015) Dysphagia in children with esophageal atresia: current diagnostic options. Eur J Pediatr Surg 25:326–332. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1559818
Krishnan U, Mousa H, Dall’oglio L et al (2016) ESPGHAN-NASPGHAN guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of gastrointestinal and nutritional complications in children with esophageal atresia-tracheoesophageal fistula. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 63:550–570. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000001401
Lemoine C, Aspirot A, Le Henaff G et al (2013) Characterization of esophageal motility following esophageal atresia repair using high-resolution esophageal manometry. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 56:609–614. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e3182868773
Mahoney L, Rosen R (2016) Feeding difficulties in children with esophageal atresia. Pediatr Respir Rev 19:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prrv.2015.06.002
SerelArslan S, Demir N, Karaduman AA et al (2021) Dysphagia in children with EA-TEF from the perspective of pediatric surgeons in clinical settings. Dysphagia 36:644–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10178-z
Conforti A, Valfre L, Falbo M et al (2015) Feeding and swallowing disorders in esophageal atresia patients: a review of a critical issue. Eur J Pediatr Surg 25:318–325. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1559819
Cartabuke RH, Lopez R, Thota PN (2016) Long-term esophageal and respiratory outcomes in children with esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula. Gastroenterol Rep 4:310–314. https://doi.org/10.1093/gastro/gov055
Yalçın S, Demir N, Serel S et al (2015) The evaluation of deglutition with videofluoroscopy after repair of esophageal atresia and/or tracheoesophageal fistula. J Pediatr Surg 50:1823–1827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2015.07.002
Demir N, Arslan SS, Yalcin S et al (2017) Alterations in hyolaryngeal elevation after esophageal anastomosis: a possible mechanism for airway aspiration. J Pediatr Surg 52:1580–1582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.04.001
Langmore SE, Shatz K, Olson N (1991) Endoscopic and videofluoroscopic evaluation of swallowing and aspiration. Ann Otol Rhinol Layrngol 100:678–681. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949110000815
Kelly AM, Drinnan MJ, Leslie P (2007) Assessing penetration and aspiration: how do videofluoroscopy and fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing compare? Laryngoscope 117:1723–1727. https://doi.org/10.1097/mlg.0b013e318123ee6a
Willging JP (1995) Endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 32:S107–S108. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-5876(94)01174-v
Castilloux J, Noble AJ, Faure C (2010) Risk factors for short-and long-term morbidity in children with esophageal atresia. J Pediatr 156:755–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.11.038
Baxter KJ, Baxter LM, Landry AM et al (2018) Structural airway abnormalities contribute to dysphagia in children with esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula. J Pediatr Surg 53:1655–1659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.12.025
Crary MA, Carnaby Mann GD, Groher ME (2005) Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:1516–1520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2004.11.049
Rosenbeck JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB et al (1996) A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 11:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417897
Marinschek S, Pahsini K, Aguiriano-Moser V et al (2020) Efficacy of a standardized tube weaning program in pediatric patients with feeding difficulties after successful repair of their esophageal atresia/tracheoesophageal fistula. Eur J Pediatr 179:1729–1737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-020-03673-w
Spitz L (2006) Esophageal atresia. Lessons I have learned in a 40-year experience. J Pediatr Surg 41:1635–1640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2006.07.004
Rommel N, Rayyan M, Scheerens C et al (2017) The potential benefits of applying recent advances in esophageal motility testing in patients with esophageal atresia. Front Pediatr 5:137. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2017.00137
Coppens CH, van den Engel-Hoek L, Scharbatke H et al (2016) Dysphagia in children with repaired oesophageal atresia. Eur J Pediatr 175:1209–1217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-016-2760-4
Yi YG, Shin HI (2019) Psychometrics of the functional oral intake scale for infants. Front Pediatr 7:156. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2019.00156
Yi YG, Shin HI (2019) Psychometrics of the functional oral intake scale for children with dysphagia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 71:686–691. https://doi.org/10.1097/mpg.0000000000002861
Mahoney L, Rosen R (2017) Feeding problems and underlying mechanism in the esophageal atresia -Tracheoesophageal fistula patient. Front Pediatr 5:127
Langmore SE (2017) History of fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing for evaluation and management of pharyngeal dysphagia: changes over the years. Dysphagia 32:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9775-x
Beer S, Hartlieb T, Müller A et al (2014) Aspiration in children and adolescents with neurogenic dysphagia: comparison of clinical judgment and fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Neuropediatrics 45:402–405. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1387814
Da Silva AP, LubiancaNeto JF, Santoro PP (2010) Comparison between videofluoroscopy and endoscopic evaluation of swallowing for the diagnosis of dysphagia in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 143:204–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.027
Pavithran J, Puthiyottil IV, Kumar M, Nikitha AV, Vidyadhaaran S, Bhaskaran R et al (2020) Exploring the utility of fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in young children–a comprasion with videofluoroscopy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 138:110339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110339
Thottam PJ, Silva RC, McLevy JD et al (2015) Use of fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) in the management of psychogenic dysphagia in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 79:108–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.11.007
Haller L, Osterbauer B, Maldonado K, Bhardwaj V, Bansal M, Peck K et al (2020) Factors impacting participation in flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 138:110323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110323
Hörmann M, Pokieser P, Scharitzer M et al (2002) Videofluoroscopy of deglutition in children after repair of esophageal atresia. Acta Radiol 43:507–510. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0455.2002.430511.x
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not for profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest to disclose
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Celtik, U., Eyigor, S., Divarci, E. et al. Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) study: the first report in children to evaluate the oropharyngeal dysphagia after esophageal atresia repair. Pediatr Surg Int 38, 1227–1233 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-022-05169-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-022-05169-0