Abstract
Background
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), one of the most severe emergencies in neonates, is a multifactorial disease with diverse risk factors.
Objectives
To compare between the clinical and laboratory characteristics of premature infants diagnosed with early-onset NEC (EO-NEC) and those with late-onset NEC (LO-NEC).
Patients and methods
Enrolled infants were identified from prospective local data collected for the Israel National very low birth weight (VLBW, < 1500 g) infant database and from the local electronic patient files data base for the period 1996–2017.
Results
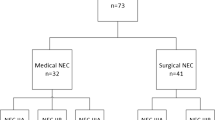
Overall, 95 VLBW infants (61, 64.21% EO-NEC and 34, 35.87% LO-NEC) were enrolled. EO-NEC infants had higher rate of IVH grade 3 and 4 (26.2% vs 2.9%, p = 0.005) and were more likely to undergo surgery (49.2% vs 26.5%, p = 0.031). LO-NEC infants had a higher incidence of previous bloodstream infections (35.3% vs 8.2%, p = 0.002) compared to EO-NEC. In multivariable analysis models, surgical intervention was associated with EO-NEC (OR: 4.627, p = 0.013) as well as PDA and positive blood culture prior to the NEC episode.
Conclusions
Our data support the hypothesis that EO-NEC has significant different clinical and microbiological attributes compared to LO-NEC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPD:
-
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- BSI:
-
Blood stream infection
- CONS:
-
Coagulase negative staphylococci
- cPVL:
-
Cystic periventricular leukomalacia
- EO:
-
Early onset
- GA:
-
Gestational age
- IVH:
-
Intra-ventricular hemorrhage
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- LO:
-
Late onset
- NEC:
-
Necrotizing enterocolitis
- PDA:
-
Patent ductus arteriosus
- RDS:
-
Respiratory distress syndrome
- ROP:
-
Retinopathy of prematurity
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Neu J (1996) Necrotizing enterocolitis: the search for a unifying pathogenic theory leading to prevention. Pediatr Clin North Am 43:409–432
Samuels N, van de Graaf RA, de Jonge RCJ, Reiss IKM, Vermeulen MJ (2017) Risk factors for necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates: a systematic review of prognostic studies. BMC Pediatr 17:105
Berkhout DJC, Klaassen P, Niemarkt HJ, de Boode WP, Cossey V, van Goudoever JB, Hulzebos CV, Andriessen P, van Kaam AH, Kramer BW, van Lingen RA, Vijlbrief DC, van Weissenbruch MM, Benninga M, de Boer NKH, de Meij TGJ (2018) Risk factors for necrotizing enterocolitis: a prospective multicenter case-control study. Neonatology 114:277–284
Kosloske AM (1984) Pathogenesis and prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis: a hypothesis based on personal observation and a review of the literature. Pediatrics 74:1086–1092
Kosloske AM (1994) Epidemiology of necrotizing enterocolitis. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway: 1992) Suppl 396:2–7
Horbar JD, Edwards EM, Greenberg LT, Morrow KA, Soll RF, Buus-Frank ME, Buzas JS (2017) Variation in performance of neonatal intensive care units in the United States. JAMA Pediatr 171:e164396
Allin BSR, Long AM, Gupta A, Lakhoo K, Knight M (2018) One-year outcomes following surgery for necrotising enterocolitis: a UK-wide cohort study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 103:F461–f466
Neu J, Walker WA (2011) Necrotizing enterocolitis. N Engl J Med 364:255–264
Moss RL, Kalish LA, Duggan C, Johnston P, Brandt ML, Dunn JC, Ehrenkranz RA, Jaksic T, Nobuhara K, Simpson BJ, McCarthy MC, Sylvester KG (2008) Clinical parameters do not adequately predict outcome in necrotizing enterocolitis: a multi-institutional study. J Perinatol 28:665–674
Yee WH, Soraisham AS, Shah VS, Aziz K, Yoon W, Lee SK (2012) Incidence and timing of presentation of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Pediatrics 129:e298-304
Li QY, An Y, Liu L, Wang XQ, Chen S, Wang ZL, Li LQ (2017) Differences in the clinical characteristics of early- and late-onset necrotizing enterocolitis in full-term infants: a retrospective case-control study. Sci Rep 7:43042
Levitzky O, Lerner-Geva L, Dollberg S, Reichman B (2016) The israel national very low birth weight infant database. Harefuah 155(32–36):67
Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L, Brotherton T (1978) Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg 187:1–7
Bizzarro MJ, Ehrenkranz RA, Gallagher PG (2014) Concurrent bloodstream infections in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 164:61–66
Limperopoulos C, Gauvreau KK, O’Leary H, Moore M, Bassan H, Eichenwald EC, Soul JS, Ringer SA, Di Salvo DN, du Plessis AJ (2008) Cerebral hemodynamic changes during intensive care of preterm infants. Pediatrics 122:e1006–1013
Dolfin T, Skidmore MB, Fong KW, Hoskins EM, Shennan AT (1983) Incidence, severity, and timing of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhages in preterm infants born in a perinatal unit as detected by serial real-time ultrasound. Pediatrics 71:541–546
Enzmann D, Murphy-Irwin K, Stevenson D, Ariagno R, Barton J, Sunshine P (1985) The natural history of subependymal germinal matrix hemorrhage. Am J Perinatol 2(2):123–133
Li X, Li L, Wang Y, Deng C, Guo C (2017) Postoperative characteristics of infants who developed necrotizing enterocolitis with different postnatal ages. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(32):e7774. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007774 (PMID: 28796074; PMCID: PMC5556240)
Josephson CD, Wesolowski A, Bao G, Sola-Visner MC, Dudell G, Castillejo MI, Shaz BH, Easley KA, Hillyer CD, Maheshwari A (2010) Do red cell transfusions increase the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants? J Pediatr 157(6):972-978.e1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.05.054 (Epub 2010 Jul 21. PMID: 20650470; PMCID: PMC4425198)
Zhou Y, Shan G, Sodergren E, Weinstock G, Walker WA, Gregory KE (2015) Longitudinal analysis of the premature infant intestinal microbiome prior to necrotizing enterocolitis: a case-control study. PLoS One 10(3):e0118632. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118632.PMID:25741698;PMCID:PMC4351051
Picaud JC, De Magistris A, Mussap M, Corbu S, Dessì A, Noto A, Fanos V, Cesare MF (2021) Urine NMR metabolomics profile of preterm infants with necrotizing enterocolitis over the first two months of life: a pilot longitudinal case-control study. Front Mol Biosci 15(8):680159. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.680159.PMID:34212004;PMCID:PMC8239193
Acknowledgements
This study was part of the MD degree requirements of Dr. Simona Yoffe Deri in Ben Gurion University of the Negev.
Funding
No funding was received for the purpose of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoffe Deri, S., Melamed, R., Marks, K. et al. Early versus late-onset necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth infants in the neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Surg Int 38, 235–240 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-021-05029-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-021-05029-3