Abstract
Purpose
Neuroblastoma is a refractory pediatric malignant solid tumor. The previous studies demonstrated that Polyphyllin D, the main constituent of Paris polyphylla, a traditional Chinese medicine, exerts an anti-tumor effect on many tumors. However, its effects against neuroblastomas are unclear.
Methods
We examined the anti-tumor effect of polyphyllin D in human neuroblastoma using IMR-32 and LA-N-2 cells, which exhibit MYCN gene amplification, and NB-69 cells, which do not exhibit MYCN gene amplification.
Results
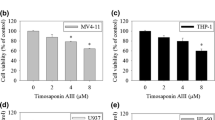
All cell lines showed reduced cell viability in response to polyphyllin D treatment. No caspase-3/-7, -8, and -9 activity was observed in IMR-32 and LA-N-2 cells treated with polyphyllin D. In contrast, activation of caspase-3/-7, and -8 activity was observed in NB-69 cells. When polyphyllin D and specific inhibitors of RIPK3 involved in necroptosis were added to IMR-32 and LA-N-2 cell lines, polyphyllin D-induced cell death was inhibited.
Conclusion
Together, this indicates that the underlying mechanism of polyphyllin D-induced cell death in NB-69 cells is apoptosis, whereas the cell death of IMR-32 and LA-N-2 cells occurs by necroptosis. We continue research on this topic and look forward the discovery of a new therapeutic agent for neuroblastoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohn SL, Pearson AD, London WB et al (2009) The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) classification system: an INRG task force report. J Clin Oncol 27:289–297
Vasudevan SA, Nuchtern JG, Shohet JM (2005) Gene profiling of high risk neuroblastoma. World J Surg 29:317–324
Westermark UK, Wilhelm M, Frenzel A, Henriksson MA (2011) The MYCN oncogene and differentiation in neuroblastoma. Semin Cancer Biol 21:256–266
Vogan K, Bernstein M, Leclerc JM et al (1994) Absence of p53 gene mutations in primary neuroblastomas. Cancer Res 53:5269–5273
Huang FJ, Hsuuw YD, Chan WH (2013) Characterization of apoptosis induced by emodin and related regulatory mechanisms in human neuroblastoma cells. J Mol Sci 14:20139–20156
Lee MS, Yuet-Wa JC, Kong SK et al (2005) Effects of polyphyllin D, a steroidal saponin in Paris polyphylla, in growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells and in xenograft. Cancer Biol Ther 4:1248–1254
Ong RC, Lei J, Lee RK et al (2008) Polyphyllin D induces mitochondrial fragmentation and acts directly on the mitochondria to induce apoptosis in drug-resistant HepG2 cells. Cancer Lett 261:158–164
Chen Y, Zhu J, Zhang W (2014) Antitumor effect of traditional Chinese herbal medicines against lung cancer. Anticancer Drugs 25:983–991
Kong M, Fan J, Dong A, Cheng H, Xu R (2010) Effects of polyphyllin I on growth inhibition of human non-small lung cancer cells and in xenograft. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 42:827–833
Li B, Yu B, Hui Y, Li M, Han X, Fung KP (2001) An improved synthesis of the saponin, polyphyllin D. Carbohydr Res 331:1–7
Burkhart CA, Cheng AJ, Madafiglio J et al (2003) Effects of MYCN antisense oligonucleotide administration on tumorigenesis in a murine model of neuroblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:1394–1403
Santiago LR, Erickson LC, Hanin I (1998) AF64A-induced changes in N-myc expression in the LA-N-2 human neuroblastoma cell line are modulated by choline and hemicholinium-3. Neurochem Res 23:743–750
Zaizen Y, Taniguchi S, Suita S (1998) The role of cellular motility in the invasion of human neuroblastoma cells with or without N-myc amplification and expression. J Pediatr Surg 33:1765–1770
Wang X, Wang Y, Ding ZJ et al (2014) The role of RIP3 mediated necroptosis in ouabain-induced spiral ganglion neurons injuries. Neurosci Lett 578:111–116
Wang H, Sun L, Su L et al (2014) Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein MLKL causes necrotic membrane disruption upon phosphorylation by RIP3. Mol Cell 54:133–146
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M et al (2005) Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nature. Chem Biol 1:112–119
Feoktistova M, Wallberg F, Tenev T, Geserick P, Leverkus M, Meier P (2016) Techniques to distinguish apoptosis from necroptosis. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. doi:10.1101/pdb.top070375.
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G (2014) MLKL regulates necrotic plasma membrane permeabilization. Cell Res 24:139–140
Fuchs Y, Stellar H (2015) Live to die another way: modes of programmed cell death and the signals emanating from dying cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16:329–344
Tabata K, Hamano A, Akihisa T, Suzuki T (2012) Kuguaglycoside C, a constituent of Momordica charantia, induces caspase-independent cell death of neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Sci 103:2153–2158
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the work of past and present members of our laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, S., Suzuki, T., Hara, F. et al. Polyphyllin D, a steroidal saponin in Paris polyphylla, induces apoptosis and necroptosis cell death of neuroblastoma cells. Pediatr Surg Int 33, 713–719 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-017-4069-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-017-4069-4