Abstract
Purpose
We compare the outcomes of fundoplication with gastrostomy vs gastrostomy alone and review the need for subsequent fundoplication after the initial gastrostomy alone.
Methods
We searched studies published from 1969 to 2016 for comparative outcomes of concomitant fundoplication with gastrostomy (FGT) vs gastrostomy insertion alone (GT) in children. Gastrostomy methods included open, laparoscopic, and endoscopic procedures. Primary aims were minor and major complications. Secondary aims included post-operative reflux-related complications, fundoplication specific complications, and need for subsequent fundoplication after GT.
Results
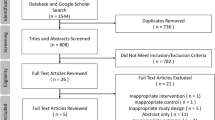
We reviewed 447 studies; 6 observational studies were included for meta-analysis, encompassing 2730 children undergoing GT (n = 1745) or FGT (n = 985). FGT was associated with more minor complications [19.9 vs 11.4%, OR 2.02, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.43–2.87, p ≤ 0.0001, I 2 = 0%], minor complications requiring revision (6.8 vs 3.0%, OR 2.27, 95% CI 1.28–4.05, p = 0.005, I 2 = 0%), and more overall complications (21.3 vs 12.0%, OR 1.99, 95% CI 1.43–2.78, p < 0.0001, I 2 = 0%). Incidence of major complications (1.8 vs 2.0%, OR 1.39, 95% CI 0.62–3.11, p = 0.42, I 2 = 5%) and reflux-related complications (8.8 vs 10.3%, OR 0.75, 95% CI 0.35–1.68, p = 0.46, I 2 = 0%) in both groups was similar. Incidence of subsequent fundoplication in GT patients was 8.6% (mean).
Conclusions
Gastrostomy alone is associated with fewer minor and overall complications. Concomitant fundoplication does not significantly reduce reflux-related complications. As few patients require fundoplication after gastrostomy, current evidence does not support concomitant fundoplication.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry JG, Poduri A, Bonkowsky JL, Zhou J, Graham DA, Welch C, Putney H, Srivastava R (2012) Trends in resource utilization by children with neurological impairment in the United States inpatient health care system: a repeat cross-sectional study. PLoS Med 9(1):e1001158. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001158
Fonkalsrud EW, Ashcraft KW, Coran AG, Ellis DG, Grosfeld JL, Tunell WP, Weber TR (1985) Surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in children: a combined hospital study of 7467 patients. Pediatrics 101:419–422
Jolley SG, Smith EI, Tunell WP (1985) Protective antireflux operation with feeding gastrostomy. Experience with children. Annals Surg 201:736–740
Wadie GM, Lobe TE (2002) Gastroesophageal reflux disease in neurologically impaired children: the role of the gastrostomy tube. Semin Laparosc Surg 9:180–189
Mahant S, Pastor AC, Deoliveira L, Nicholas DB, Langer JC (2011) Well-being of children with neurologic impairment after fundoplication and gastrojejunostomy tube feeding. Pediatrics 128:395–403
Fonkalsrud EW, Ament ME (1996) Gastroesophageal reflux in childhood. Curr Probl Surg 33:1–70
Viswanath N, Wong D, Channappa D, Kukkady A, Brown S, Samarakkody U (2010) Is prophylactic fundoplication necessary in neurologically impaired children? Eur J Paediatr Surg 20:226–229
Wilson GJ, van der Zee DC, Bax NM (2006) Endoscopic gastrostomy placement in the child with gastroesophageal reflux: is concomitant antireflux surgery indicated? J Paediatr Surg 41:1441–1445
Vernon-Roberts A, Sullivan PB (2007) Fundoplication versus post-operative medication for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children with neurological impairment undergoing gastrostomy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 24:1
Nah SA, Narayanaswamy B, Eaton S, Coppi PD, Kiely EM, Curry JI, Drake DP, Barnacle AM, Roebuck DJ, Pierro A (2010) Gastrostomy insertion in children: percutaneous endoscopic or percutaneous image-guided? J Pediatr Surg 45:1153–1158
Catto-Smith AG, Jimenez S (2006) Morbidity and mortality after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children with neurological disability. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21:734–738
Toporowska-Kowalska E, Gębora-Kowalska B, Fendler W, Popińska K, Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz A, Grzybowska-Chlebowczyk U, Wiernicka A, Borkowska A, Sibilska M, Więcek S, Hapyn E, Kierkuś J (2013) Diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux and anti-reflux procedures among Polish children with gastrostomies: a 10-year nationwide analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr 67:1169–1174
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J (2003) Methodological index for non-randomised studies (MINORS): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg 733:712–716
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151:264–269
Pacilli M, Macharia-Coates E, Cross K, Curry J, Pierro A, De Coppi P, Eaton S (2016) Follow-up of randomised controlled trial of gastrostomy with medical treatment versus gastrostomy with fundoplication in children with neurological impairment. British Association of Paediatric Surgeons. Conference abstract
Carpenter JL, Soeken TA, Correa AJ, Zamora IJ, Fallon SC, Kissler MJ, Fraser CD Jr, Wesson DE (2016) Feeding gastrostomy in children with complex heart disease: when is a fundoplication indicated? Pediatr Surg Int 32:285–289
Acker SN, Trinh BB, Partrick DA, Stewart CL, Bensard DD (2016) Is routine upper gastrointestinal contrast study necessary prior to laparoscopic gastrostomy tube placement in children? Eur J Pediatr Surg 26:9–33
Stey AM, Kenney BD, Cohen ME, Moss RL, Hall BL, Berman L, Kraemer K, Ko CY, Vinocur CD (2016) Estimating adverse events after gastrostomy tube placement. Acad Pediatr 16:129–135
Slater B, Rangel S, Ramamoorthy C, Abrajano C, Albanese CT (2007) Outcomes after laparoscopic surgery in neonates with hypoplastic heart left heart syndrome. J Pediatr Surg 42:1118–1121
Ledermann SE, Spitz L, Moloney J, Rees L, Trompeter RS (2002) Gastrostomy feeding in infants and children on peritoneal dialysis. Pediatr Nephrology 17:246–250
Rothenberg SS, Bealer JF, Chang JH (1999) Primary laparoscopic placement of gastrostomy buttons for feeding tubes. A safer and simpler technique. Surgical Endoscopy 13:995–997
Chung DH, Georgeson KE (1998) Fundoplication and gastrostomy. Semin Pediatr Surg 7:213–219
Collins JB 3rd, Georgeson KE, Vicente Y, Hardin WD Jr (1995) Comparison of open and laparoscopic gastrostomy and fundoplication in 120 patients. J Pediatr Surg 30:1065–1070
Mollitt DL, Golladay ES, Seibert JJ (1985) Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux following gastrostomy in neurologically impaired patients. Pediatrics 75:1124–1126
Fraser JD, Ponsky TA, Aguayo P, Boulanger S, Parry R, Nixdorf N, DiLuciano J, Smith P, Sharp SW, Holcomb GW, Ostlie DJ, St Peter SD (2009) Short-term natural history of the standard approaches for gastrostomy tube placement in the pediatric patient. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech Part A 19:567–569
Yu SC, Petty JK, Bensard DD, Partrick DA, Bruny JL, Hendrickson RJ (2005) Laparoscopic-assisted percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children and adolescents. J Soc Laparoendosc Surg 9:302–304
El-Sayed Ahmed MM, Alfares FA, Hynes CF, Ramakrishnan K, Louis C, Dou C, Costello JP, Zurakowski D, Jonas RA, Nath DS (2016) Timing of gastrostomy tube feeding in three-stage palliation of single-ventricle physiology. Congenit Heart Dis 11:34–38
Wyrick DL, Bozeman AP, Smith SD, Jackson RJ, Maxson RT, Kelley KR, Mathews DL, Li J, Swearingen CJ, Dassinger MS (2013) Persistent gastrocutaneous fistula: factors affecting the need for closure. J Pediatr Surg 48:2506–2510
Bratu I, Bharmal A (2011) Incidence and predictors of gastrocutaneous fistula in the pediatric patient. ISRN Gastroenterol 2011:1–3
Barnhart DC, Hall M, Mahant S, Goldin AB, Berry JG, Faix RG, Dean JM, Srivastava R (2013) Effectiveness of fundoplication at the time of gastrostomy in infants with neurological impairment. JAMA Pediatr 167:911–918
Thomas C, Forrest A, Klingberg H, Moore D, Abu-Assi R, Barry SC, Khurana S (2016) Does gastrostomy placement with concurrent fundoplication increase the risk of gastrostomy-related complications? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 63:29–33
Berman L, Sharif I, Rothstein D, Hossain J, Vinocur C (2015) Concomitant fundoplication increases morbidity of gastrostomy tube placement. J Pediatr Surg 50:1104–1108
Conlon SJ, Janik TA, Janik JS, Hendrickson RJ, Landholm AE (2001) Gastrostomy revision: incidence and indications. J Pediatr Surg 39:1390–1395
Ackroyd R, Saincher M, Cheng S, El-Matary W (2011) Gastrostomy tube insertion in children: the edmonton experience. Can J Gastroenterol 25:265–268
Hament JM, Bax NM, van der Zee DC, De Schryver JE, Nesselaar C (2001) Complications of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy with or without concomitant antireflux surgery in 96 children. J Pediatr Surg 36:1412–1415
Noble LJ, Dalzell AM, El-Matary W (2012) The relationship between percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children: a systematic review. Surg Endosc 26:2504–2512
Lasser MS, Liao JG, Burd RS (2006) National trends in the use of antireflux procedures for children. Pediatrics 118:1828–1835. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1185
Pearl RH, Robie DK, Ein SH, Shandling B, Wesson DE, Superina R, Mctaggart K, Garcia VF, O’Connor JA, Filler RM (1990) Complications of gastroesophageal antireflux surgery in neurologically impaired versus neurologically normal children. J Pediatr Surg 25:1169–1173
Puntis JW, Thwaites R, Abel G, Stringer MD (2000) Children with neurological disorders do not always need fundoplication concomitant with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Dev Med Child Neurol 42:97–99
Sulaeman E, Udall JN Jr, Brown RF, Mannick EE, Loe WA, Hill CB, Schmidt-Sommerfeld E (1998) Gastroesophageal reflux and Nissen fundoplication following percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 26:269–273
Goldin AB, Garrison M, Christakis D (2009) Variations between hospitals in antireflux procedures in children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 163:658–663
Barsness KA, St Peter SD, Holcomb GW 3rd, Ostlie DJ, Kane TD (2009) Laparoscopic fundoplication after previous open abdominal operations in infants and children. J Laparosc Adv Surg Tech Part A Supp 1:S47–S49
Lintula H, Antila P, Kokki H (2003) Laparoscopic fundoplication in children with a preexisting gastrostomy. Journal of laparoendoscopic Advanced surgical techniques part A 13:381–385
O’Loughlin EV, Somerville H, Shun A, Gangemi R, La Hei E, Desphande A, O’Loughlin TF (2013) Antireflux surgery in children with neurological impairment: caregiver perceptions and complications. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 56:46–50
Tawfik R, Dickson A, Clarke M, Thomas AG (1997) Dev Med Child Neurol 39:746–751
Kubiak R, Eaton S, Andrews J, Grant HW (2013) Long-term catch-up weight gain following fundoplication in children. Eur J Pediatr Surg 23:121–126
Apelgren KN, Zambos J (1989) Is percutaneous better than open gastrostomy? A clinical study in one surgical department. Am Surg 55:596–600
Ruiwen Liu A, Jiwane A, Varjavandi A, Kennedy G, Henry A, Dilley B, Currie S, Adams U Krishnan (2013) Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic, laparoscopic and open gastrostomy insertion in children. Pediatr Surg Int 29:613–621
Koca T, Sivrice AÇ, Dereci S, Duman L, Akçam M (2015) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children: a single center experience. Turk Pediatri Arsivi 1:211–216
Kakade M, Coyle D, McDowell DT, Gillick J (2015) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) does not worsen vomiting in children. Pediatr Surg Int 31:557–562
Viktorsdóttir MB, Óskarsson K, Gunnarsdóttir A, Sigurdsson L (2015) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children: a population-based study from iceland, 1999–2010. J Laparosc Adv surg Tech Part A 25:248–251
Van Biervliet S, Van Renterghem K, Vande Putte D, Vande Velde S, De Bruyne R, Van Winckel M (2013) Gastrostomy use in children: a 3-year single centre experience. Acta gastro-enterologica Belgica 77:8–12
Ponsky TA, Gasior AC, Parry J, Sharp SW, Boulanger S, Parry R, Ostlie DJ, St Peter SD (2013) Need for subsequent fundoplication after gastrostomy based on patient characteristics. J Surg Res 179:1–4
Lintula H, Juvonen P, Hämynen I, Heikkinen M, Eskelinen M (2013) Severe gastro-oesophageal reflux necessitating fundoplication after percutaneous endoscopic and open gastrostomy in children. Langenbecks’ Arch Surg 398:703–707
Kawahara H, Mitani Y, Nose K, Nakai H, Yoneda A, Kubota A, Fukuzawa M (2010) Should fundoplication be added at the time of gastrostomy placement in patients who are neurologically impaired? J Pediatr Surg 45:2373–2376
Corona C, Cañizo A, Cerda J, Laín A, Fanjul M, Carrera N, Tardáguila A, García-Casillas MA, Parente A, Molina E, Matute JA, Peláez D (2010) Percutaneous gastrostomy: when should antireflux surgery be associated? Cir Pediatr 23:189–192
Fortunato JE, Troy AL, Cuffari C, Davis JE, Loza MJ, Oliva-Hemker M, Schwarz KB (2010) Outcome after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children and young adults. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 50:390–393
Novotny NM, Jester AL, Ladd AP (2009) Preoperative prediction of need for fundoplication before gastrostomy tube placement in children. J Pediatr Surg 44:176–177
Canali R, Sciascia Cannizzaro G, Scaldaferri A, Retrosi R, Contini AC, Buonuomo V, Pintus C (2008) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) in pediatric patients: our experience and proposal of follow-up methodology. La clinica terapeutica159:243–248
Yeh TC, Yeung CY, Sheu JC, Lee HC, Lin SP, Hsu CH, Lee YJ, Chiu NC, Ho CS (2003) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children: 15 cases experience. Acta Paediatrica Taiwanica 44:135–139
Khattak IU, Kimber C, Kiely EM, Spitz L (1998) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in paediatric practice: complications and outcome. J Pediatr Surg 33:67–72
Isch JA, Rescorla FJ, Scherer LR 3rd, West KW, Grosfeld JL (1997) The development of gastroesophageal reflux after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. J Pediatr Surg 32:321–323
Cameron BH, Blair GK, Murphy JJ 3rd, Fraser GC (1995) Morbidity in neurologically impaired children after percutaneous endoscopic versus Stamm gastrostomy. Gastrointest Endosc 42:41–44
Heine RG, Reddihough DS, Catto-Smith AG (1995) Gastro-oesophageal reflux and feeding problems after gastrostomy in children with severe neurological impairment. Dev Med Child Neurol 37:320–329
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yap, B.K.Y., Nah, S.A., Chen, Y. et al. Fundoplication with gastrostomy vs gastrostomy alone: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes and complications. Pediatr Surg Int 33, 217–228 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-4028-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-4028-5