Abstract
Purpose
To present the medium to long-term outcome of the largest pediatric series of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplications (LTF) performed at a single institution.
Patients and methods
Subjects were 131 neurologically impaired children (81 M, 50 F) who underwent LTF between 2003 and 2013. Our LTF involves full dissection of the crus of the diaphragm to allow the intraabdominal esophagus to be mobilized at least 3–4 cm.
Results
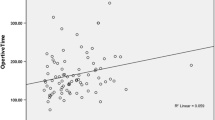
Preoperative mean fraction time for pH <4 was 14.6 %. Mean age at LTF was 6.7 years (3 months–18 years). Mean duration of follow-up was 5.7 years (range 1.2–12.1 years). One case required conversion to open surgery. Intra-operative complications were all injuries to the esophagus/gastric wall (n = 4; 3.0 %) including full-thickness perforation (n = 1; 0.8 %). Postoperative complications included pyloric stenosis (n = 4; 3.0 %), dysphagia (n = 1; 0.8 %), incisional hernia (n = 1; 0.8 %), hemorrhage requiring transfusion (n = 1; 0.8 %), recurrence (n = 3; 2.3 % at 11, 13, and 48 months, respectively), and gastrostomy site infection (n = 7; 5.3 %). Mean operative time decreased significantly with experience from 180.8 min for the first quarter of subjects to 150.6 (2nd quarter), 128.6 (3rd) and 109.2 min (4th).
Conclusions
Our LTF would appear to be safe for treating GERD in children because of reliable outcome and low recurrence.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lobe TE, Schropp KP, Lunsford K (1993) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in childhood. J Pediatr Surg 28(3):358–360 (discussion 360–361)
Georgeson KE (1993) Laparoscopic gastrostomy and fundoplication. Pediatr Ann 22(11):675–677
Fonkalsrud EW, Ashcraft KW, Coran AG et al (1998) Surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in children: a combined hospital study of 7467 patients. Pediatrics 101(3 Pt 1):419–422
Toupet A (1963) Technic of esophago-gastroplasty with phrenogastropexy used in radical treatment of hiatal hernias as a supplement to Heller’s operation in cardiospasms. Mem Acad Chir (Paris) 89:384–389
McKernan JB (1994) Laparoscopic repair of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Toupet partial fundoplication versus Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc 8(8):851–856
Patti MG, De Pinto M, de Bellis M et al (1997) Comparison of laparoscopic total and partial fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux. J Gastrointest Surg 1(4):309–314 (discussion 314–315)
Zornig C, Strate U, Fibbe C et al (2002) Nissen vs Toupet laparoscopic fundoplication. Surg Endosc 16(5):758–766
Esposito C, Van Der Zee DC, Settimi A et al (2003) Risks and benefits of surgical management of gastroesophageal reflux in neurologically impaired children. Surg Endosc 17(5):708–710
Kamolz T, Granderath FA, Bammer T et al (2002) “Floppy” Nissen vs. Toupet laparoscopic fundoplication: quality of life assessment in a 5-year follow-up (part 2). Endoscopy 34(11):917–922
Hunter JG, Swanstrom L, Waring JP (1996) Dysphagia after laparoscopic antireflux surgery. The impact of operative technique. Ann Surg 224(1):51–57
Jobe BA, Wallace J, Hansen PD et al (1997) Evaluation of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication as a primary repair for all patients with medically resistant gastroesophageal reflux. Surg Endosc 11(11):1080–1083
Davis CS, Baldea A, Johns JR et al (2010) The evolution and long-term results of laparoscopic antireflux surgery for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. JSLS 14(3):332–341
Rothenberg SS (2013) Two decades of experience with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in infants and children: a critical evaluation of indications, technique, and results. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 23(9):791–794
Bloomston M, Nields W, Rosemurgy AS (2003) Symptoms and antireflux medication use following laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: outcome at 1 and 4 years. JSLS 7(3):211–218
Koch OO, Kaindlstorfer A, Antoniou SA et al (2013) Comparison of results from a randomized trial 1 year after laparoscopic Nissen and Toupet fundoplications. Surg Endosc 27(7):2383–2390
Lundell L, Abrahamsson H, Ruth M, Rydberg L, Lonroth H, Olbe L (1996) Long-term results of a prospective randomized comparison of total fundic wrap (Nissen-Rossetti) or semifundoplication (Toupet) for gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg 83(6):830–835
Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Granderath UM, Pointner R (2007) Gas-related symptoms after laparoscopic 360 degrees Nissen or 270 degrees Toupet fundoplication in gastrooesophageal reflux disease patients with aerophagia as comorbidity. Dig Liver Dis 39(4):312–318
Esposito C, De Luca C, Alicchio F et al (2010) Long-term outcome of laparoscopic Nissen procedure in pediatric patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease measured using the modified QPSG Roma III European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition’s questionnaire. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 20(7):661–664
Shariff F, Kiely E, Curry J et al (2010) Outcome after laparoscopic fundoplication in children under 1 year. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 20(7):661–664
Capito C, Leclair MD, Piloquet H et al (2008) Long-term outcome of laparoscopic Nissen-Rossetti fundoplication for neurologically impaired and normal children. Surg Endosc 22(4):875–880
Meehan JJ, Georgeson KE (1997) The learning curve associated with laparoscopic antireflux surgery in infants and children. J Pediatr Surg 32(3):426–429
Hagedorn C, Lonroth H, Rydberg L, Ruth M, Lundell L (2002) Long-term efficacy of total (Nissen-Rossetti) and posterior partial (Toupet) fundoplication: results of a randomized clinical trial. J Gastrointest Surg 6(4):540–545
Steyaert H, Al Mohaidly M, Lembo MA et al (2003) Long-term outcome of laparoscopic Nissen and Toupet fundoplication in normal and neurologically impaired children. Surg Endosc 17(4):543–546
Zehetner J, Holzinger F, Breuhahn T et al (2006) Five-year results of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication as the primary surgical repair in GERD patients: is it durable? Surg Endosc 20(2):220–225
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our appreciation to Dr. Geoffrey J. Lane who reviewed this manuscript as a native English speaker.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyano, G., Yamoto, M., Morita, K. et al. Laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux: a series of 131 neurologically impaired pediatric cases at a single children’s hospital. Pediatr Surg Int 31, 925–929 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3770-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3770-4