Abstract
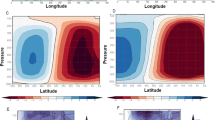
We study inter-model spreads of the climatological annual mean Hadley circulation (HC), using 37 models from Coupled Model Intercomparison Project phase 6 (CMIP6) Atmospheric Model Intercomparison Project (AMIP). Our results show significant inter-model spreads of the climatological annual mean HC although the models are driven with identical sea surface temperatures (SSTs). Two leading modes of inter-model HC spreads are identified, using the method of inter-model empirical orthogonal function (EOF) decomposition. The EOF1 mode exhibits an equatorial symmetric dipole pattern, explains 40.5% of the total inter-model variance of mean meridional mass streamfunction (MMS), and reflects inter-model spreads of the HC strength and latitudinal locations of the ascending branch in AMIP simulations. The EOF2 mode explains 23.1% of the MMS variance, and mainly reflects inter-model spreads of latitudinal locations of the ascending branch and poleward edges of the Hadley cells. Regression of tropical precipitation on PC1 and PC2 shows that both two leading modes are closely related to model performance in simulating tropical convective precipitation. It suggests that inter-model spreads of the HC are due to different cloud-convection parameterization schemes among the AMIP models. Models that simulate heavier tropical convective precipitation generate concentrated equatorial convective heating and stronger, but narrower, Hadley cells, and the associated ascending branch is located more southward. Models that simulate stronger tropical convective precipitation in the south of the equator exhibit southward biases of the latitudinal position of the ascending branch and a narrower Northern-Hemispheric cell. This study indicates that improvements of cloud-convection parameterizations are of critical importance in simulating the HC.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The meteorological data for this paper are available in the following websites: ERA 5 (https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/datasets/reanalysis-datasets/era5), ECMWF Interim reanalysis (http://apps.ecmwf.int/datasets/data/interim-full-daily/levtype=pl), NCEP versions 1 and 2 reanalysis data (https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/data/), JRA-55 reanalysis (http://jra.kishou.go. jp), MERRA2 (https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets), and CFSR reanalysis (https://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html). Model data of CMIP6 are available from https://esgf-node.llnl.gov/projects/cmip6/.
References
Arakawa A, Schubert WH (1974) Interaction of a cumulus cloud ensemble with the large-scale environment. Part I. J Atmos Sci 31:674–701. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1974)031%3c0674:IOACCE%3e2.0.CO;2
Arnold NP, Kuang ZM, Tziperman E (2013) Enhanced MJO-like variability at high SST. J Clim 26:988–1001. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-12-00272.1
Bechtold P, Semane N, Lopez P, Chaboureau JP, Beljaars A, Bormann N (2014) Representing equilibrium and nonequilibrium convection in large-scale models. J Atmos Sci 71:734–753. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jas-D-13-0163.1
Bethke I, Wang YG, Counillon F et al. (2021) NorCPM1 and its contribution to CMIP6 DCPP. Geosci Model Dev 14:7073–7116. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-14-7073-2021
Betts AK (1986) A new convective adjustment scheme. part i: observational and theoretical basis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 112:677–691. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49711247307
Bi DH, Dix M, Marsland S (2020) Configuration and spin-up of ACCESS-CM2, the new generation Australian community climate and earth system simulator coupled model. J South Hemisph Earth Syst Sci 70:225–251. https://doi.org/10.1071/Es19040
Bindoff NL et al. (2013) Detection and attribution of climate change: from global to regional. In: Stocker TF et al. (eds) Climate Change 2013. The physical science basis Contribution of working group i to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Boucher O, Servonnat J, Albright AL et al. (2020) Presentation and evaluation of the IPSL-CM6A-LR climate model. J Adv Model Earth Syst. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS002010
Cai WJ, Cowan T (2013) Southeast Australia autumn rainfall reduction: a climate-change-induced poleward shift of ocean-atmosphere circulation. J Clim 26:189–205. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-12-00035.1
Cao J, Ma LB, Li J et al. (2019) Introduction of NUIST-ESM model and its CMIP6 activities. Climate Change Res 15:566–570. https://doi.org/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2019.064
Chemke R, Polvani LM (2019) Opposite tropical circulation trends in climate models and in reanalyses. Nat Geosci 12:528–532. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-019-0383-x
Chen D, Dai AG (2019) Precipitation characteristics in the community atmosphere model and their dependence on model physics and resolution. J Adv Model Earth Syst 11:2352–2374. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018ms001536
Chen S, Wei K, Chen W et al. (2014) Regional changes in the annual mean Hadley circulation in recent decades. J Geophys Res: Atmosp 119:7815–7832. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD021540
Cherchi A, Fogli PG, Lovato T et al. (2019) Global mean climate and main patterns of variability in the CMCC-CM2 coupled model. J Adv Model Earth Syst 11:185–209. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018ms001369
Chikira M, Sugiyama M (2010) A cumulus parameterization with state-dependent entrainment rate. Part I: description and sensitivity to temperature and humidity profiles. J Atmos Sci 67:2171–2193. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010jas3316.1
Danabasoglu G, Lamarque JF, Bacmeister J et al. (2020) The community earth system model version 2 (CESM2). J Adv Model Earth Syst 12:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS001916
Davis N, Birner T (2013) Seasonal to multidecadal variability of the width of the tropical belt. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Med Sci 118:7773–7787. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50610
Davis N, Birner T (2016) Climate model biases in the width of the tropical belt. J Clim 29:1935–1954. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-15-0336.1
Döscher R, Acosta M, Alessandri A et al. (2022) The EC-Earth3 earth system model for the coupled model intercomparison project 6. Geosci Model Dev 15:2973–3020. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-15-2973-2022
Emanuel KA (1991) A scheme for representing cumulus convection in large-scale models. J Atmos Sci 48:2313–2335. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1991)048%3c2313:ASFRCC%3e2.0.CO;2
Frierson DMW (2007) The dynamics of idealized convection schemes and their effect on the zonally averaged tropical circulation. J Atmos Sci 64:1959–1976. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jas3935.1
Fu R, Yin L, Li WH et al. (2013) Increased dry-season length over southern Amazonia in recent decades and its implication for future climate projection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:18110–18115. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1302584110
Galin VY (1998) Parametrization of radiative processes in the DNM atmospheric model. Russian Feder 34:380–389
Gelaro R, McCarty W, Suarez MJ et al. (2017) The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J Clim 30:5419–5454. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-16-0758.1
Gettelman A, Morrison H (2015) Advanced two-moment bulk microphysics for global models. Part I: off-line tests and comparison with other schemes. J Clim 28:1268–1287. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-14-00102.1
Gettelman A, Liu X, Ghan SJ et al. (2010) Global simulations of ice nucleation and ice super saturation with an improved cloud scheme in the community atmosphere model. J Geophys Res 115:D18216. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD013797
Golaz JC, van Roekel LP, Zheng X et al. (2022) The DOE E3SM model version 2: overview of the physical model and initial model evaluation. J Adv Model Earth Syst 14:1–51. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022MS003156
Gregory D, Rowntree PR (1990) A mass flux convection scheme with representation of cloud ensemble characteristics and stability-dependent closure. Mon Weather Rev 118:1483–1506. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1990)118%3c1483:Amfcsw%3e2.0.Co;2
Grise KM, Davis SM (2020) Hadley cell expansion in CMIP6 models. Atmos Chem Phys 20:5249–5268. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-20-5249-2020
Guo Z, Zhou T (2014) An improved diagnostic stratocumulus scheme based on estimated inversion strength and its performance in GAMIL2. Science China-Earth Sci 57:2637–2649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-014-4891-7
Guo YP, Li JP, Feng J (2016) Climatology and interannual variability of the annual mean Hadley circulation in CMIP5 models. Adv Clim Chang Res 7:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accre.2016.04.005
Hack JJ (1994) Parameterization of moist convection in the National Center for Atmospheric Research Community Climate Model (CCM2). J Geophys Res 99:5551–5568. https://doi.org/10.1029/93JD03478
Hajima T, Watanabe M, Yamamoto A et al (2020) Development of the MIROC-ES2L Earth system model and the evaluation of biogeochemical processes and feedbacks. Geosci Model Dev 13:2197–2244. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-13-2197-2020
Hannachi A, Jolliffe IT, Stephenson DB (2007) Empirical orthogonal functions and related techniques in atmospheric science: a review. Int J Climatol 27:1119–1152. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1499
He B, Bao Q, Wang XC et al. (2019) CAS FGOALS-f3-L model datasets for CMIP6 historical atmospheric model intercomparison project simulation. Adv Atmos Sci 36:771–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-019-9027-8
Held IM, Guo H, Adcroft A et al. (2019) Structure and performance of GFDL’s CM4.0 climate model. J Adv Model Earth Syst 11:3691–3727. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019ms001829
Hersbach H, Bell B, Berrisford P et al. (2020) The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 146:1999–2049. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3803
Hirota N, Takayabu YN (2013) Reproducibility of precipitation distribution over the tropical oceans in CMIP5 multi-climate models compared to CMIP3. Clim Dyn 41:2909–2920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1839-0
Hirota N, Takayabu YN, Watanabe M, Kimoto M (2011) Precipitation reproducibility over tropical oceans and its relationship to the double ITCZ problem in CMIP3 and MIROC5 climate models. J Clim 24:4859–4873. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011jcli4156.1
Hu Y, Fu Q (2007) Observed poleward expansion of the Hadley circulation since 1979. Atmos Chem Phys 7:5229–5236. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-5229-2007
Hu Y, Tao L, Liu J (2013) Poleward expansion of the Hadley circulation in CMIP5 simulations. Adv Atmos Sci 30:790–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-2187-4
Hu Y, Huang H, Zhou C (2018) Widening and weakening of the Hadley circulation under global warming. Sci Bullet 63:640–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2018.04.020
Hwang YT, Frierson DMW (2013) Link between the double-intertropical convergence zone problem and cloud biases over the southern ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:4935–4940. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1213302110
James I (1994) Introduction to circulating atmosphere. Cambridge University Press, New York, p 422
Johanson CM, Fu Q (2009) Hadley cell widening: model simulations versus observations. J Clim 22:2713–2725. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008jcli2620.1
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R et al. (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–471
Kanamitsu M, Ebisuzaki W, Woollen J et al (2002) NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull Am Meteor Soc 83:1631–1643. https://doi.org/10.1175/Bams-83-11-1631(2002)083%3c1631:Nar%3e2.3.Co;2
Kawai H (2005) Improvement of a cloud ice fall scheme in GCM. In: Côté J (ed) CAS/JSC WGNE research activities in atmospheric and oceanic modelling/WMO, vol 35, pp 4.11–4.12
Kawai H, Koshiro T, Webb MJ (2017) Interpretation of factors controlling low cloud cover and low cloud feedback using a unified predictive index. J Clim 30:9119–9131. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-16-0825.1
Kobayashi S, Ota Y, Harada Y et al. (2015) The JRA-55 Reanalysis: general specifications and basic characteristics. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 93:5–48. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2015-001
Kuo HL (1965) On formation and intensification of tropical cyclones through latent heat release by cumulus convection. J Atmos Sci 22:40–63. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1965)022%3c0040:OFAIOT%3e2.0.CO;2
Law RM, Ziehn T, Matear RJ et al. (2017) The carbon cycle in the Australian community climate and earth system simulator (ACCESS-ESM1)-Part 1: model description and pre-industrial simulation. Geoscientific Model Dev 10:2567–2590. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-10-2567-2017
Lee J, Kim J, Sun MA et al. (2020) Evaluation of the Korea meteorological administration advanced community earth-system model (K-ACE). Asia-Pac J Atmos Sci 56:381–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-019-00144-7
Li L, Yu Y, Tang Y et al. (2020) The flexible global ocean-atmosphere-land system model grid-point version 3 (FGOALS-g3): description and evaluation. J Adv Model Earth Syst. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS002012
Lin Y, Farley RD, Orville HD (1983) Bulk parameterization of the snow field in a cloud model. J Climate Appl Meteorol 22:1065–1092. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1983)022%3c1065:Bpotsf%3e2.0.Co;2
Lin Y, Zhao M, Ming Y et al. (2013) Precipitation partitioning, tropical clouds, and intraseasonal variability in GFDL AM2. J Clim 26:5453–5466. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-12-00442.1
Lin Y, Peng Y, Wang L et al. (2019) Tsinghua university CIESM model and its participation in cmip6. Climate Change Res Prog 15:545–550
Lin ZD, Li Y, Liu Y, Hu AX (2020) The decadal reduction of southeastern Australian autumn rainfall since the early 1990s: a response to sea surface temperature warming in the subtropical south pacific. J Clim 33:2249–2261. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0686.1
Lohmann U, Roeckner E (1996) Design and performance of a new cloud microphysics parameterization developed for the ECHAM general circulation model. Clim Dyn 12:557–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207939
Lohmann U, Stier P, Hoose C et al (2007) Cloud microphysics and aerosol indirect effects in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM. Atmos Chem Phys 7:3425–3446. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-3425-2007
Lorenz EN (1956) Empirical orthogonal functions and statistical weather prediction, Scientific Report No. 1, 49 pp, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge.
Lu J, Vecchi GA, Reichler T (2007) Expansion of the Hadley cell under global warming. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL028443
Madeleine JB, Hourdin F, Grandpeix JY et al. (2020) Improved representation of clouds in the atmospheric component LMDZ6A of the IPSL-CM6A Earth System Model. J Adv Modeling Earth Syst. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020MS002046
Manabe S, Smagorinsky J, Strickler RF (1965) Simulated climatology of a general circulation model with a hydrological cycle. Mon Weather Rev 93:769–798. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1965)093%3c0769:SCOAGC%3e2.3.CO;2
Mobis B, Stevens B (2012) Factors controlling the position of the intertropical convergence zone on an aquaplanet. J Adv Model Earth Syst. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012ms000199
Morrison H, Gettelman A (2008) A new two-moment bulk stratiform cloud microphysics scheme in the community atmosphere model, version 3 (CAM3). Part I: Description and numerical tests. J Clim 21:3642–3659. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JCLI2105.1
Müller WA, Jungclaus JH, Mauritsen T et al. (2018) A higher-resolution version of the max planck institute earth system model (MPI-ESM1.2-HR). J Adv Model Earth Syst 10:1383–1413. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017ms001217
Nguyen H, Hendon HH, Lim EP et al. (2018) Variability of the extent of the Hadley circulation in the southern hemisphere: a regional perspective. Clim Dyn 50:129–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3592-2
Nordeng TE (1994) Extended versions of the convective parameterization scheme at ECMWF and their impact on the mean and transient activity of the model in the tropics. Technical Memorandum 206, ECMWF, Reading, UK.
Oueslati B, Bellon G (2013) Convective entrainment and large-scale organization of tropical precipitation: sensitivity of the CNRM-CM5 hierarchy of models. J Clim 26:2931–2946. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-12-00314.1
Pak G, Noh Y, Lee MI et al. (2021) Korea institute of ocean science and technology earth system model and its simulation characteristics. Ocean Sci J 56:18–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-021-00001-7
Park S (2014) A unified convection scheme (UNICON). part I: formulation. J Atmos Sci 71:3902–3930. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jas-D-13-0233.1
Park S, Bretherton CS (2009) The University of Washington shallow convection and moist turbulence schemes and their impact on climate simulations with the community atmosphere model. J Clim 22:3449–3469. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008jcli2557.1
Park S, Bretherton CS, Rasch PJ (2014) Integrating cloud processes in the community atmosphere model, version 5. J Clim 27:6821–6856. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-14-00087.1
Park S, Shin J, Kim S, Oh E, Kim Y (2019) Global climate simulated by the Seoul national university atmosphere model version 0 with a unified convection scheme (SAM0-UNICON). J Clim 32:2917–2949. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli-D-18-0796.1
Plant RS, Craig GC (2008) A stochastic parameterization for deep convection based on equilibrium statistics. J Atmos Sci 65:87–105. https://doi.org/10.1175/2007jas2263.1
Qin Y, Lin Y, Xu S et al. (2018) A diagnostic PDF cloud scheme to improve subtropical low clouds in NCAR community atmosphere model (CAM5). J Adv Model Earth Syst 10:320–341. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017ms001095
Quan X, Hoerling MP, Perlwitz J, Diaz HF, Xu T (2014) How fast are the tropics expanding? J Clim 27:1999–2013. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00287.1
Rasch PJ, Kristjansson JE (1998) A comparison of the CCM3 model climate using diagnosed and predicted condensate parameterizations. J Clim 11:1587–1614. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1998)011%3c1587:ACOTCM%3e2.0.CO;2
Rio C, Hourdin F, Grandpeix JY, Lafore JP (2009) Shifting the diurnal cycle of parameterized deep convection over land. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008gl036779
Roeckner E, Brokopf R, Esch M et al. (2006) Sensitivity of simulated climate to horizontal and vertical resolution in the ECHAM5 atmosphere model. J Clim 19:3771–3791. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jcli3824.1
Rong X, Li J, Chen H et al. (2019) CAMS-CSM model and its participation in CMIP6. Climate Change Res Prog 15:540–544
Rotstayn LD (1997) A physically based scheme for the treatment of stratiform clouds and precipitation in large-scale models. I: description and evaluation of the microphysical processes. Q J R Meteorol Soc 123:1227–1282. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49712354106
Saha S, Moorthi S, Pan HL et al. (2010) The NCEP Climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull Am Meteor Soc 91:1015–1057. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010bams3001.1
Schiro KA, Su H, Wang Y et al. (2019) Relationships between tropical ascent and high cloud fraction changes with warming revealed by perturbation physics experiments in CAM5. Geophys Res Lett 46:10112–10121. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL083026
Seland O, Bentsen M, Olivie D et al. (2020) Overview of the Norwegian Earth System Model (NorESM2) and key climate response of CMIP6 DECK, historical, and scenario simulations. Geosci Model Dev 13:6165–6200. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-13-6165-2020
Seviour WJM, Davis SM, Grise KM, Waugh DW (2018) Large uncertainty in the relative rates of dynamical and hydrological tropical expansion. Geophys Res Lett 45:1106–1113. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL076335
Slingo JM (1987) The development and verification of a cloud prediction scheme for the ECMWF Model. Quart J Royal Meteorolo Soc 113:899–927. https://doi.org/10.1256/smsqj.47708
Song XL, Zhang GJ (2018) The roles of convection parameterization in the formation of double ITCZ syndrome in the NCAR CESM: I. atmospheric processes. J Adv Model Earth Syst 10:842–866. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017MS001191
Song ZY, Bao Y, Qiao FL (2019) Introduction of FIO-ESM v2.0 and its participation plan in CMIP6 experiments. Clim Change Res 15:558–565. https://doi.org/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2019.033 (in Chinese)
Staten PW, Lu J, Grise KM, Davis SM, Birner T (2018) Re-examining tropical expansion. Nat Clim Change 8:768–775. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-018-0246-2
Sterl A, Bintanja R, Brodeau L et al. (2012) A look at the ocean in the EC-Earth climate model. Clim Dyn 39:2631–2657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1239-2
Stevens B, Giorgetta M, Esch M et al. (2013) Atmospheric component of the MPI-M earth system model: ECHAM6. J Adv Model Earth Syst 5:146–172. https://doi.org/10.1002/jame.20015
Sundqvist H, Berge E, Kristjansson JE (1989) Condensation and cloud parameterization studies with a mesoscale numerical weather prediction model. Mon Weather Rev 117:1641–1657. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1989)117%3c1641:Cacpsw%3e2.0.Co;2
Swart NC, Cole JNS, Kharin VV et al. (2019) The Canadian Earth syst model version 5 (CanESM5.0.3). Geosci Model Dev 12:4823–4873. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-12-4823-2019
Tao L, Hu Y, Liu J (2016) Anthropogenic forcing on the Hadley circulation in CMIP5 simulations. Clim Dyn 46:3337–3350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2772-1
Tatebe H, Ogura T, Nitta T et al. (2019) Description and basic evaluation of simulated mean state, internal variability, and climate sensitivity in MIROC6. Geosci Model Dev 12:2727–2765. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-12-2727-2019
Tiedtke M (1989) A comprehensive mass flux scheme for cumulus parameterization in large-scale models. Mon Weather Rev 117:1779–1800. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1989)117%3c1779:Acmfsf%3e2.0.Co;2
Tiedtke M (1993) Representation of clouds in large-scale models. Mon Weather Rev 121:3040–3061. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1993)121<3040:ROCILS>2.0.CO;2
Tivig M, Grutzun V, John VO, Buehler SA (2020) Trends in upper-tropospheric humidity: expansion of the subtropical dry zones? J Clim 33:2149–2161. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0046.1
Tompkins AM (2002) A prognostic parameterization for the subgrid-scale variability of water vapor and clouds in large-scale models and its use to diagnose cloud cover. J Atmos Sci 59:1917–1942
Toniazzo T, Bentsen M, Craig C et al. (2020) Enforcing conservation of axial angular momentum in the atmospheric general circulation model CAM6. Geosci Model Dev 13:685–705. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-13-685-2020
Volodin E (2021) The mechanisms of cloudiness evolution responsible for equilibrium climate sensitivity in climate model INM-CM4–8. Geophy Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL096204
Volodin EM, Mortikov EV, Kostrykin SV et al. (2017) Simulation of the present-day climate with the climate model INMCM5. Clim Dyn 49:3715–3734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3539-7
von Salzen K, McFarlane NA, Lazare M (2005) The role of shallow convection in the water and energy cycles of the atmosphere. Clim Dyn 25:671–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-005-0051-2
Wang C, Hu Y, Wen X, Zhou C, Liu J (2020) Inter-model spread of the climatological annual mean Hadley circulation and its relationship with the double ITCZ bias in CMIP5. Clim Dyn 55:2823–2834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05414-z
Wang YC, Hsu HH, Chen CA et al. (2021) Performance of the Taiwan earth system model in simulating climate variability compared with observations and CMIP6 model simulations. J Adv Model Earth Syst. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020MS002353
Watanabe M, Emori S, Satoh M, Miura H (2009) A PDF-based hybrid prognostic cloud scheme for general circulation models. Clim Dyn 33:795–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-008-0489-0
Wilson DR, Ballard SP (1999) A microphysically based precipitation scheme for the UK meteorological office unified model. Q J Roy Meteor Soc 125:1607–1636. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49712555707
Wilson DR, Bushell AC, Kerr-Munslow AM et al (2008) PC2: a prognostic cloud fraction and condensation scheme. II: Climate model simulations Quarterly. J R Meteorol Soc 134:2109–2125. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.332
Wu T (2012) A mass-flux cumulus parameterization scheme for large-scale models: description and test with observations. Clim Dyn 38:725–744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-0995-3
Wu X, Deng L, Song X, Zhang G (2007) Coupling of convective momentum transport with convective heating in global climate simulations. J Atmos Sci 64:1334–1349. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jas3894.1
Wu T, Lu Y, Fang Y et al. (2019) The Beijing climate center climate system model (BCC-CSM): the main progress from CMIP5 to CMIP6. Geosci Model Dev 12:1573–1600. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-12-1573-2019
Xia Y, Hu Y, Liu J (2020) Comparison of trends in the Hadley circulation between CMIP6 and CMIP5. Sci Bull 65:1667–1674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2020.06.011
Xie SC, Lin WY, Rasch PJ et al. (2018) Understanding cloud and convective characteristics in version 1 of the E3SM atmosphere model. J Adv Model Earth Syst 10:2618–2644. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018ms001350
Xu KM, Randall DA (1996) A semiempirical cloudiness parameterization for use in climate models. J Atmos Sci 53:3084–3102. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1996)053%3c3084:Ascpfu%3e2.0.Co;2
Yang YM, Wang B (2019) Improving MJO simulation by enhancing the interaction between boundary layer convergence and lower tropospheric heating. Clim Dyn 52:4671–4693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4407-9
Yoshimura H, Mizuta R, Murakami H (2015) A spectral cumulus parameterization scheme interpolating between two convective updrafts with semi-Lagrangian calculation of transport by compensatory subsidence. Mon Weather Rev 143:597–621. https://doi.org/10.1175/Mwr-D-14-00068.1
Yukimoto S, Kawai H, Koshiro T et al. (2019) The meteorological research institute earth system model version 2.0, MRI-ESM2.0: description and basic evaluation of the physical component. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 97:931–965. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2019-051
Zhang GJ, Mcfarlane NA (1995) Sensitivity of climate simulations to the parameterization of cumulus convection in the Canadian climate center general-circulation model. Atmos-Ocean. 33:407–446. https://doi.org/10.1080/07055900.1995.9649539
Zhang M, Lin W, Bretherton C, Hack J, Rasch P (2003) A modified formulation of fractional stratiform condensation rate in the NCAR Community Atmospheric Model (CAM2). J Geophys Res 108:4035. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002523
Zhang H, Zhang M, Jin J et al. (2020) Description and climate simulation performance of CAS-ESM version 2. J Adv Model Earth Syst. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020MS002210
Zhao M, Golaz JC, Held I et al. (2018) The GFDL global atmosphere and land model AM4. 0/LM4.0- Part II: Model description, sensitivity studies, and tuning strategies. J Adv Model Earth Syst 10:735–769. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017MS001208
Zhou W, Xie S (2017) Intermodel spread of the double-ITCZ bias in coupled GCMs tied to land surface temperature in AMIP GCMs. Geophys Res Lett 44:7975–7984. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017gl074377
Acknowledgements
The analyses were performed on High-performance Computing Platform of Peking University.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant 41888101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY contributed to the study conception, design and writing. ZS contributed to data collection, analysis and writing-original draft. LJ provided constructive discussions and writing-review. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Hu, Y. & Liu, J. Inter-model spreads of the climatological mean Hadley circulation in AMIP/CMIP6 simulations. Clim Dyn 61, 4411–4427 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-023-06813-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-023-06813-8