Abstract
To get a better overview of atmosphere-driven mass changes at Urumqi Glacier No.1, Chinese Tien Shan, the surface energy budget and mass balance is modeled by linking the COupled Snowpack and Ice surface energy and MAss balance model (COSIMA) with in-situ measured meteorological records for the ablation period in 2018. The COSIMA is calibrated by manual optimization and the modeled results agree well with the in-situ surface temperature, snow height and seasonal mass balance. Our results reveal that Urumqi Glacier No.1 experienced a significant mass loss, with an average value of − 0.77 m w.e. over the ablation period 2018. The surface energy budget components can be classified into two categories: radiation (shortwave and longwave) and turbulent fluxes. Surface melt and solid precipitation were dominated components of mass balance. The COSIMA can reproduce the glaciological mass balance compared with other models. Sensitivity analysis showed that the mass balance was more sensitive to the temperature than precipitation, and mass loss caused by temperature increase of 1 K needed to be compensated by at least 40% precipitation increase. Air temperature during the ablation period was more important than annual precipitation in controlling mass balance changes on Urumqi Glacier No. 1. These findings will enhance our understanding of the mechanisms underlying mass balance processes of ablation period and their contribution to the acceleration of glacier retreat in Tien Shan.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
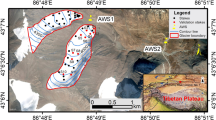
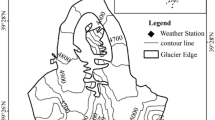
Glaciological mass balance data related to this study are submitted to the WGMS and be available at the following website: https://doi.org/10.5904/wgms-fog-2019-12 (WGMS, 2019). COSIMA is available online as an open-source software and used for this study (https://bitbucket.org/glaciermodel/cosima; Huintjes et al. 2015a). The meteorological data are available upon request by email to the corresponding author (wangpuyu@lzb.ac.cn).
References
Anderson EA (1976) A point energy and mass balance model of a snow cover. Technical Report NWS19, NOAA
Azam M, Wagnon P, Vincent C, Ramanathan A, Linda A, Singh V (2014) Reconstruction of the annual mass balance of Chhota Shigri glacier, Western Himalaya, India, since 1969. Ann Glaciol 55(66):69–80. https://doi.org/10.3189/2014AoG66A104
Bintanja R, van den Broeke M (1995) The surface energy balance of Antarctic snow and blue ice. J Appl Meteorol 34:902–926
Bintanja R, Jonsson S, Knap WH (1997) The annual cycle of the surface energy balance of Antarctic blue ice. J Geophys Res 102(D2):1867–1881. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JD01801
Braithwaite RJ (1995) Aerodynamic stability and turbulent sensible heat flux over a melting ice surface, the Greenland ice sheet. J Glaciol 41:562–571
Brock BW, Willis IC, Martin MJ (2006) Measurement and parameterization of aerodynamic roughness length variations at Haut Glacier d’Arolla Switzerland. J Glaciol 52:281–297
Che YJ, Zhang MJ, Li ZQ, Wei YQ, Nan ZT, Li HL, Wang SJ, Su B (2019) Energy balance model of mass balance and its sensitivity to meteorological variability on Urumqi River Glacier No 1 in the Chinese Tien Shan. Sci Rep 9(1):13958. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50398-4
Cogley JG, Hock R, Rasmussen LA, Arendt AA, Bauder A, Braithwaite RJ, Jansson P, Kaser G, Möller M, Nicholson L, Zemp M (2011) Glossary of glacier mass balance and related terms. Paris:UNESCO-IHP
Cuffey K, Paterson W (2010) The physics of glaciers, 4th edn. Elsevier
Cullen NJ, Mölg T, Kaser G, Steffen K, Hardy DR (2007) Energy-balance model validation on the top of Kilimanjaro, Tanzania, using eddy covariance data. Ann Glaciol 46:227–233
Cullen NJ, Mölg T, Conway J, Steffen K (2014) Assessing the role of sublimation in the dry snow zone of the Greenland ice sheet in a warming world. J Geophys Res-Atmos 119(11):6563–6577. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD021557
Duffie JA, Beckman WA (1991) Solar engineering of thermal processes, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Farinotti D, Longuevergne L, Moholdt G, Duethmann D, Mölg T, Bolch T, Vorogushyn S, Güntner A (2015) Substantial glacier mass loss in the Tien Shan over the past 50 years. Nat Geosci 8(9):716–722. https://doi.org/10.1038/NGEO2513
Favier V, Wagnon P, Chazarin JP, Maisincho L, Coudrain A (2004) One year measurements of surface heat budget on the ablation zone of Antizana Glacier 15, Ecuadorian Andes. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JD004359
Fujita K, Ageta Y (2000) Effect of summer accumulation on glacier mass balance on the tibetan plateau revealed by mass-balance model. J Glaciol 46(153):244–252
Gabbi J, Carenzo M, Pellicciotti F, Bauder A, Funk M (2014) A comparison of empirical and physically based glacier surface melt models for long-term simulations of glacier response. J Glaciol 60(224):1140–1154. https://doi.org/10.3189/2014JoG14J011
Gromke C, Manes C, Walter B, Lehning M, Guala M (2011) Aerodynamic roughness length of fresh snow. Bound Layer Meteorol 141:21–34
Han HD, Ding YJ, Liu SY (2005) Estimation and analysis of heat balance parameters in the ablation season of debris-covered kerqikaer glacier Tianshan mountains. J Glaciol Geocryol 27:88–94
He XB, Ye BS, Ding YJ (2009) Bias correction for precipitation measuament in tanggula mountain Tibetan plateau. Adv Water Sci 20(3):403–408
Herron MH, Langway CC (1980) Firn densification: an empirical model. J Glaciol 25:373–385
Hock R, Holmgren B (2005) A distributed surface energy-balance model for complex topography and its application to Storglaciren Sweden. J Glaciol 51(172):25–36
Huintjes E, Li HL, Sauter T, Li ZQ, Schneider C (2010) Degree-day modelling of the surface mass balance of Urumqi Glacier No. 1 Tian Shan, China. Cryosphere Discuss. 4:207–232. https://doi.org/10.5194/tcd-4-207-2010
Huintjes E, Sauter T, Schröter B, Maussion F, Yang W, Kropáček J, Buchroithner M, Scherer D, Kang SC, Schneider C (2015a) Evaluation of a coupled snow and energy balance model for Zhadang glacier, Tibetan Plateau, using glaciological measurements and time-lapse photography. Arct Antarct Alp Res 47:573–590
Huintjes E, Neckel N, Hochschild V, Schneider C (2015b) Surface energy and mass balance at Purogangri Ice Cap, central Tibetan Plateau, 2001–2011. J Glaciol 61(230):1048–1061
Immerzeel WW, Beek LPHV, Bierkens MP (2010) Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science (new York, NY) 328(5984):1382–1385. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183188
Jia YF, Li ZQ, Xu CH, Jin S, Deng HJ (2020) A comparison of precipitation measurements with a PWS100 laser sensor and a geonor T-200B precipitation gauge at a nival Glacial Zone in Eastern Tianshan Central Asia. Atmosphere 11:1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101079
Kang ES, Yang DQ, Zhang YS (1992) An experiment study of the water and heat balance in the source area of the Urumqi River in the Tian Shan Moutains. Ann Glaciol 16:55–66
Kaser G, Hardy DR, Mölg T, Bradley RS, Hyera TM (2004) Modern glacier retreat on Kilimanjaro as evidence of climate change: observations and facts. Int J Climatol 24:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1008
Klok EJ, Oerlemans J (2002) Model study of the spatial distribution of the energy and mass balance of Morteratschgletscher Switzerland. J Glaciol 48:505–518
Kumar L, Skidmore AK, Knowles E (1997) Modelling topographic variation in solar radiation in a GIS environment. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 11(5):475–497. https://doi.org/10.1080/136588197242266)
Li HL (2020) Spatial and temporal transferability of degree-day model and simplified energy balance model: a case study. Sci Cold Arid Reg 12(2):0095–0103. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1226.2020.00095
Li ZQ, Li HL, Chen YN (2011) Mechanisms and simulation of accelerated shrinkage of continental glaciers: a case study of Urumqi Glacier No 1 in eastern Tianshan, central Asia. J Earth Sci 22(4):423–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-011-0194-5
Li SH, Yao TD, Yang W, Yu WS, Zhu ML (2018) Glacier energy and mass balance in the inland Tibetan Plateau: seasonal and interannual variability in relation to atmospheric changes. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:6390–6409. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JD028120
Li SH, Yao TD, Yu WS, Yang W, Zhu ML (2019) Energy and mass balance characteristics of the Guliya ice cap in the West Kunlun Mountains, Tibetan Plateau. Cold Reg Sci Technol 2019:159
Li HL, Wang PY, Li ZQ, Jin S, Xu CH, Liu SS, Zhang ZY, Xu LP (2021) An application of three different field methods to monitor changes in Urumqi Glacier No 1, Chinese Tien Shan, during 2012–2018. J Glaciol. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2021.71
Liu CG, Han TD (1992) Relation between recent glacier variations and climate in the Tien Shan mountains, Central Asia. Ann Glaciol 16:11–16. https://doi.org/10.3189/1992AoG16-1-11-16
MacDougall AH, Wheler BA, Flowers GE (2011) A preliminary assessment of glacier melt-model parameter sensitivity and transferability in a dry subarctic environment. Cryosphere 5(4):1011–1028. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-5-1011-2011
Miles E, McCarthy M, Dehecq A, Kneib M, Fugger S, Pellicciotti F (2021) Health and sustainability of glaciers in High Mountain Asia. Nat Commun 12:2868. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23073-4
Mölg T, Cullen NJ, Hardy DR, Winkler M, Kaser G (2009) Quantifying climate change in the tropical midtroposphere over East Africa from glacier shrinkage on Kilimanjaro. J Clim 22:4162–4181
Mölg T, Maussion F, Yang W, Scherer D (2012) The footprint of Asian monsoon dynamics in the mass and energy balance of a Tibetan glacier. Cryosphere 6(6):1445–1461. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-6-1445-2012
Mölg T, Hardy DR, Collier E, Kropac E, Schmid C, Cullen NJ, Kaser G, Prinz R, Winkler M (2020) Mesoscale atmospheric circulation controls of local meteorological elevation gradients on Kersten Glacier near Kilimanjaro summit. Earth Syst Dyn 11(3):653–672. https://doi.org/10.5194/esd-11-653-2020
Oerlemans J (2001) Glaciers and climate change. AA Balkema Publishers, Lisse, Abingdon, Exton, Tokyo
Oerlemans J, Klok EJ (2002) Energy balance of a glacier surface: analysis of automatic weather station data from the Morteratschgletscher, Switzerland. Arct Antarct Alp Res 34:477–485. https://doi.org/10.2307/1552206
Oerlemans J, Knap WH (1998) A 1 year record of global radiation and albedo in the ablation zone of Morteratschgletscher Switzerland. J Glaciol 44(147):231–238
Pellicciotti F, Brock BW, Strasser U, Burlando P, Funk M, Corripio JG (2005) An enhanced temperature-index glacier melt model including shortwave radiation balance: development and testing for Haut Glacier d’Arolla Switzerland. J Glaciol 51(175):573–587. https://doi.org/10.3189/172756505781829124
Pellicciotti F, Ragettli S, Carenzo M, McPhee J (2013) Changes of glaciers in the Andes of Chile and priorities for future work. Sci Total Environ 493:1197–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.055
Pieczonka T, Bolch T (2015) Region-wide glacier mass budgets and area changes for the Central Tien Shan between ∼1975 and 1999 using Hexagon KH-9 imagery, Global Planet. Change 128:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2014.11.014,2015
Sakai A, Fujita K (2017) Contrasting glacier responses to recent climate change in high-mountain Asia. Sci Rep 7(13717):2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14256-5
Schaefer M, Fonseca-Gallardo D, Farías-Barahona D, Casassa G (2020) Surface energy fluxes on Chilean glaciers: measurements and models. Cryosphere 14:2545–2565. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-14-2545-2020
Sun WJ, Qin X, Wang YT, Chen JZ, Du WT, Zhang T, Huai BJ (2018) The response of surface mass and energy balance of a continental glacier to climate variability, western Qilian Mountains China. Clim Dyn 50(9/10):3557–3570
Sturm M, Benson C 1997 Vapor transport, grain growth and depth-hoar development in the subarctic snow. J Glaciol 43(143):42–59. https://doi.org/10.3189/S0022143000002793
van den Broeke MR, As DV, Reijmer C, Wal R (2004) Assessing and improving the quality of unattended radiation observations in Antarctica. J Atmos Ocean Technol 21(9):1417–1431
Wang S, Pu JC, Wang NL (2011) Study of mass balance and sensibility to climate change of Qiyi Glacier in Qilian Mountains. J Glaciol Geocryol 33(06):1214–1221
Wang NL, Wu HB, Wu YW, Chen AA (2015) Variations of the glacier mass balance and lake water storage in the Tarim Basin, northwest China, over the period of 2003–2009 estimated by the ICESat-GLAS data. Environ Earth Sci 74(3):1997–2008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4662-6
Wang PY, Li ZQ, Li HL, Yao HB, Xu CH, Zhou P, Jin S, Wang WB (2016) Analyses of recent observations of Urumqi Glacier No 1, Chinese Tianshan Mountains. Environ Earth Sci 75(8):720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5551-3
Wang PY, Li ZQ, Li HL, Wang WB, Zhou P, Wang L (2017) Characteristics of a partially debris-covered glacier and its response to atmospheric warming in Mt. Tomor, Tien Shan China. Glob Planet Change 159:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.10.006
Wang PY, Li ZQ, Zhou P, Li HL, Yu GB, Xu CH, Wang L (2018) Long-term change in ice velocity of Urumqi Glacier No. 1, Tian Shan China. Cold Reg Sci Technol 145:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2017.10.008
Wang NL, Yao TD, Xu BQ, Chen AA, Wang WC (2019) Spatiotemporal pattern, trend, and influence of glacier change in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings under global warming. Bull Chin Acad Sci 34(11):1220–1232. https://doi.org/10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2019.11.005
Wang PY, Li ZQ, Li HL, Zhang ZY, Xu LP, Yue XY (2020a) Glaciers in Xinjiang, China: past changes and current status. Water 12(9):2367. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092367
Wang PY, Li ZQ, Schneider C, Li HL, Hamm A, Jin S, Xu CH, Li HL, Yue XY, Yang M (2020b) A test study of an energy and mass balance model application to a site on Urumqi Glacier No 1 Chinese Tian Shan. Water 12:2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102865
Wang PY, Li HL, Li ZQ, Liu YS, Xu CH, Mu JX, Zhang H (2021) Seasonal surface change of Urumqi Glacier No 1, Eastern Tien Shan, China, revealed by repeated high-resolution UAV photogrammetry. Remote Sens 13(17):3398. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173398
Wu LH, Li HL, Wang L (2011) Application of a degree-day model for determination of mass balance of Urumqi Glacier No. 1, eastern Tianshan China. J Earth Sci 22:470–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-011-0201-x
Xu CH, Li ZQ, Li HL, Wang FT, Zhou P (2019) Long-range terrestrial laser scanning measurements of annual and intra-annual mass balances for Urumqi Glacier No. 1, eastern Tien Shan China. Cryosphere 13:2361–2383. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-13-2361-2019
Yang W, Guo XF, Yao TD, Yang K, Zhao L, Li SH, Zhu ML (2011) Summertime surface energy budget and ablation modeling in the ablation zone of a maritime Tibetan glacier. J Geophys Res 116(D14):D14116
Yang W, Yao TD, Guo XF, Zhu ML, Li SH, Kattel DB (2013) Mass balance of a maritime glacier on the southeast Tibetan Plateau and its climatic sensitivity. J Geophys Res Atmos 118(17):9579–9594
Yang W, Guo XF, Yao TD, Zhu ML, Wang YJ (2016) Recent accelerating mass loss of southeast Tibetan glaciers and the relationship with changes in macroscale atmospheric circulations. Clim Dyn 47:805–815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2872-y
Yao TD, Thompson L, Yang W, Yu WS, Gao Y, Guo XJ, Yang XX, Duan KQ, Zhao HB, Xu BQ, Pu JC, Lu AX, Xiang Y, Kattel DB, Joswiak D (2012) Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat Clim Change 2(9):663–667
Yue XY, Zhao J, Li ZQ, Zhang MJ, Fan J, Wang L, Wang PY (2017) Spatial and temporal variations of the surface albedo and other factors influencing Urumqi Glacier No 1 in Tien Shan China. J Glaciol 63(899):911. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2017.57
Zhang GS, Kang SC, Fujita K, Huintjes E, Xu JQ, Yamazaki T, Haginoya S, Yang W, Scherer D, Schneider C, Yao TD (2013) Energy and mass balance of Zhadang glacier surface, central Tibetan Plateau. J Glaciol 59(213):137–148. https://doi.org/10.3189/2013JoG12J152
Zhang H, Li ZQ, Zhou P, Zhu XF, Wang L (2018) Mass-balance observations and reconstruction for Haxilegen Glacier No 51, eastern Tien Shan, from 1999 to 2015. J Glaciol 64(247):689–699. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2018.58
Zhang H, Li ZQ, Zhou P (2021) Mass balance reconstruction for Shiyi Glacier in the Qilian Mountains, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, and its climatic drivers. Clim Dyn 56:969–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05514-w
Zhou SZ, Zhang RY, Zhang C (1997) Meteorology and climatology. Higher Education Press, Beijing, pp 84–86
Zhu ML, Yao TD, Yang W, Xu BQ, Wang XJ (2017) Evaluation of parameterizations of incoming longwave radiation in the high-mountain region of the Tibetan Plateau. J Appl Meteorol Clim 56(4):833–848
Zhu ML, Yao TD, Yang W, Xu BQ, Wu GJ, Wang XJ, Xie Y (2018) Reconstruction of the mass balance of Muztag Ata No 15 glacier, eastern Pamir, and its climatic drivers. J Glaciol 64(244):259–274
Zhu ML, Yao TD, Xie Y, Xu BQ, Yang W, Yang S (2020) Mass balance of Muji Glacier, northeastern Pamir, and its controlling climate factors. J Hydrol 590(195):125447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125447
Funding
This research was jointly funded by the Third Xinjiang Scientific Expedition Program (Grant No. 2021xjkk0801), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS (Grant No.Y2021110), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41771077, 42001067), and the State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Science (Grant No. SKLCS-ZZ-2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Wang, P., Li, Z. et al. Summertime surface mass balance and energy balance of Urumqi Glacier No. 1, Chinese Tien Shan, modeled by linking COSIMA and in-situ measured meteorological records. Clim Dyn 61, 765–787 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06571-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06571-z