Abstract
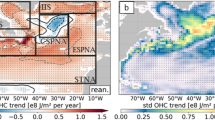
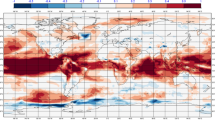
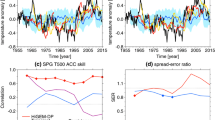
The fundamental mechanisms that explain high subpolar North Atlantic (SPNA) decadal predictability within a particular modeling framework are described. The focus is on the Community Earth System Model (CESM), run in both a historical forced-ocean configuration as well as in a fully coupled configuration initialized from the former. The initialized prediction experiments comprise the CESM Decadal Prediction Large Ensemble (CESM-DPLE)—a 40-member set of retrospective hindcasts documented in Yeager et al. (Bull Am Meteorol Soc 99:1867–1886. https://doi.org/10.1175/bams-d-17-0098.1, 2018). Heat budget analysis confirms the driving role of advective heat convergence in skillful prediction of SPNA upper ocean heat content out to decadal lead times. The key ocean dynamics are topographically-coupled overturning/gyre fluctuations that are geographically centered over the mid-Atlantic ridge (MAR). Long-lasting predictive skill for ocean heat transport can be related to predictable barotropic gyre and sigma-coordinate AMOC circulations, but depth-coordinate AMOC is far less predictable except in the deepest layers. The foundation of ocean memory (and circulation predictive skill) in CESM-DPLE is Labrador Sea Water thickness, which propagates predictably through interior pathways towards the MAR where large anomalies accumulate and persist. Abyssal thickness anomalies drive predictable decadal changes in the gyre circulation, including changes in sea level gradient and near surface flow, that account for the high predictability of SPNA upper ocean heat content.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athanasiadis PJ, Yeager SG, Kwon Y, Bellucci A, Smith DW, Tibaldi S (2020) Decadal predictability of North Atlantic blocking and the NAO. NPJ Clim Atmos Sci 3:20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-020-0120-6
Boer GJ, Kharin VV, Merryfield WJ (2013) Decadal predictability and forecast skill. Clim Dyn 41:1817–1833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1705-0
Boer GJ, Smith DM, Cassou C, Doblas-Reyes F, Danabasoglu G, Kirtman B et al (2016) The Decadal Climate Prediction Project (DCPP) contribution to CMIP6. Geosci Model Dev 9:3751–3777. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-9-3751-2016
Bretherton CS, Widmann M, Dymnikov VP, Wallace JM, Bladé I (1999) The effective number of spatial degrees of freedom of a time-varying field. J Clim 12:1990–2009
Bryan K, Manabe S, Pacanowski RC (1975) A global ocean-atmosphere climate model. Part II. The oceanic circulation. J Phys Oceanogr 5:30–46. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(1975)005<0030:AGOACM>2.0.CO;2
Buckley MW, Ponte RM, Forget G, Heimbach P (2014) Low-frequency SST and upper-ocean heat content variability in the North Atlantic. J Clim 27:4996–5018. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-13-00316.1
Buckley MW, Ponte RM, Forget G, Heimbach P (2015) Determining the origins of advective heat transport convergence variability in the North Atlantic. J Clim 28:3943–3956. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-14-00579.1
Choudhury D, Sen Gupta A, Sharma A, Mehrotra R, Sivakumar B (2017) An assessment of drift correction alternatives for CMIP5 decadal predictions. J Geophys Res Atmos 122:10282–10296. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD026900
Collins M, Botzet M, Carril AF, Drange H, Jouzeau A, Latif M et al (2006) Interannual to decadal climate predictability in the North Atlantic: a multimodel-ensemble study. J Clim 19:1195–1203
Danabasoglu G, Yeager SG, Bailey D, Behrens E, Bentsen M, Bi D et al (2014) North Atlantic simulations in coordinated ocean-ice reference experiments phase II (CORE-II). Part I: mean states. Ocean Model 73:76–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2013.10.005
Danabasoglu G, Yeager SG, Kim WM, Behrens E, Bentsen M, Bi D et al (2016) North Atlantic simulations in coordinated ocean-ice reference experiments phase II (CORE-II). Part II: inter-annual to decadal variability. Ocean Model 97:65–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2015.11.007
Doblas-Reyes FJ, Andreu-Burillo I, Chikamoto Y, García-Serrano J, Guemas V, Kimoto M et al (2013) Initialized near-term regional climate change prediction. Nat Commun 4:1715. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2704
Downes SM, Farneti R, Uotila P, Griffies SM, Marsland SJ, Bailey D et al (2015) An assessment of Southern Ocean water masses and sea ice during 1988–2007 in a suite of interannual CORE-II simulations. Ocean Model 94:67–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2015.07.022
Eade R, Smith D, Scaife A, Wallace E, Dunstone N, Hermanson L et al (2014) Do seasonal-to-decadal climate predictions underestimate the predictability of the real world? Geophys Res Lett 41:5620–5628. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GL061146
Farneti R, Downes SM, Griffies SM, Marsland SJ, Behrens E, Bentsen M et al (2015) An assessment of Antarctic circumpolar current and southern ocean meridional overturning circulation during 1958–2007 in a suite of interannual CORE-II simulations. Ocean Model 93:84–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2015.07.009
Fox-Kemper B, Danabasoglu G, Ferrari R, Griffies S, Hallberg R, Holland M et al (2011) Parameterization of mixed layer eddies. III: implementation and impact in global ocean climate simulations. Ocean Model 39:61–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2010.09.002 Modelling and Understanding the Ocean Mesoscale and Submesoscale
Gent PR, Mcwilliams JC (1990) Isopycnal mixing in ocean circulation models. J Phys Oceanogr 20:150–155. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(1990)020<0150:imiocm>2.0.co;2
Goddard L, Kumar A, Solomon A, Smith D, Boer G, Gonzalez P et al (2013) A verification framework for interannual-to-decadal predictions experiments. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1481-2
Good SA, Martin MJ, Rayner NA (2013) EN4: quality controlled ocean temperature and salinity profiles and monthly objective analyses with uncertainty estimates: THE EN4 DATA SET. J Geophys Res Oceans 118:6704–6716. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JC009067
Griffies SM, Bryan K (1997) Predictability of North Atlantic multidecadal climate variability. Science 275:181–184
Griffies SM, Biastoch A, Böning C, Bryan F, Danabasoglu G, Chassignet EP et al (2009) Coordinated ocean-ice reference experiments (COREs). Ocean Model 26:1–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2008.08.007
Griffies SM, Yin J, Durack PJ, Goddard P, Bates SC, Behrens E et al (2014) An assessment of global and regional sea level for years 1993–2007 in a suite of interannual CORE-II simulations. Ocean Model 78:35–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2014.03.004
Ilicak M, Drange H, Wang Q, Gerdes R, Aksenov Y, Bailey D et al (2016) An assessment of the Arctic Ocean in a suite of interannual CORE-II simulations. Part III: hydrography and fluxes. Ocean Model 100:141–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2016.02.004
Josey SA, Hirschi JJ-M, Sinha B, Duchez A, Grist JP, Marsh R (2018) The recent atlantic cold anomaly: causes, consequences, and related phenomena. Annu Rev Mar Sci 10:475–501. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-marine-121916-063102
Karspeck AR, Stammer D, Köhl A, Danabasoglu G, Balmaseda M, Smith DM et al (2015) Comparison of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation between 1960 and 2007 in six ocean reanalysis products. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2787-7
Kay JE, Deser C, Phillips A, Mai A, Hannay C, Strand G et al (2015) The Community Earth System Model (CESM) large ensemble project: a community resource for studying climate change in the presence of internal climate variability. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 96:1333–1349. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-13-00255.1
Kim WM, Yeager S, Danabasoglu G (2020) Atlantic multidecadal variability and associated climate impacts initiated by ocean thermohaline dynamics. J Clim 33:1317–1334. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-19-0530.1
Kirtman B, Power SB, Adedoyin AJ, Boer GJ, Bojariu R, Camilloni I et al (2013) Near-term climate change: projections and predictability. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Climate Change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change, chap. 11
Kwon Y-O, Frankignoul C (2014) Mechanisms of multidecadal Atlantic meridional overturning circulation variability diagnosed in depth versus density space. J Clim 27:9359–9376. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00228.1
Langehaug HR, Rhines PB, Eldevik T, Mignot J, Lohmann K (2012) Water mass transformation and the North Atlantic current in three multicentury climate model simulations. J Geophys Res Oceans. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JC008021
Large WG, Nurser AG (2001) Chapter 5.1 ocean surface water mass transformation. In Siedler G, Church J, Gould J. (eds) Ocean Circulation and Climate, vol 77 of International Geophysics. Academic Press, pp 317 – 336. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-6142(01)80126-1
Large WG, Yeager SG (2004) Diurnal to decadal global forcing for ocean and sea-ice models: the data sets and flux climatologies. NCAR technical note NCAR/TN-460+STR. https://doi.org/10.5065/D6KK98Q6
Large WG, Yeager SG (2009) The global climatology of an interannually varying air-sea flux data set. Clim Dyn 33:341–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-008-0441-3
Li F, Lozier MS, Danabasoglu G, Holliday NP, Kwon Y-O, Romanou A et al (2019) Local and downstream relationships between labrador sea water volume and North Atlantic meridional overturning circulation variability. J Clim 32:3883–3898. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-18-0735.1
Msadek R, Delworth TL, Rosati A, Anderson W, Vecchi G, Chang Y-S et al (2014) Predicting a decadal shift in North Atlantic climate variability using the GFDL forecast system. J Clim 27:6472–6496. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00476.1
Müller WA, Baehr J, Haak H, Jungclaus JH, Kröger J, Matei D et al (2012) Forecast skill of multi-year seasonal means in the decadal prediction system of the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012GL053326
O’Reilly CH, Huber M, Woollings T, Zanna L (2016) The signature of low-frequency oceanic forcing in the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. Geophys Res Lett 43:2810–2818. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL067925
Pohlmann H, Smith DM, Balmaseda MA, Keenlyside NS, Masina S, Matei D et al (2013) Predictability of the mid-latitude Atlantic meridional overturning circulation in a multi-model system. Clim Dyn 41:775–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1663-6
Robson JI, Sutton RT, Smith DM (2012) Initialized decadal predictions of the rapid warming of the North Atlantic Ocean in the mid 1990s. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012GL053370
Robson J, Polo I, Hodson DLR, Stevens DP, Shaffrey LC (2017) Decadal prediction of the North Atlantic subpolar gyre in the higem high-resolution climate model. Clim Dyn 50:921–937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3649-2
Scaife AA, Smith D (2018) A signal-to-noise paradox in climate science. NPJ Clim Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-018-0038-4
Smith DM, Eade R, Scaife AA, Caron L-P, Danabasoglu G, DelSole TM et al (2019) Robust skill of decadal climate predictions. NPJ Clim Atmos Sci 2:13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-019-0071-y
Tseng YH, Lin H, Chen HC, Thompson K, Bentsen M, Böning CW et al (2016) North and equatorial Pacific Ocean circulation in the core-II hindcast simulations. Ocean Model 104:143–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2016.06.003
Wang Q, Ilicak M, Gerdes R, Drange H, Aksenov Y, Bailey DA et al (2016a) An assessment of the Arctic Ocean in a suite of interannual CORE-II simulations. Part I: sea ice and solid freshwater. Ocean Model 99:110–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2015.12.008
Wang Q, Ilicak M, Gerdes R, Drange H, Aksenov Y, Bailey DA et al (2016b) An assessment of the Arctic Ocean in a suite of interannual CORE-II simulations. Part II: liquid freshwater. Ocean Model 99:86–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2015.12.009
Yashayaev I (2007) Hydrographic changes in the labrador sea, 1960–2005. Prog Oceanogr 73:242–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2007.04.015
Yeager S (2015) Topographic coupling of the Atlantic overturning and gyre circulations. J Phys Oceanogr 45:1258–1284. https://doi.org/10.1175/JPO-D-14-0100.1
Yeager S, Danabasoglu G (2014) The origins of late-twentieth-century variations in the large-scale North Atlantic circulation. J Clim 27:3222–3247. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00125.1
Yeager SG, Robson JI (2017) Recent progress in understanding and predicting Atlantic decadal climate variability. Curr Clim Change Rep 3:112–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40641-017-0064-z
Yeager S, Karspeck A, Danabasoglu G, Tribbia J, Teng H (2012) A decadal prediction case study: late twentieth-century North Atlantic ocean heat content. J Clim 25:5173–5189. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00595.1
Yeager SG, Karspeck AR, Danabasoglu G (2015) Predicted slowdown in the rate of Atlantic Sea ice loss. Geophys Res Lett 42:10704–10713. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL065364
Yeager SG, Kim WM, Robson J (2016) What caused the Atlantic cold blob of 2015? US CLIVAR Var 14:24–31
Yeager SG, Danabasoglu G, Rosenbloom NA, Strand W, Bates SC, Meehl GA et al (2018) Predicting near-term changes in the earth system: a large ensemble of initialized decadal prediction simulations using the community earth system model. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 99:1867–1886. https://doi.org/10.1175/bams-d-17-0098.1
Zhang R (2010) Latitudinal dependence of Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) variations: LATITUDINAL DEPENDENCE OF AMOC VARIATION. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL044474
Zhang R, Vallis GK (2007) The role of bottom vortex stretching on the path of the North Atlantic western boundary current and on the northern recirculation gyre. J Phys Oceanogr 37:2053–2080. https://doi.org/10.1175/jpo3102.1
Zhang R, Sutton R, Danabasoglu G, Delworth TL, Kim WM, Robson J et al (2016) Comment on “The Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation without a role for ocean circulation”. Science 352:1527–1527
Acknowledgements
SY acknowledges support from the National Science Foundation (NSF) Grants OPP-1737377 and OCE-1243015, as well as from the Blue-Action project (European Unions Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme, #727852). NCAR is a major facility sponsored by NSF under Cooperative Agreement No. 1852977. The CESM-DPLE was generated using computational resources provided by the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, which is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract DE-AC02-05CH11231, as well as by an Accelerated Scientific Discovery grant for Cheyenne (https://doi.org/10.5065/D6RX99HX) that was awarded by NCAR’s Computational and Information Systems Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (mp4 27404 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeager, S. The abyssal origins of North Atlantic decadal predictability. Clim Dyn 55, 2253–2271 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05382-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05382-4