Abstract
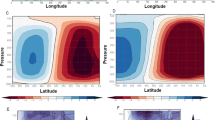
We investigate the impact of tropical tropopause warming on the stratospheric water vapor using the Specified-Dynamics version of the NCAR Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model. We find that the tropical tropopause warming results in a strengthening of the Brewer–Dobson circulation (BDC). The strengthening of BDC induced by a narrow warming of tropical tropopause within 12° latitude, which is much stronger in boreal winter than that in boreal summer, propagates more dry air from the tropical tropopause into the stratosphere and thus causes a reduction of water vapor in the middle stratosphere. On the contrary, the seasonal difference of the BDC strengthening is weaker in the experiment with a broader tropical tropopause warming within 25° latitude. The drying effect of the BDC is counteracted by the moistening effects of the tropical tropopause warming and methane oxidation. This leads to the moistening in both the lower and upper stratosphere. The results suggest the control of the stratospheric humidity by the tropical tropopause temperature could be significantly offset by the associated BDC changes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews DG, Holton JR, Leovy CB (1987) Middle atmosphere dynamics. Academic Press, Orlando, Florida
Brasseur GP, Solomon S (2005) Aeronomy of the middle atmosphere: chemistry and physics of the stratosphere and mesosphere, 3rd edn. Springer, Dordrecht
Chandran A, Garcia RR, Collins RL, Chang LC (2013) Secondary planetary waves in the middle and upper atmosphere following the stratospheric sudden warming event of January 2012. Geophys Res Lett 40:1861–1867
Collins M, Knutti R, Arblaster J, Dufresne J-L, Fichefet T, Friedlingstein P, Gao X, Gutowski WJ, Johns T, Krinner G, Shongwe M, Tebaldi C, Weaver AJ, Wehner M (2013) Long-term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1029–1136
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ, Berrisford P, Poli P, Kobayashi S, Andrae U, Balmaseda MA, Balsamo G, Bauer P, Bechtold P, Beljaars ACM, van de Berg L, Bidlot J, Bormann N, Delsol C, Dragani R, Fuentes M, Geer AJ, Haimberger L, Healy SB, Hersbach H, Holm EV, Isaksen L, Kallberg P, Kohler M, Matricardi M, McNally AP, Monge-Sanz BM, Morcrette JJ, Park BK, Peubey C, de Rosnay P, Tavolato C, Thepaut JN, Vitart F (2011) The ERA-interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:553–597
Dessler AE, Schoeberl MR, Wang T, Davis SM, Rosenlof KH (2013) Stratospheric water vapor feedback. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:18087–18091
Forster PMdF, Shine KP (2002) Assessing the climate impact of trends in stratospheric water vapor. Geophys Res Lett 29:10-11–10-14
Fueglistaler S, Haynes PH (2005) Control of interannual and longer-term variability of stratospheric water vapor. J Geophys Res Atmos 110:D24108
Fueglistaler S, Bonazzola M, Haynes PH, Peter T (2005) Stratospheric water vapor predicted from the Lagrangian temperature history of air entering the stratosphere in the tropics. J Geophys Res Atmos 110:D08107
Fueglistaler S, Dessler AE, Dunkerton TJ, Folkins I, Fu Q, Mote PW (2009) Tropical tropopause layer. Rev Geophys 47:RG1004
Garcia RR, Randel WJ (2008) Acceleration of the Brewer–Dobson circulation due to increases in greenhouse gases. J Atmos Sci 65:2731–2739
Garcia RR, Lopez-Puertas M, Funke B, Marsh DR, Kinnison DE, Smith AK, Gonzalez-Galindo F (2014) On the distribution of CO2 and CO in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. J Geophys Res Atmos 119:5700–5718
Gettelman A, Forster PMdF, Fujiwara M, Fu Q, Vömel H, Gohar LK, Johanson C, Ammerman M (2004) Radiation balance of the tropical tropopause layer. J Geophys Res Atmos 109:D7
Gettelman A, Hegglin MI, Son SW, Kim J, Fujiwara M, Birner T, Kremser S, Rex M, Añel JA, Akiyoshi H, Austin J, Bekki S, Braesike P, Brühl C, Butchart N, Chipperfield M, Dameris M, Dhomse S, Garny H, Hardiman SC, Jöckel P, Kinnison DE, Lamarque JF, Mancini E, Marchand M, Michou M, Morgenstern O, Pawson S, Pitari G, Plummer D, Pyle JA, Rozanov E, Scinocca J, Shepherd TG, Shibata K, Smale D, Teyssèdre H, Tian W (2010) Multimodel assessment of the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere: tropics and global trends. J Geophys Res Atmos 115:D3
Hartmann DL (1981) Some aspects of the coupling between radiation, chemistry, and dynamics in the stratosphere. J Geophys Res Oceans 86:9631–9640
Haynes PH, McIntyre ME, Shepherd TG, Marks CJ, Shine KP (1991) On the “Downward Control” of extratropical diabatic circulations by eddy-induced mean zonal forces. J Atmos Sci 48:651–678
Hegglin MI, Plummer DA, Shepherd TG, Scinocca JF, Anderson J, Froidevaux L, Funke B, Hurst D, Rozanov A, Urban J, von Clarmann T, Walker KA, Wang HJ, Tegtmeier S, Weigel K (2014) Vertical structure of stratospheric water vapour trends derived from merged satellite data. Nat Geosci 7:768
Herman RL, Ray EA, Rosenlof KH, Bedka KM, Schwartz MJ, Read WG, Troy RF, Chin K, Christensen LE, Fu D (2017) Enhanced stratospheric water vapor over the summertime continental United States and the role of overshooting convection. Atmos Chem Phys 17:9
Huang Y, Zhang MH, Xia Y, Hu YY, Son SW (2016) Is there a stratospheric radiative feedback in global warming simulations? Clim Dyn 46:177–186
Jiang JH, Su H, Zhai C, Wu L, Minschwaner K, Molod AM, Tompkins AM (2015) An assessment of upper troposphere and lower stratosphere water vapor in MERRA, MERRA2, and ECMWF reanalyses using Aura MLS observations. J Geophys Res Atmos 120:11468–411485
Kunz A, Pan LL, Konopka P, Kinnison DE, Tilmes S (2011) Chemical and dynamical discontinuity at the extratropical tropopause based on START08 and WACCM analyses. J Geophys Res Atmos 116:D24
Lamarque JF, Emmons LK, Hess PG, Kinnison DE, Tilmes S, Vitt F, Heald CL, Holland EA, Lauritzen PH, Neu J, Orlando JJ, Rasch PJ, Tyndall GK (2012) CAM-chem: description and evaluation of interactive atmospheric chemistry in the Community Earth System Model. Geosci Model Dev 5:369–411
le Texier H, Solomon S, Garcia RR (1988) The role of molecular hydrogen and methane oxidation in the water vapour budget of the stratosphere. Q J R Meteorol Soc 114:281–295
Lei D, Jin L (2012) Advances in the study of water vapor vertical transport into stratosphere by deep convections. J Nanjing Univ Inf Sci Technol 65:609–619
Liang CK, Eldering A, Gettelman A, Tian B, Wong S, Fetzer EJ, Liou KN (2011) Record of tropical interannual variability of temperature and water vapor from a combined AIRS-MLS data set. J Geophys Res Atmos 116:D6
Lin P, Fu Q (2013) Changes in various branches of the Brewer–Dobson circulation from an ensemble of chemistry climate models. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:73–84
Lin P, Paynter D, Ming Y, Ramaswamy V (2017) Changes of the tropical tropopause layer under global warming. J Clim 30:1245–1258
Marsh D (2011) Chemical–dynamical coupling in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. In: Abdu MA, Pancheva D (eds) Aeronomy of the Earth’s atmosphere and ionosphere. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 3–17
Mote PW, Rosenlof KH, McIntyre ME, Carr ES, Gille JC, Holton JR, Kinnersley JS, Pumphrey HC, Russell JM, Waters JW (1996) An atmospheric tape recorder: the imprint of tropical tropopause temperatures on stratospheric water vapor. J Geophys Res Atmos 101:3989–4006
Oberländer S, Langematz U, Meul S (2013) Unraveling impact factors for future changes in the Brewer–Dobson circulation. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:10296–210312
Randel WJ, Wu F, Oltmans SJ, Rosenlof K, Nedoluha GE (2004) Interannual changes of stratospheric water vapor and correlations with tropical tropopause temperatures. J Atmos Sci 61:2133–2148
Rienecker MM, Suarez MJ, Todling R, Bacmeister J, Takacs L, Liu H-C, Gu W, Sienkiewicz M, Koster RD, Gelaro R, Stajner I, Nielsen JE (2008) The GEOS-5 data assimilation system documentation of versions 5.0.1, 5.1.0, and 5.2.0. NASA/TM-2008-104606, technical report series on global modeling and data assimilation, p 118
Sakazaki T, Fujiwara M, Mitsuda C, Imai K, Manago N, Naito Y, Nakamura T, Akiyoshi H, Kinnison D, Sano T, Suzuki M, Shiotani M (2013) Diurnal ozone variations in the stratosphere revealed in observations from the Superconducting Submillimeter-Wave Limb-Emission Sounder (SMILES) on board the International Space Station (ISS). J Geophys Res Atmos 118:2991–3006
Shepherd TG, McLandress C (2011) A robust mechanism for strengthening of the Brewer–Dobson circulation in response to climate change: critical-layer control of subtropical wave breaking. J Atmos Sci 68:784–797
Solomon S, Rosenlof KH, Portmann RW, Daniel JS, Davis SM, Sanford TJ, Plattner G-K (2010) Contributions of stratospheric water vapor to decadal changes in the rate of global warming. Science 327:1219–1223
Stenke A, Grewe V (2005) Simulation of stratospheric water vapor trends: impact on stratospheric ozone chemistry. Atmos Chem Phys 5:1257–1272
Straub C, Tschanz B, Hocke K, Kampfer N, Smith AK (2012) Transport of mesospheric H2O during and after the stratospheric sudden warming of January 2010: observation and simulation. Atmos Chem Phys 12:5413–5427
Thuburn J, Craig GC (2002) On the temperature structure of the tropical substratosphere. J Geophys Res Atmos 107:ACL 10-11–ACL 10-10
Tweedy OV, Limpasuvan V, Orsolini YJ, Smith AK, Garcia RR, Kinnison D, Randall CE, Kvissel OK, Stordal F, Harvey VL, Chandran A (2013) Nighttime secondary ozone layer during major stratospheric sudden warmings in Specified-Dynamics WACCM. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:8346–8358
Wegner T, Kinnison DE, Garcia RR, Solomon S (2013) Simulation of polar stratospheric clouds in the specified dynamics version of the whole atmosphere community climate model. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:4991–5002
Yan X, Zheng X, Zhou X, Vömel H, Song J, Li W, Ma Y, Zhang Y (2015) Validation of Aura Microwave Limb Sounder water vapor and ozone profiles over the Tibetan Plateau and its adjacent region during boreal summer. Sci China Earth Sci 58:589–603
Yuan T, Thurairajah B, She CY, Chandran A, Collins RL, Krueger DA (2012) Wind and temperature response of midlatitude mesopause region to the 2009 sudden stratospheric warming. J Geophys Res Atmos 117:D9
Acknowledgements
We thank Jian Yue for helpful comments. The data used are listed in the references, figures, and tables. This work is supported by the Discovery Program of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada (RGPIN 418305) and the Class G&C Program of the Canadian Space Agency (16SUASURDC). Y. Xia is supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (2018M630027). Y. Huang is supported by Grants from the Discovery Program of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada (RGPIN 418305-13) and the Team Research Project Program of the Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Nature et Technologies (PR-190145). Y. Hu is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, under Grants 41375072 and 41530423. J. Yang acknowledges support from the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Grant 41861124002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Y., Huang, Y., Hu, Y. et al. Impacts of tropical tropopause warming on the stratospheric water vapor. Clim Dyn 53, 3409–3418 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04714-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04714-3