Abstract
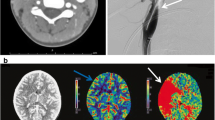
Craniocervical dissection is one of the most common causes of stroke in children. Although the most common cause of dissection is trauma, spontaneous dissections in which no cause can be revealed may also occur. The diagnosis of this type of dissection in children can be challenging with the preferred non-invasive imaging methods (MRA, CTA). Intracranial vessel wall imaging is a promising novel method for identifying specific signs of dissection. We report an 11-year-old girl with spontaneous ICA dissection, whose diagnosis was confirmed by an MRI of the intracranial vessel wall. Vessel wall imaging has contributed substantially to the diagnosis and follow-up of this case.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Nash M, Rafay MF (2019) Craniocervical arterial dissection in children: pathophysiology and management. Pediatr Neurol 95:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2019.01.020
Fullerton HJ, Johnston SC, Smith WS (2001) Arterial dissection and stroke in children. Neurology 57(7):1155 LP - 1160. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.57.7.1155
Schievink WI (2000) The treatment of spontaneous carotid and vertebral artery dissections. Curr Opin Cardiol 15(5):316–321. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001573-200009000-00002
Rafay MF, Armstrong D, deVeber G, Domi T, Chan A, MacGregor DL (2006) Craniocervical arterial dissection in children: clinical and radiographic presentation and outcome. J Child Neurol 21(1):8–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/08830738060210010101
Cinelli G, Loizzo V, Montanari L et al (2021) Internal carotid dissection as the cause of stroke in childhood. Das B, ed. Case Rep Pediatr 2021:5568827. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5568827
Chaves C, Estol C, Esnaola MM et al (2002) Spontaneous ıntracranial ınternal carotid artery dissection: report of 10 patients. Arch Neurol 59(6):977–981. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.59.6.977
Mandell DM, Mossa-Basha M, Qiao Y et al (2017) Intracranial vessel wall MRI: principles and expert consensus recommendations of the American society of neuroradiology. Am J Neuroradiol 38(2):218 LP - 229. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4893
Robertson WC, Given CA (2006) Spontaneous intracranial arterial dissection in the young: diagnosis by CT angiography. BMC Neurol 6(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-6-16
Dlamini N, Yau I, Muthusami P et al (2018) Arterial wall ımaging in pediatric stroke. Stroke 49(4):891–898. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.019827
Simsek E, Yilmaz S, Oran I, Aktan G, Tekgul H, Gokben S (2020) A rare cause of ischemic stroke in childhood: spontaneous long segment intracranial dissection. Child’s Nerv Syst 36(11):2871–2875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04530-9
Egemen E, Yakar F, Civlan S, Güngör O, Akçay G (2021) Spontaneous intracranial internal carotid artery dissection in an adolescent after heavy exercise. Child’s Nerv Syst 37(10):2959–2961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05334-1
Cuvinciuc V, Viallon M, Momjian-Mayor I et al (2013) 3D fat-saturated T1 SPACE sequence for the diagnosis of cervical artery dissection. Neuroradiology 55(5):595–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1141-1
Wang Y, Lou X, Li Y et al (2014) Imaging investigation of intracranial arterial dissecting aneurysms by using 3 T high-resolution MRI and DSA: from the interventional neuroradiologists’ view. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 156(3):515–525
Lindenholz A, van der Kolk AG, Zwanenburg JJM, Hendrikse J (2018) The use and pitfalls of intracranial vessel wall imaging: how we do it. Radiology 286(1):12–28. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017162096
Cornelissen BMW, Leemans EL, Slump CH, Marquering HA, Majoie CBLM, van den Berg R (2019) Vessel wall enhancement of intracranial aneurysms: fact or artifact? Neurosurg Focus FOC 47(1):E18. https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.4.FOCUS19236
Heo S, Han M, Kim SH, Choi JW (2019) Spontaneous ıntracranial vertebral artery dissection in a 2-year-old child diagnosed with high-resolution MRI: a case report. Investig Magn Reson Imaging 23(3):259–263. https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2019.23.3.259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
Parental informed consent was obtained.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karaman, A.K., Korkmazer, B., Arslan, S. et al. Spontaneous internal carotid artery dissection in a child diagnosed by high resolution vessel wall MRI. Childs Nerv Syst 39, 1101–1105 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-022-05745-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-022-05745-8