Abstract
Introduction
Extracranial carotid artery pseudoaneurysm is a rare complication of deep neck space infection, and no evidence-based treatment guidelines are available in the literature.
Method
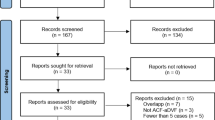
To clarify the existing experience of the different treatment strategies, the authors performed a systematic literature search using the PubMed, Ovid EMBASE, and Scopus databases in accordance with PRISMA guidelines to review all reported cases of pediatric patients with infectious carotid pseudoaneurysms larger than 1 cm.
Results
Twenty-six patients with a median age of 4 years (range 6 months–15 years) were identified. Eighteen patients (69.2%) were treated with endovascular methods, 6 patients (23.1%) with surgical methods, 1 patient (3.8%) with a hybrid endovascular/surgical approach, and 1 patient (3.8%) with conservative management. Recurrence of the pseudoaneurysm occurred in 2 cases (7.7%), both of which were successfully retreated. Of the 6 patients (23.1%) who presented with pre-procedure neurologic deficits, 3 patients had complete or near complete resolution of symptoms after intervention and 3 patients had persistent deficits at last follow-up. Four patients (15.4%) experienced new neurologic deficits post-procedure that resolved at last follow-up.
Conclusion
The endovascular treatment tends to be the preferred option to treat a large or giant infectious pseudoaneurysm of the carotid artery in the pediatric patient. However, more evidence is necessary to elucidate comparative safety and efficacy profiles of endovascular and surgical management strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abud DG, Spelle L, Piotin M, Mounayer C, Vanzin JR, Moret J (2005) Venous phase timing during balloon test occlusion as a criterion for permanent internal carotid artery sacrifice. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2602–2609
Anderson E, Chalouhi N, Dumont A, Tjoumakaris S, Zanaty M, Rosenwasser R, Starke RM, Jabbour P (2014) Management of head and neck pseudoaneurysms: a review of 33 consecutive cases. ScientificWorldJournal 2014:419803–419804. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/419803
Badloo K, Levi E, Downie L, Rose E, Wagner T, Lubitz L (2012) Mycotic pseudoaneurysm of the lingual artery: a rare complication of parapharyngeal abscess. J Paediatr Child Health 48:1045–1046. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1754.2012.02599.x
Balasundaram P, Sebastian LJD, Jain N, Prabhakar A, Garg A, Gaikwad S (2019) Management of arterial pseudoaneurysms of the neck in a pediatric population: an endovascular case series and review of literature. World Neurosurg 125:e273–e281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.061
Beningfield A, Nehus E, Chen AY, Yellin S (2006) Pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery after retropharyngeal abscess. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:338–339
Bhogal P, Perez MA, Wendl C, Bazner H, Ganslandt O, Henkes H (2017) Paediatric aneurysms - review of endovascular treatment strategies. J Clin Neurosci 45:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2017.08.009
Biron A, Berkowitz RG, Bekhit EK, Rose EA (2006) Ultrasound diagnosis of an internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in a young child. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 70:1975–1979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2006.06.011
Brinjikji W, Diehn FE, Lindsay CW, Morris JM (2015) Endovascular treatment of an infected pseudoaneurysm secondary to retropharyngeal abscess in a child. Interv Neuroradiol 21:538–542. https://doi.org/10.1177/1591019915590073
Brochu B, Dubois J, Garel L, Quintal M-C, Roy D (2004) Complications of ENT infections: pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery. Pediatr Radiol 34:417–420
Cicek MT, Yildirim IO, Gunduz E (2020) Endovascular treatment of carotid pseudoaneurysm bleeding due to parapharyngeal abscess. J Craniofac Surg 31:e324–e326. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000006204
Davidson C, Holihan C, de Oliveira Sillero R, Lee K, Mitchell RB, Shah G (2021) Infectious pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery in a child secondary to parapharyngeal abscess. Ear Nose Throat J.:014556132098458. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561320984582
DeFatta RJ, Verret DJ, Bauer P (2005) Extracranial internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 69:1135–1139
Forbes TL, Tong M (2008) External carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in an immunocompromised patient. Can J Surg 51:E11–E12
Garg K, Rockman CB, Lee V, Maldonado TS, Jacobowitz GR, Adelman MA, Mussa FF (2012) Presentation and management of carotid artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Surg 55:1618–1622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2011.12.054
Garino JP, Ryan TJ (1987) Carotid hemorrhage: a complication of peritonsillar abscess. Am J Emerg Med 5:220–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/0735-6757(87)90325-1
Glaiberman CB, Towbin RB, Boal DK (2003) Giant mycotic aneurysm of the internal carotid artery in a child: endovascular treatment. Pediatr Radiol 33:211–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-002-0844-y
Gonda RL Jr, Gutierrez OH, Hengerer AS, De Weese JA (1990) Pharyngeal abscess with external carotid artery erosion and pseudoaneurysm. A combined radiologic and surgical management. Pediatr Neurosurg 16:21–24
Gralla J, Brekenfeld C, Schmidli J, Caversaccio M, Do D-D, Schroth G (2004) Internal carotid artery aneurysm with life-threatening hemorrhages in a pediatric patient: endovascular treatment options. J Endovasc Ther 11:734–738
Gupta V, Niranjan K, Rawat L, Gupta AK (2009) Stent-graft repair of a large cervical internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm causing dysphagia. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32:558–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-008-9421-6
Gupta R, Patro SK, Chauhan N, Kumar A (2019) A giant pseudoaneurysm mimicking retropharyngeal abscess in a child. Pediatr Emerg Care 35:e79–e83. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000001100
Jagetia A, Sharma D, Singh D, Sinha S, Ganjoo P, Narang P, Mathod V (2015) Endovascular occlusion of cervical internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in a child treated by N-butyl cyanoacrylate: a rare case report. Pediatr Neurosurg 50:168–172. https://doi.org/10.1159/000381861
Jarvis SJ, Parker AJ (2001) External carotid artery aneurysm in an infant presenting with oropharyngeal haemorrhage. J Laryngol Otol 115:500–501. https://doi.org/10.1258/0022215011908045
Kato T, Oto K, Endo T, Furusho J, Iwasaki A, Sasaki Y, Iikura Y (1999) Microbial extracranial aneurysm of the internal carotid artery: complication of cervical lymphadenitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:314–317
Knouse MC, Madeira RG, Celani VJ (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa causing a right carotid artery mycotic aneurysm after a dental extraction procedure. Mayo Clin Proc 77:1125–1130. https://doi.org/10.4065/77.10.1125
Krysl J, Noel de Tilly L, Armstrong D (1993) Pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery: complication of deep neck space infection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:696–698
Kumar A, Prabhakar A, Gupta V, Khandelwal N, Ahuja C, Singhal M, Vyas S, Panda N, Vaidhya P (2018) Endovascular management of internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysms: a single-centre experience of 20 patients. Neurol India 66:1067–1074. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.236958
Lisan Q, Tran H, Verillaud B, Herman P (2016) Infectious arteritis of the internal carotid artery complicating retropharyngeal abscess. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngology Head Neck Dis 133:55–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2015.08.039
Lueg EA, Awerbuck D, Forte V (1995) Ligation of the common carotid artery for the management of a mycotic pseudoaneurysm of an extracranial internal carotid artery. A case report and review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 33:67–74
Madhusudhan KS, Venkatesh HA, Gamanagatti S, Garg P, Srivastava DN (2016) Interventional radiology in the management of visceral artery pseudoaneurysms: a review of techniques and embolic materials. Korean journal of radiology 17:351–363. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.3.351
Manjila S, Singh G, Ndubuizu O, Jones Z, Hsu DP, Cohen AR (2017) Endovascular plug for internal carotid artery occlusion in the management of a cavernous pseudoaneurysm with bifrontal subdural empyema: technical note. J Neurosurg Pediatr 20:239–246. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.3.Peds16370
Mathis JM, Barr JD, Jungreis CA, Yonas H, Sekhar LN, Vincent D, Pentheny SL, Horton JA (1995) Temporary balloon test occlusion of the internal carotid artery: experience in 500 cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:749–754
McEachern W, Walz A, Dantuluri K, Dulek D, Betters K (2019) Case 3: anisocoria in a 5-year old girl. Pediatr Rev 40:366–368. https://doi.org/10.1542/pir.2018-0132
Meher R, Garg A, Malhotra V, Singh I (2006) Pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery in an infant aged 8 months. N Z Med J 119:U1815
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151:264–269, W264. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
Mordekar SR, Bradley PJ, Whitehouse WP, Goddard AJ (2005) Occult carotid pseudoaneurysm following streptococcal throat infection. J Paediatr Child Health 41:682–684
Pearson SE, Choi SS (2005) Pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:454–456
Pourhassan S, Grotemeyer D, Fokou M, Heinen W, Balzer K, Ramp U, Sandmann W (2007) Extracranial carotid arteries aneurysms in children: single-center experiences in 4 patients and review of the literature. J Pediatr Surg 42:1961–1968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.07.052
Reisner A, Marshall GS, Bryant K, Postel GC, Eberly SM (1999) Endovascular occlusion of a carotid pseudoaneurysm complicating deep neck space infection in a child. J Neurosurg 91:510–514. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1999.91.3.0510
Requejo F, Sierre S, Lipsich J, Zuccaro G (2013) Endovascular treatment of post-pharyngitis internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm with a covered stent in a child: a case report. Childs Nerv Syst 29:1369–1373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2083-y
Robertson F, Platts A (2014) Parent Artery Sacrifice. In: Murphy K, Robertson F (eds) Interventional Neuroradiology. Springer London, London, pp 85–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-4582-0_7
Roos M, Butler I (2016) Extracranial internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in a two-year-old child: case report. J Laryngol Otol 130:596–599. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215116001109
Ruff MW, Nasr DM, Klaas JP, Renaud DL (2017) Internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm and ischemic stroke secondary to retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscess: a case report and review of the literature. J Child Neurol 32:230–236. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073816678556
Sankararaman S, Velayuthan S, Gonzalez-Toledo E (2012) Internal carotid artery stenosis as the sequela of a pseudoaneurysm after methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Pediatr Neurol 47:312–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2012.06.008
Semple CW, Berkowitz RG, Mitchell PJ (2005) Embolization of an extracranial internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 114:90–94. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940511400202
Tannuri U, De Almeida NM, Piske R, Matsumoto T (2003) Giant pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery causing upper airway obstruction in a 10-month-old infant treated by endovascular occlusion and surgical drainage. J Pediatr Surg 38:1393–1395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3468%2803%2900404-4
Timperman PE, Tomsick TA, Tew JM Jr, van Loveren HR (1995) Aneurysm formation after carotid occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:329–331
Watson MG, Robertson AS, Colquhoun IR (1991) Pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery: a forgotten complication of tonsillitis? J Laryngol Otol 105:588–590. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002221510011669X
Wells RG, Sty JR (1991) Cervical lymphadenitis complicated by mycotic carotid artery aneurysm. Pediatr Radiol 21:402–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02026669
Willemsen P, De Roover D, Kockx M, Gerard Y (1997) Mycotic common carotid artery aneurysm in an immunosuppressed pediatric patient: case report. J Vasc Surg 25:784–785
Windfuhr JP (2001) Aneurysm of the internal carotid artery following soft tissue penetration injury. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 61:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5876(01)00557-2
Wolfe SQ, Mueller-Kronast N, Aziz-Sultan MA, Zauner A, Bhatia S (2008) Extracranial carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with embolic stroke in a pediatric patient. Case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1:240–243. https://doi.org/10.3171/PED/2008/1/3/240
Zhong J, Islim F, Sundararajan S, Tahir N, Goddard T, Patel J (2019) Endovascular treatment of a giant extracranial carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in a child using vascular plugs. Ear Nose Throat J 145561319859308. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561319859308
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.S., S.A.I., J.P.C., R.S.: conception of the work. C.S., S.A.I., J.P.C.: acquisition of the data. C.S., S.A.I., J.P.C., V.S.B., G.B.S., B.A.W., R.S.: analysis and interpretation of the data. C.S., S.A.I., J.P.C.: drafting of the work. J.P.C., V.S.B., G.B.S., B.A.W., R.S.: critically revising the work for intellectual content. C.S., S.A.I., J.P.C., V.S.B., G.B.S., B.A.W., and R.S.: gave approval of the final manuscript and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval/consent for publication
IRB and informed consent were waived, as no identifiable or protected patient information is disclosed.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Previous/future presentations
This work was submitted as an abstract to the 59th Annual UT Southwestern Medical Student Research Forum. February 2, 2021. Dallas, TX.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundarrajan, C., Isa, S.A., Caruso, J.P. et al. Treatment of large infectious extracranial carotid artery pseudoaneurysms in children: a systematic review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 37, 1461–1470 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05084-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05084-0