Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study is to show the characteristics of pediatric intracranial aneurysms in a sub-Saharan country and to analyze the results of treatment in this challenging medical environment.
Method
The authors reviewed retrospectively ten patients ≤ 18 years old between May 2013 and December 2016 in Neurosurgery department of Fann Hospital in Dakar. For each child, clinical features, radiological findings, and outcome were determined with mean follow-up of 22 months.
Results
Ten children were treated for intracranial aneurysm including four boys and six girls. Two patients had evolutive infectious endocarditis with rheumatic heart disease at the time of diagnosis. Neurological signs of deficiency were present in six patients (WFNS ≥ 3).
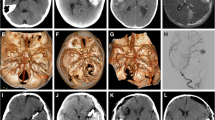
The diagnosis of aneurysm was made by CT angiography in all patients, and in two of them respectively arteriography and angioMRI were performed in complement. The aneurysm was on the middle cerebral artery in six patients, on the internal carotid artery in two others, anterior communicating artery in another, and the last one was located on the anterior cerebral artery on its 3rd segment. The treatment of the aneurysm was surgical in seven patients and endovascular in one of them. The postoperative course was excellent in two patients and good in the five patients. No postoperative worsening was noted. One child died 4 months in the postoperative course from acute cardiac deterioration.
Conclusions
In Senegal, pediatric aneurysms represent about 8.3% of all intracranial aneurysms. They are most often located on the MCA and have commonly fusiform shape. Despite difficult treatment conditions, overall outcome was good.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blount JP, Oakes WJ, Tubbs RS et al (2006) History of surgery for cerebrovascular disease in children. Part I Intracranial arterial aneurysms. Neurosurg Focus 20(6):E10
Drake CG (1975) Ligation of the vertebral (unilateral or bilateral) or basilar artery in the treatment of large intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 43:255–274
Ferrante L, Fortuna A, Celli P, Santoro A, Fraioli B (1988) Intracranial arterial aneurysms in early childhood. Surg Neurol 29:39–56
Fisher CM, Roberson GH, Ojemann RG (1977) Cerebral vasospasm with ruptured saccular aneurysm—the clinical manifestations. Neurosurgery 1:245–248
Fulkerson DH, Voorhies JM, Payner T, Cohen-Gadol A (2011) Middle cerebral artery aneurysms in children: case series and review. Neurosurg Pediatr 8:000–000
Garg K, Singh PK, Sharma BS (2014) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms--our experience and review of literature. Childs Nerv Syst 30(5):873–883
Gueye M, Koné S, Kabre A, Badiane SB, Sakho Y Ndiaye IP (1988) Anevrysmes arteriels et malformations arterioveineuses cerebrales (a propos de 60 cas opérés à la Clinique Neuro-chirurgicale du CHU de Dakar). Afr J Neurol/Sci 7 n°2
Heiskanen O, Vilkki J (1981) Intracranial arterial aneurysms in children and adolescents. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 59(1–2):55–63
Koroknai-Pal, Letho H, Niemela M (2012) Long-term outcome of 114 children with cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg Pediatrics 9:636–645
Matson DD (1965) Intracranial arterial aneurysms in childhood. J Neurosurg 23:578–583
Mehrotra A, Anup P, Kuma R (2012) Clinical and radiological profiles and outcomes in pediatric patients with intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10:340–346
Patel AN, Richardson AE (1971) Ruptured intracranial aneurysms in the first two decades of life. A study of 58 patients. J Neurosurgery 35:571–576
Proust F, Toussaint P, JOSÉ Garnieri J & al : Pediatric cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 94 :733–739, 2001
Rankin J (1957) Cerebral vascular accidents in patients over the age of 60. Scott Med J 2:200–215
Sanai N, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Gupta NM, Lawton MT (2006) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms: durability of treatment following microsurgical and endovascular management. J Neurosurg (2 Suppl Pediatrics) 104:82–89
Zhang YJ, Barrow DL, Day AL (2002) Extracranial-intracranial vein graft bypass for giant intracranial aneurysm surgery for pediatric patients: two technical case reports. Neurosurgery 50:663–668
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thioub, M., Mbaye, M., Thiam, A.B. et al. Pediatric intracranial aneurysms in Senegal: a series of 10 cases treated in unfavorable socio-economic conditions. Childs Nerv Syst 35, 165–168 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3943-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3943-2