Abstract
Purpose
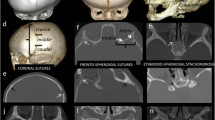
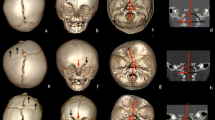
This study aimed to explain the functional role of lambdoid arch sutures in the development of cerebellar tonsillar herniation. Posterior cranial fossa (PCF) changes were investigated in infants with premature synostosis of the major and minor sutures of the lambdoid arch without premature synostosis of the PCF synchondroses.
Methods
Morphometric and volumetric PCF measurements were performed on preoperative high-resolution CT studies in 12 infants with multisutural craniosynostosis involving the lambdoid arch and compared with those of 12 age-matched healthy subjects.
Results
All 12 patients had hypoplasia of PCF bone structures and normal volumes of the PCF and neural structures. PCF hypoplasia was related to exocciput length in infants with isolated involvement of major sutures, while it was related to posterior skull base hemifossae in infants with isolated involvement of minor lambdoid arch sutures. Foramen magnum AP diameter was reduced in babies with major suture involvement and tonsillar herniation, while foramen magnum AP and LL diameters were reduced in babies with minor suture involvement without tonsillar herniation. Right and left jugular foramen (JF) areas differed in all infants; however, the area of the smaller JF was significantly reduced only in infants with involvement of minor lambdoid arch sutures.
Conclusion
Hypoplasia of PCF bone structures due to sutural synostosis of the lambdoid arch is a required predisposing but not sufficient factor for the development of cerebellar tonsillar herniation through the foramen magnum. Normal PCF volume and foramen magnum anatomy may partly explain the development of cerebellar tonsil herniation in infants with lambdoid arch synostosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calandrelli R, D’Apolito G, Gaudino S, Sciandra MC, Caldarelli M, Colosimo C (2014) Identification of skull base sutures and craniofacial anomalies in children with craniosynostosis: utility of multidetector CT. Radiol Med 119:694–704
Canpolat A, Akcakaya MO, Altunrende E, Ozlu HM, Duman H, Ton T, Akdemir O (2014) Chiari type I malformation yielded to the diagnosis of Crouzon syndrome. J Neurosci Rural Pract 5:81–83
Chumas PD, Cinalli G, Arnaud E, Marchac D, Renier D (1997) Classification of previously unclassified cases of craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 86:177–181
Cinalli G, Renier D, Sebag G, Sainte-Rose C, Arnaud E, Pierre-Kahn A (1995) Chronic tonsillar herniation in Crouzon’s and Apert’s syndromes: the role of premature synostosis of the lambdoid suture. J Neurosurg 83:575–582
Cinalli G, Spennato P, Sainte-Rose C, Arnaud E, Aliberti F, Brunelle F, Cianciulli E, Renier D (2005) Chiari malformation in craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 21:889–901
Di Rocco C, Frassanito P, Massimi L, Peraio S (2011) Hydrocephalus and Chiari type I malformation. Childs Nerv Syst 27:1653–1664
Fearon JA, Rhodes J (2009) Pfeiffer syndrome: a treatment evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg 123:1560–1569
Francis PM, Beals S, Rekate HL, Pittman HW, Manwaring K, Reiff J (1992) Chronic tonsillar herniation and Crouzon’s syndrome. Pediatr Neurosurg 18:202–206
Johnston I, Jacobson E, Besser M (1998) The acquired Chiari malformation and syringomyelia following spinal CSF drainage: a study of incidence and management. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140:417–427, discussion 427–418
Kreiborg S, Marsh JL, Cohen MM Jr, Liversage M, Pedersen H, Skovby F, Borgesen SE, Vannier MW (1993) Comparative three-dimensional analysis of CT-scans of the calvaria and cranial base in Apert and Crouzon syndromes. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 21:181–188
Leikola J, Koljonen V, Valanne L, Hukki J (2010) The incidence of Chiari malformation in nonsyndromic, single suture craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 26:771–774
Loukas M, Shayota BJ, Oelhafen K, Miller JH, Chern JJ, Tubbs RS, Oakes WJ (2011) Associated disorders of Chiari type I malformations: a review. Neurosurg Focus 31:E3
Medina LS, Richardson RR, Crone K (2002) Children with suspected craniosynostosis: a cost-effectiveness analysis of diagnostic strategies. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:215–221
Noudel R, Jovenin N, Eap C, Scherpereel B, Pierot L, Rousseaux P (2009) Incidence of basioccipital hypoplasia in Chiari malformation type I: comparative morphometric study of the posterior cranial fossa. Clinical article. J Neurosurg 111:1046–1052
Novegno F, Caldarelli M, Massa A, Chieffo D, Massimi L, Pettorini B, Tamburrini G, Di Rocco C (2008) The natural history of the Chiari type I anomaly. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2:179–187
Pouratian N, Sansur CA, Newman SA, Jane JA Jr, Jane JA Sr (2007) Chiari malformations in patients with uncorrected sagittal synostosis. Surg Neurol 67:422–427, discussion 427–428
Richtsmeier JT, Lele S (1990) Analysis of craniofacial growth in Crouzon syndrome using landmark data. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol 10:39–62
Rodrigues VJ, Elsayed S, Loeys BL, Dietz HC, Yousem DM (2009) Neuroradiologic manifestations of Loeys-Dietz syndrome type 1. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1614–1619
Saldino RM, Steinbach HL, Epstein CJ (1972) Familial acrocephalosyndactyly (Pfeiffer syndrome). Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 116:609–622
Schweitzer T, Bohm H, Meyer-Marcotty P, Collmann H, Ernestus RI, Krauss J (2012) Avoiding CT scans in children with single-suture craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 28:1077–1082
Sgouros S, Natarajan K, Hockley AD, Goldin JH, Wake M (1999) Skull base growth in craniosynostosis. Pediatr Neurosurg 31:281–293
Stovner LJ, Bergan U, Nilsen G, Sjaastad O (1993) Posterior cranial fossa dimensions in the Chiari I malformation: relation to pathogenesis and clinical presentation. Neuroradiology 35:113–118
Strahle J, Muraszko KM, Buchman SR, Kapurch J, Garton HJ, Maher CO (2011) Chiari malformation associated with craniosynostosis. Neurosurg Focus 31:E2
Taylor WJ, Hayward RD, Lasjaunias P, Britto JA, Thompson DN, Jones BM, Evans RD (2001) Enigma of raised intracranial pressure in patients with complex craniosynostosis: the role of abnormal intracranial venous drainage. J Neurosurg 94:377–385
Thompson DN, Harkness W, Jones BM, Hayward RD (1997) Aetiology of herniation of the hindbrain in craniosynostosis. An investigation incorporating intracranial pressure monitoring and magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Neurosurg 26:288–295
Tubbs RS, Elton S, Blount JP, Oakes WJ (2001) Preliminary observations on the association between simple metopic ridging in children without trigonocephaly and the Chiari I malformation. Pediatr Neurosurg 35:136–139
Vatansever D, Kyriakopoulou V, Allsop JM, Fox M, Chew A, Hajnal JV, Rutherford MA (2013) Multidimensional analysis of fetal posterior fossa in health and disease. Cerebellum 12:632–644
Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, Smith RG, Ho S, Gee JC, Gerig G (2006) User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 31:1116–1128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calandrelli, R., D’Apolito, G., Panfili, M. et al. Role of “major” and “minor” lambdoid arch sutures in posterior cranial fossa changes: mechanism of cerebellar tonsillar herniation in infants with multisutural craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 32, 451–459 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2956-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2956-3