Abstract
Purpose
Cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is traditionally thought of as a congenital diagnosis. In recent years, there has been infrequent reports of this neurovascular condition presenting as de novo entities.
Methods
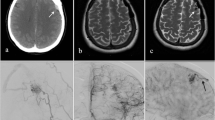
The authors report two cases of pediatric patients who present with de novo cerebral AVMs. In both cases, the patients had magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain done as part of the work-up for first-onset seizures. At that point in time, the scans were unremarkable. After a latent period of approximately 6 and 9 years respectively, a repeated MRI brain scan showed evidence of de novo AVM for each patient.
Results
Both patients did not have radiological evidence of cerebral AVM during their first presentation of seizures. However, a repeated MRI brain scan after a period of 6 and 9 years demonstrated new findings of cerebral AVM for each patient.
Conclusions
Currently, the disease of cerebral de novo AVM remain as an ambiguous condition that is poorly understood. With the advances in molecular diagnostics, there are possibilities of exploring biochemical profiles for better understanding of the origin of cerebral AVMs. However, in the meantime, owing to the unpredictable nature of cerebral AVMs, clinicians should have increased awareness of this unique condition. This is especially important, as definitive treatment is available to prevent devastating neurological sequelae from cerebral AVM rupture.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimoto H, Komatsu K, Kubota Y (2003) Symptomatic de novo arteriovenous malformation appearing 17 years after the resection of two other arteriovenous malformations in childhood: case report. Neurosurgery 52(1):228–232
Al-Rodhan NR, Al-Mefty O, Rifai A, Fox JL (1986) Persistence of primitive cerebral vasculature in a newborn. A case report of whole brain AVM. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 88(4):283–287
Alvarez H, Perry V, Solle M, Castillo M (2012) De novo cerebral arteriovenous malformation in a child with previous cavernous malformation and developmental venous anomaly. J Neurosurg Pediatr 9(3):327–330. doi:10.3171/2011.12.peds11312
Arisato T, Hashiguchi T, Sarker KP, Arimura K, Asano M, Matsuo K, Osame M, Maruyama I (2003) Highly accumulated platelet vascular endothelial growth factor in coagulant thrombotic region. J thromb haemost : JTH 1(12):2589–2593
Bulsara KR, Alexander MJ, Villavicencio AT, Graffagnino C (2002) De novo cerebral arteriovenous malformation: case report. Neurosurgery 50(5):1137–1141
Chen W, Sun Z, Han Z, Jun K, Camus M, Wankhede M, Mao L, Arnold T, Young WL, Su H (2014) De novo cerebrovascular malformation in the adult mouse after endothelial alk1 deletion and angiogenic stimulation. Stroke 45(3):900–902
Choi JH, Mohr JP (2005) Brain arteriovenous malformations in adults. Lancet Neurol 4(5):299–308
DeCesare B, Omojola MF, Fogarty EF, Brown JC, Taylon C (2006) Spontaneous thrombosis of congenital cerebral arteriovenous malformation complicated by subdural collection: in utero detection with disappearance in infancy. Br J radiol 79(946):e140–144. doi:10.1259/bjr/44174031
Delitala A, Delfini R, Vagnozzi R, Esposito S (1982) Increase in size of cerebral angiomas: case report. J Neurosurg 57(4):556–558
Gonzalez LF, Bristol RE, Porter RW, Spetzler RF (2005) De novo presentation of an arteriovenous malformation: Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 102(4):726–729
Gunsilius E, Petzer A, Stockhammer G, Nussbaumer W, Schumacher P, Clausen J, Gastl G (2000) Thrombocytes are the major source for soluble vascular endothelial growth factor in peripheral blood. Oncology 58(2):169–174
Hao Q, Zhu Y, Su H, Shen F, Yang GY, Kim H, Young WL (2010) VEGF Induces More Severe Cerebrovascular Dysplasia in Endoglin than in Alk1 Mice. Transl stroke res 1(3):197–201. doi:10.1007/s12975-010-0020-x
Heidaran MA, Pierce JH, Yu JC, Lombardi D, Artrip JE, Fleming TP, Thomason A, Aaronson SA (1991) Role of alpha beta receptor heterodimer formation in beta platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor activation by PDGF-AB. J biol chem 266(30):20232–20237
Hladky J-P, Lejeune J-P, Blond S, Pruvo J-P, Dhellemmes P (1994) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children: report on 62 cases. Childs Nerv Syst 10(5):328–333
Hofmeister C, Stapf C, Hartmann A, Sciacca RR, Mansmann U, terBrugge K, Lasjaunias P, Mohr JP, Mast H, Meisel J (2000) Demographic, morphological, and clinical characteristics of 1289 patients with brain arteriovenous malformation. Stroke; J cereb circ 31(6):1307–1310
Hoh BL, Chapman PH, Loeffler JS, Carter BS, Ogilvy CS (2002) Results of multimodality treatment for 141 patients with brain arteriovenous malformations and seizures: factors associated with seizure incidence and seizure outcomes. Neurosurgery 51(2):303–309, discussion 309-311
Iwama T, Hayashida K, Takahashi JC, Nagata I, Hashimoto N (2002) Cerebral hemodynamics and metabolism in patients with cerebral arteriovenous malformations: an evaluation using positron emission tomography scanning. J Neurosurg 97(6):1314–1321. doi:10.3171/jns.2002.97.6.1314
Jeffree RL, Stoodley MA (2009) Postnatal development of arteriovenous malformations. Pediatr Neurosurg 45(4):296–304
Kilbourn KJ, Spiegel G, Killory BD, Kureshi I (2014) Case report of a de novo brainstem arteriovenous malformation in an 18-year-old male and review of the literature. Neurosurgical review:1-7
Kilic T, Pamir MN, Kullu S, Eren F, Ozek MM, Black PM (2000) Expression of structural proteins and angiogenic factors in cerebrovascular anomalies. Neurosurgery 46(5):1179–1191, discussion 1191-1172
Lasjaunias P (1997) A revised concept of the congenital nature of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Interv Neuroradiol : J peritherapeutic neuroradiol, surg proced relat neurosci 3(4):275–281
Mahajan A, Manchandia TC, Gould G, Bulsara KR (2010) De novo arteriovenous malformations: case report and review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev 33(1):115–119
Mullan S, Mojtahedi S, Johnson DL, Macdonald RL (1996) Embryological basis of some aspects of cerebral vascular fistulas and malformations. J Neurosurg 85(1):1–8. doi:10.3171/jns.1996.85.1.0001
O’Shaughnessy BA, DiPatri AJ Jr, Parkinson RJ, Batjer HH (2005) Development of a de novo cerebral arteriovenous malformation in a child with sickle cell disease and moyamoya arteriopathy: case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr 102(2):238–243
Perret G, Nishioka H (1966) Report on the cooperative study of intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage. IV. Cerebral angiography. An analysis of the diagnostic value and complications of carotid and vertebral angiography in 5,484 patients. J Neurosurg 25(1):98–114. doi:10.3171/jns.1966.25.1.0098
Potter JM (1955) Angiomatous malformations of the brain: their nature and prognosis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 16(4):227–243
Sakamoto S, Kiura Y, Yamasaki F, Shibukawa M, Ohba S, Shrestha P, Sugiyama K, Kurisu K (2008) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in duramater of patients with moyamoya disease. Neurosurg Rev 31(1):77–81. doi:10.1007/s10143-007-0102-8, discussion 81
Sandalcioglu IE, Wende D, Eggert A, Müller D, Roggenbuck U, Gasser T, Wiedemayer H, Stolke D (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor plasma levels are significantly elevated in patients with cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Cerebrovasc Dis 21(3):154–158
Schmit BP, Burrows PE, Kuban K, Goumnerova L, Scott RM (1996) Acquired cerebral arteriovenous malformation in a child with moyamoya disease: case report. J Neurosurg 84(4):677–680
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65(4):476–483. doi:10.3171/jns.1986.65.4.0476
Stevens J, Leach J, Abruzzo T, Jones B (2009) De novo cerebral arteriovenous malformation: case report and literature review. Am J Neuroradiol 30(1):111–112
Turjman F, Massoud TF, Sayre JW, Vinuela F, Guglielmi G, Duckwiler G (1995) Epilepsy associated with cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a multivariate analysis of angioarchitectural characteristics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16(2):345–350
Conflict of interest
We, the authors of this manuscript, report no funding, financial support, or industrial affiliations received for the writing of this article. In addition, we report no conflict of interest concerning the material or methods used in this paper. This manuscript has not been published and is not being considered for publication elsewhere.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeo, J.J.Y., Low, S.Y.Y., Seow, W.T. et al. Pediatric de novo cerebral AVM: report of two cases and review of literature. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 609–614 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2609-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2609-y