Abstract
Case report
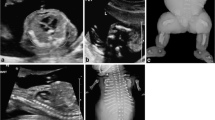
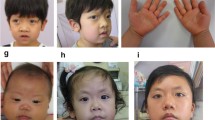
We describe an unusual clinical case with an 11-Mb deletion at 4q27 (chr4: 123094652-134164491), craniosynostosis (CS), mild psychomotor retardation, and facial dysmorphic features. This deletion involves 18 genes; FGF2, NUDT6, and SPRY1 are primarily or secondarily implicated in human cranial bone and sagittal suture development and could play an important role in CS.
Conclusions
Clinicians should always contemplate genetic studies in patients with syndromic CS. Mutational targeted genetic testing is appropriate for patients with classical or specific CS syndrome. Nevertheless, array comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH) should be considered as a first-line test in nontypical syndromic CS phenotype. Cytogenetic studies are decisive for genetic counseling indeed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panigrahi I (2011) Craniosynostosis genetics: the mystery unfolds. Indian J Hum Genet 17:48–53
Slater BJ, Lenton KA, Kwan MD, Gupta DM, Wan DC, Longaker MT (2008) Cranial sutures: a brief review. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:170e–178e
Johnson D, Wilkie AO (2011) Craniosynostosis. Eur J Hum Genet 19:369–376
Liu Y, Kadlub N, da Silva Freitas R, Persing JA, Duncan C, Shin JH (2008) The misdiagnosis of craniosynostosis as deformational plagiocephaly. J Craniofac Surg 19:132–136
Lajeunie E, Le Merrer M, Bonaiti-Pellie C, Marchac D, Renier D (1995) Genetic study of nonsyndromic coronal craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet 55:500–504
Mulliken JB, Gripp KW, Stolle CA, Steinberger D, Muller U (2004) Molecular analysis of patients with synostotic frontal plagiocephaly (unilateral coronal synostosis). Plast Reconstr Surg 113:1899–1909
Wilkie AO (1997) Craniosynostosis: genes and mechanisms. Hum Mol Genet 6:1647–1656
Wilkie AO, Byren JC, Hurst JA, Jayamohan J, Johnson D, Knight SJ, Lester T, Richards PG, Twigg SR, Wall SA (2010) Prevalence and complications of single-gene and chromosomal disorders in craniosynostosis. Pediatrics 126:e391–e400
McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine (1995) OMIM : Online Mendelian inheritance in man. National Center for Biotechnology Information, [Bethesda, Maryland]
Baraitser M, Winter R (2005) London dysmorphology database, London medical databases, version 1.0.4 [CD-ROM]. Oxford medical databases. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Lajeunie E, Le Merrer M, Bonaiti-Pellie C, Marchac D, Renier D (1996) Genetic study of scaphocephaly. Am J Med Genet 62:282–285
del Valle Torrado M, Labarta JD, Migliorini AM (1982) Interstitial deletion of the long arm of chromosome 4 in a patient with mental retardation and abnormal phenotype. J Med Genet 19:477–479
Firth HV, Richards SM, Bevan AP, Clayton S, Corpas M, Rajan D, Van Vooren S, Moreau Y, Pettett RM, Carter NP (2009) DECIPHER: Database of Chromosomal Imbalance and Phenotype in Humans Using Ensembl Resources. Am J Hum Genet 84:524–533
Beenken A, Mohammadi M (2009) The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:235–253
Hatch NE, Li Y, Franceschi RT (2009) FGF2 stimulation of the pyrophosphate-generating enzyme, PC-1, in pre-osteoblast cells is mediated by RUNX2. J Bone Miner Res 24:652–662
Canalis E, Raisz LG (1980) Effect of fibroblast growth factor on cultured fetal rat calvaria. Metabolism 29:108–114
Rice DP, Aberg T, Chan Y, Tang Z, Kettunen PJ, Pakarinen L, Maxson RE, Thesleff I (2000) Integration of FGF and TWIST in calvarial bone and suture development. Development 127:1845–1855
Greenwald JA, Mehrara BJ, Spector JA, Warren SM, Fagenholz PJ, Smith LE, Bouletreau PJ, Crisera FE, Ueno H, Longaker MT (2001) In vivo modulation of FGF biological activity alters cranial suture fate. Am J Pathol 158:441–452
Connerney J, Andreeva V, Leshem Y, Mercado MA, Dowell K, Yang X, Lindner V, Friesel RE, Spicer DB (2008) Twist1 homodimers enhance FGF responsiveness of the cranial sutures and promote suture closure. Dev Biol 318:323–334
Choi KY, Kim HJ, Lee MH, Kwon TG, Nah HD, Furuichi T, Komori T, Nam SH, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Ryoo HM (2005) Runx2 regulates FGF2-induced Bmp2 expression during cranial bone development. Dev Dyn 233:115–121
Zhou M, Sutliff RL, Paul RJ, Lorenz JN, Hoying JB, Haudenschild CC, Yin M, Coffin JD, Kong L, Kranias EG, Luo W, Boivin GP, Duffy JJ, Pawlowski SA, Doetschman T (1998) Fibroblast growth factor 2 control of vascular tone. Nat Med 4:201–207
Li AW, Murphy PR (2000) Expression of alternatively spliced FGF-2 antisense RNA transcripts in the central nervous system: regulation of FGF-2 mRNA translation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 162:69–78
Minowada G, Jarvis LA, Chi CL, Neubuser A, Sun X, Hacohen N, Krasnow MA, Martin GR (1999) Vertebrate Sprouty genes are induced by FGF signaling and can cause chondrodysplasia when overexpressed. Development 126:4465–4475
Jones KL, Smith DW (2006) Smith’s recognizable patterns of human malformation. Saunders, Philadelphia
Liu C, Cummins TR, Tyrrell L, Black JA, Waxman SG, Dib-Hajj SD (2005) CAP-1A is a novel linker that binds clathrin and the voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.8. Mol Cell Neurosci 28:636–649
Imbrici P, Camerino DC, Tricarico D (2013) Major channels involved in neuropsychiatric disorders and therapeutic perspectives. Front Genet 4:76
Eijkelkamp N, Linley JE, Baker MD, Minett MS, Cregg R, Werdehausen R, Rugiero F, Wood JN (2012) Neurological perspectives on voltage-gated sodium channels. Brain 135:2585–2612
Redies C, Hertel N, Hubner CA (2012) Cadherins and neuropsychiatric disorders. Brain Res 1470:130–144
Morrow EM, Yoo SY, Flavell SW, Kim TK, Lin Y, Hill RS, Mukaddes NM, Balkhy S, Gascon G, Hashmi A, Al-Saad S, Ware J, Joseph RM, Greenblatt R, Gleason D, Ertelt JA, Apse KA, Bodell A, Partlow JN, Barry B, Yao H, Markianos K, Ferland RJ, Greenberg ME, Walsh CA (2008) Identifying autism loci and genes by tracing recent shared ancestry. Science 321:218–223
Jehee FS, Krepischi-Santos AC, Rocha KM, Cavalcanti DP, Kim CA, Bertola DR, Alonso LG, D'Angelo CS, Mazzeu JF, Froyen G, Lugtenberg D, Vianna-Morgante AM, Rosenberg C, Passos-Bueno MR (2008) High frequency of submicroscopic chromosomal imbalances in patients with syndromic craniosynostosis detected by a combined approach of microsatellite segregation analysis, multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification and array-based comparative genome hybridisation. J Med Genet 45:447–450
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Jaén, A., Fernández-Perrone, A.L., Fernández-Mayoralas, D.M. et al. Craniosynostosis, psychomotor retardation, and facial dysmorphic features in a Spanish patient with a 4q27q28.3 deletion. Childs Nerv Syst 30, 2157–2161 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2474-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2474-8