Abstract
Background
Cavernous malformations (CMs) of the central nervous system (CNS) are angiographically occult vascular lesions that affect approximately 0.5 % of the general population, and one quarter of all CMs occurs in children.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed demographic, clinical, radiological, management, and follow-up data of 36 pediatric patients with CMs from a single institution.
Results
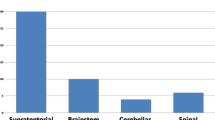
The mean age of the children at first presentation and at operation was 8.7 and 9.6 years, respectively. However, a bimodal age distribution was found with peak under 4 years and above 12 years. Seizure was the most common single presenting symptom (38.9 %), and 61.1 % of patients had at least one seizure before the admission. Focal neurological deficits (410.7 %), intracranial hypertension (27.8 %), and headache (2.8 %) were the other manifestations. Acute/subacute hemorrhage was evident at presentation in 63.9 %. The patients under 6 years of age were found to have significantly more giant cavernomas (69 vs 20 %; p = 0.011), and more overt hemorrhages (81 vs 47 %; p = 0.065) at diagnosis than those patients above 12 years. Surgery was performed in 31 patients (32 CMs), with 26 total and 6 incomplete resections. Mean follow-up duration was 6.9 ± 4.1 years. Of all patients, 63.8 % had excellent and 30.5 % had good clinical outcomes, and also 90.9 % of the epileptic patients were seizure-free (Engel Class I) at the last follow-up.
Conclusions
Younger children tend to harbor larger CMs and present with hemorrhage more frequently than older ones. Microsurgical resection should be the treatment of choice in symptomatic and accessible CMs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acciarri N, Galassi E, Giulioni M, Pozzati E, Grasso V, Palandri G et al (2009) Cavernous malformations of the central nervous system in the pediatric age group. Pediatr Neurosurg 45(2):81–104
Aiba T, Tanaka R, Koike T, Kameyama S, Takeda N, Komata T (1995) Natural history of intracranial cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg 83(1):56–59
Al-Holou WN, O’Lynnger TM, Pandey AS, Gemmete JJ, Thompson BG, Muraszko KM et al (2012) Natural history and imaging prevalence of cavernous malformations in children and young adults. J Neurosurg Pediatr 9(2):198–205
Amato MC, Madureira JF, Oliveira RS (2013) Intracranial cavernous malformation in children: a single-centered experience with 30 consecutive cases. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 71(4):220–228
Batra S, Lin D, Recinos PF, Zhang J, Rigamonti D (2009) Cavernous malformations: natural history, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Neurol 5(12):659–670
Campeau NG, Lane JI (2005) De novo development of a lesion with the appearance of a cavernous malformation adjacent to an existing developmental venous anomaly. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26(1):156–159
Clatterbuck RE, Moriarity JL, Elmaci I, Lee RR, Breiter SN, Rigamonti D (2000) Dynamic nature of cavernous malformations: a prospective magnetic resonance imaging study with volumetric analysis. J Neurosurg 93(6):981–986
Cohen DS, Zubay GP, Goodman RR (1995) Seizure outcome after lesionectomy for cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg 83(2):237–242
Cohen-Gadol AA, Jacob JT, Edwards DA, Krauss WE (2006) Coexistence of intracranial and spinal cavernous malformations: a study of prevalence and natural history. J Neurosurg 104(3):376–381
Consales A, Piatelli G, Ravegnani M, Pavanello M, Striano P, Zoli ML et al (2010) Treatment and outcome of children with cerebral cavernomas: a survey on 32 patients. Neurol Sci 31(2):117–123
Di Rocco C, Iannelli A, Tamburrini G (1996) Cavernomas of the central nervous system in children: a report of 22 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 138(11):1267–1274
Di Rocco C, Iannelli A, Tamburrini G (1997) Surgical management of paediatric cerebral cavernomas. J Neurosurg Sci 41(4):343–347
Engel J Jr, Van Ness PC, Rasmussen TB, Ojemann LM (1993) Outcome with respect to epileptic seizures. In: Engel J Jr (ed) Surgical treatment of the epilepsies, 2nd edn. Raven, New York, pp 609–621
Fortuna A, Ferrante L, Mastronardi L, Acqui M, D’Addetta R (1989) Cerebral cavernous angioma in children. Childs Nerv Syst 5(4):201–207
Gault J, Sarin H, Awadallah NA, Shenkar R, Awad IA (2004) Pathobiology of human cerebrovascular malformations: basic mechanisms and clinical relevance. Neurosurgery 55(1):1–17
Giulioni M, Acciarri N, Padovani R, Frank F, Galassi E, Gaist G (1994) Surgical management of cavernous angiomas in children. Surg Neurol 42(3):194–199
Gross BA, Lin N, Du R, Day AL (2011) The natural history of intracranial cavernous malformations. Neurosurg Focus 30(6):E24
Gross BA, Smith ER, Goumnerova L, Proctor MR, Madsen JR, Scott RM (2013) Resection of supratentorial lobar cavernous malformations in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 12(4):367–373
Hugelshofer M, Acciarri N, Sure U, Georgiadis D, Baumgartner RW, Bertalanffy H, Siegel AM (2011) Effective surgical treatment of cerebral cavernous malformations: a multicenter study of 79 pediatric patients. J Neurosurg Pediatr 8(5):522–525
Kim LJ, Lanzino G, Rekate HL, Zabramski JM, Spetzler RF (2002) Cavernous malformations of the pediatric central nervous system. Operat Tech Neurosurg 5(3):150–154
Kim W, Stramotas S, Choy W, Dye J, Nagasawa D, Yang I (2011) Prognostic factors for post-operative seizure outcomes after cavernous malformation treatment. J Clin Neurosci 18(7):877–880
Kivelev J, Niemelä M, Kivisaari R, Hernesniemi J (2010) Intraventricular cerebral cavernomas: a series of 12 patients and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 112(1):140–149
Labauge P, Denier C, Bergametti F, Tournier-Lasserve E (2007) Genetics of cavernous angiomas. Lancet Neurol 6(3):237–244
Lee JW, Kim DS, Shim KW, Chang JH, Huh SK, Park YG, Choi JU (2008) Management of intracranial cavernous malformation in pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 24(3):321–327
Maeder P, Gudinchet F, Meuli R, de Tribolet N (1998) Development of a cavernous malformation of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19(6):1141–1143
Mazza C, Scienza R, Beltramello A, Da Pian R (1991) Cerebral cavernous malformations (cavernomas) in the pediatric age-group. Childs Nerv Syst 7(3):139–146
Mottolese C, Hermier M, Stan H, Jouvet A, Saint-Pierre G, Froment JC, Bret P, Lapras C (2001) Central nervous system cavernomas in the pediatric age group. Neurosurg Rev 24(2–3):55–71
Nimjee SM, Powers CJ, Bulsara KR (2006) Review of the literature on de novo formation of cavernous malformations of the central nervous system after radiation therapy. Neurosurg Focus 21(1):1–6
Ozgen B, Senocak E, Oguz KK, Soylemezoglu F, Akalan N (2011) Radiological features of childhood giant cavernous malformations. Neuroradiology 53(4):283–289
Perrini P, Lanzino G (2006) The association of venous developmental anomalies and cavernous malformations: pathophysiological, diagnostic, and surgical considerations. Neurosurg Focus 21(1):1–4
Petersen TA, Morrison LA, Schrader RM, Hart BL (2010) Familial versus sporadic cavernous malformations: differences in developmental venous anomaly association and lesion phenotype. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31(2):377–382
Rigamonti D, Drayer BP, Johnson PC, Hadley MN, Zabramski J, Spetzler RF (1987) The MRI appearance of cavernous malformations (angiomas). J Neurosurg 67(4):518–524
Robinson JR, Awad IA, Little JR (1991) Natural history of the cavernous angioma. J Neurosurg 75(5):709–714
Rosenow F, Alonso-Vanegas MA, Baumgartner C, Blümcke I, Carreño M, Gizewski ER et al (2013) Cavernoma-related epilepsy: review and recommendations for management—report of the Surgical Task Force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 54(12):2025–2035
Scott RM, Barnes P, Kupsky W, Adelman LS (1992) Cavernous angiomas of the central nervous system in children. J Neurosurg 76(1):38–46
Van Gompel JJ, Rubio J, Cascino GD, Worrell GA, Meyer FB (2009) Electrocorticography-guided resection of temporal cavernoma: is electrocorticography warranted and does it alter the surgical approach? J Neurosurg 110(6):1179–1185
Wurm G, Schnizer M, Fellner FA (2005) Cerebral cavernous malformations associated with venous anomalies: surgical considerations. Neurosurgery 57(1 Suppl):42–58
Xia C, Zhang R, Mao Y, Zhou L (2009) Pediatric cavernous malformation in the central nervous system: report of 66 cases. Pediatr Neurosurg 45(2):105–113
Yeon JY, Kim JS, Choi SJ, Seo DW, Hong SB, Hong SC (2009) Supratentorial cavernous angiomas presenting with seizures: surgical outcomes in 60 consecutive patients. Seizure 18(1):14–20
Zabramski JM, Wascher TM, Spetzler RF, Johnson B, Golfinos J, Drayer BP, Brown B, Rigamonti D, Brown G (1994) The natural history of familial cavernous malformations: results of an ongoing study. J Neurosurg 80(3):422–432
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilginer, B., Narin, F., Hanalioglu, S. et al. Cavernous malformations of the central nervous system (CNS) in children: clinico-radiological features and management outcomes of 36 cases. Childs Nerv Syst 30, 1355–1366 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2442-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2442-3