Abstract
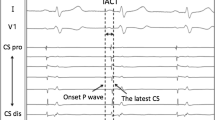
P-wave morphology reflects atrial remodeling and indicates prognosis after radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) for atrial fibrillation (AF). The impact of p-wave morphology after excluding the effect of pulmonary vein (PV) substrate on outcomes is unknown. We evaluated the p-wave morphology on electrocardiography immediately after PV isolation for clinical outcomes. Eighty-four consecutive patients (47 with paroxysmal AF and 37 with persistent AF) who underwent RFCA were included. P-wave duration (PWD) and amplitude in all leads were examined during sinus rhythm immediately after PV isolation. We evaluated the relationship between electrocardiogram parameters and AF recurrence, according to the type of AF and following ablation, and the correlation with left atrial (LA) volume, low voltage ratio, and fixed conduction time. During 12 months of follow-up, 20 patients experienced recurrence. The cut-off value of PWD > 120 ms in lead I showed a sensitivity of 75% and specificity of 69% for predicting recurrence. PWD was significantly correlated with LA volume, low voltage, and conduction velocity. Significantly higher recurrence rates were observed in patients with PWD > 120 ms than in those with PWD ≤ 120 ms (p < 0.001), and the difference was more pronounced in patients with persistent AF. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that PWD > 120 ms was independently associated with recurrence in the total population (hazard ratio 2.00; 95% confidence interval 1.27–3.22; p = 0.003) and in patients with persistent AF. In conclusion, long PWD after PV isolation predicts AF recurrence, which might be associated with the extent of the LA substrate in persistent AF.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, Kim YH, Saad EB, Aguinaga L, Akar JG, Badhwar V, Brugada J, Camm J, Chen PS, Chen SA, Chung MK, Nielsen JC, Curtis AB, Davies DW, Day JD, d’Avila A, de Groot N, Di Biase L, Duytschaever M, Edgerton JR, Ellenbogen KA, Ellinor PT, Ernst S, Fenelon G, Gerstenfeld EP, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, Helm RH, Hylek E, Jackman WM, Jalife J, Kalman JM, Kautzner J, Kottkamp H, Kuck KH, Kumagai K, Lee R, Lewalter T, Lindsay BD, Macle L, Mansour M, Marchlinski FE, Michaud GF, Nakagawa H, Natale A, Nattel S, Okumura K, Packer D, Pokushalov E, Reynolds MR, Sanders P, Scanavacca M, Schilling R, Tondo C, Tsao HM, Verma A, Wilber DJ, Yamane T (2017) 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 14:e275–e444
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, Garrigue S, Le Mouroux A, Le Metayer P, Clementy J (1998) Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 339:659–666
Hoit BD (2014) Left atrial size and function: role in prognosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 63:493–505
Boriani G, Vitolo M, Diemberger I, Proietti M, Valenti AC, Malavasi VL, Lip GYH (2021) Optimizing indices of AF susceptibility and burden to evaluate AF severity, risk and outcomes. Cardiovasc Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvab147
Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Boriani G, Castella M, Dan GA, Dilaveris PE, Fauchier L, Filippatos G, Kalman JM, La Meir M, Lane DA, Lebeau JP, Lettino M, Lip GYH, Pinto FJ, Thomas GN, Valgimigli M, Van Gelder IC, Van Putte BP, Watkins CL (2021) 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the task force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 42:373–498
Mugnai G, Chierchia GB, de Asmundis C, Julia J, Conte G, Sieira-Moret J, Capulzini L, Wauters K, Rodriguez-Manero M, Ciconte G, Baltogiannis G, Di Giovanni G, Saitoh Y, Brugada P (2016) P-wave indices as predictors of atrial fibrillation recurrence after pulmonary vein isolation in normal left atrial size. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 17:194–200
Pranata R, Yonas E, Vania R (2019) Prolonged P-wave duration in sinus rhythm pre-ablation is associated with atrial fibrillation recurrence after pulmonary vein isolation-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 24:e12653
Wu JT, Long DY, Dong JZ, Wang SL, Fan XW, Yang HT, Duan HY, Yan LJ, Qian P, Yang CK (2016) Advanced interatrial block predicts clinical recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. J Cardiol 68:352–356
Park JK, Park J, Uhm JS, Joung B, Lee MH, Pak HN (2016) Low P-wave amplitude (<0.1 mV) in lead I is associated with displaced inter-atrial conduction and clinical recurrence of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation. Europace 18:384–391
Caldwell J, Koppikar S, Barake W, Redfearn D, Michael K, Simpson C, Hopman W, Baranchuk A (2014) Prolonged P-wave duration is associated with atrial fibrillation recurrence after successful pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 39:131–138
Okumura Y, Watanabe I, Ohkubo K, Ashino S, Kofune M, Hashimoto K, Shindo A, Sugimura H, Nakai T, Kasamaki Y, Saito S (2007) Prediction of the efficacy of pulmonary vein isolation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation by the signal-averaged P-wave duration. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 30:304–313
Kaypakli O, Koca H, Şahin DY, Okar S, Karataş F, Koç M (2018) Association of P wave duration index with atrial fibrillation recurrence after cryoballoon catheter ablation. J Electrocardiol 51:182–187
Salah A, Zhou S, Liu Q, Yan H (2013) P wave indices to predict atrial fibrillation recurrences post pulmonary vein isolation. Arq Bras Cardiol 101:519–527
Nakatani Y, Sakamoto T, Mizumaki K, Nishida K, Kataoka N, Tsujino Y, Yamaguchi Y, Inoue H (2016) Coefficient of variation of P-wave duration is a novel atrial heterogeneity index to predict recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 27:542–548
Nogami A, Kurita T, Abe H, Ando K, Ishikawa T, Imai K, Usui A, Okishige K, Kusano K, Kumagai K, Goya M, Kobayashi Y, Shimizu A, Shimizu W, Shoda M, Sumitomo N, Seo Y, Takahashi A, Tada H, Naito S, Nakazato Y, Nishimura T, Nitta T, Niwano S, Hagiwara N, Murakawa Y, Yamane T, Aiba T, Inoue K, Iwasaki Y, Inden Y, Uno K, Ogano M, Kimura M, Si S, Sasaki S, Satomi K, Shiga T, Suzuki T, Sekiguchi Y, Soejima K, Takagi M, Chinushi M, Nishi N, Noda T, Hachiya H, Mitsuno M, Mitsuhashi T, Miyauchi Y, Miyazaki A, Morimoto T, Yamasaki H, Aizawa Y, Ohe T, Kimura T, Tanemoto K, Tsutsui H, Mitamura H (2021) JCS/JHRS 2019 guideline on non-pharmacotherapy of cardiac arrhythmias. J Arrhythm 37:709–870
Kanzaki Y, Inden Y, Ando M, Kamikubo Y, Ito T, Mizutani Y, Kato H, Fujii A, Yanagisawa S, Hirai M, Murohara T (2016) An ECG index of P-wave force predicts the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 39:1191–1197
Doi A, Takagi M, Katayama H, Yoshiyama T, Hayashi Y, Tatsumi H, Yoshiyama M (2018) Diagnostic value of electrocardiographic P-wave characteristics in atrial fibrillation recurrence and tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy after catheter ablation. Heart Vessels 33:1381–1389
Kubala M, Lucena-Padros I, Xie S, Casado-Arroyo R, Frankel DS, Lin D, Santangeli P, Supple GE, Dixit S, Tschabrunn CM, Liang JJ, Yang J, Hyman MC, Zado ES, Marchlinski FE (2019) P-wave morphology and multipolar intracardiac atrial activation to facilitate nonpulmonary vein trigger localization. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 30:865–876
Kanemaru Y, Arima Y, Kaikita K, Kiyama T, Kaneko S, Ito M, Yamabe H, Motozato K, Yamanaga K, Fujisue K, Sueta D, Takashio S, Araki S, Usuku H, Nakamura T, Fukunaga T, Suzuki S, Izumiya Y, Sakamoto K, Soejima H, Yamamoto E, Kawano H, Kanazawa H, Tsujita K (2020) Elongation of the high right atrium to coronary sinus conduction time predicts the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation. Int J Cardiol 300:147–153
Yanagisawa S, Inden Y, Okamoto H, Fujii A, Sakamoto Y, Mamiya K, Tomomatsu T, Shibata R, Murohara T (2020) Electrocardiogram characteristics of P wave associated with successful pulmonary vein isolation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: significance of changes in P-wave duration and notched P wave. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 25:e12712
Ogawa M, Kumagai K, Vakulenko M, Yasuda T, Siegerman C, Garfinkel A, Chen PS, Saku K (2007) Reduction of P-wave duration and successful pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 18:931–938
Nakatani Y, Sakamoto T, Yamaguchi Y, Tsujino Y, Kataoka N, Kinugawa K (2020) P-wave vector magnitude predicts the left atrial low-voltage area in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Electrocardiol 59:35–40
Boriani G, Diemberger I, Biffi M, Camanini C, Valzania C, Corazza I, Martignani C, Zannoli R, Branzi A (2005) P wave dispersion and short-term vs. late atrial fibrillation recurrences after cardioversion. Int J Cardiol 101:355–361
Hazen MS, Marwick TH, Underwood DA (1991) Diagnostic accuracy of the resting electrocardiogram in detection and estimation of left atrial enlargement: an echocardiographic correlation in 551 patients. Am Heart J 122:823–828
Andlauer R, Seemann G, Baron L, Dossel O, Kohl P, Platonov P, Loewe A (2018) Influence of left atrial size on P-wave morphology: differential effects of dilation and hypertrophy. Europace 20:iii36–iii44
Kim DH, Kim GC, Kim SH, Yu HK, Choi WG, An IS, Kwan J, Park KS, Lee WH (2007) The relationship between the left atrial volume and the maximum P-wave and P-wave dispersion in patients with congestive heart failure. Yonsei Med J 48:810–817
Nattel S, Burstein B, Dobrev D (2008) Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: mechanisms and implications. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 1:62–73
Jadidi A, Muller-Edenborn B, Chen J, Keyl C, Weber R, Allgeier J, Moreno-Weidmann Z, Trenk D, Neumann FJ, Lehrmann H, Arentz T (2018) The duration of the amplified sinus-P-wave identifies presence of left atrial low voltage substrate and predicts outcome after pulmonary vein isolation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 4:531–543
Kirchhof P, Camm AJ, Goette A, Brandes A, Eckardt L, Elvan A, Fetsch T, van Gelder IC, Haase D, Haegeli LM, Hamann F, Heidbüchel H, Hindricks G, Kautzner J, Kuck KH, Mont L, Ng GA, Rekosz J, Schoen N, Schotten U, Suling A, Taggeselle J, Themistoclakis S, Vettorazzi E, Vardas P, Wegscheider K, Willems S, Crijns H, Breithardt G (2020) Early rhythm-control therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 383:1305–1316
Potpara TS, Lip GYH, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Boriani G, Van Gelder IC, Heidbuchel H, Hindricks G, Camm AJ (2021) The 4S-AF scheme (stroke risk; symptoms; severity of burden; substrate): a novel approach to in-depth characterization (rather than classification) of atrial fibrillation. Thromb Haemost 121:270–278
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Yanagisawa is affiliated with a department sponsored by Medtronic Japan. All other authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by local institutional ethics committee at Kasugai Municipal Hospital.
Consent to participate
All patients provided written informed consent prior to the procedure.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
380_2021_1932_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 (TIF 81 KB) Comparison of the Kaplan–Meier survival curves of AF-free survival after the ablation for patients with paroxysmal/persistent AF and with PWD ≤120 ms/ >120 ms in lead I. AF, atrial fibrillation; PWD, p-wave duration
380_2021_1932_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary file2 (TIF 85 KB) Comparison of the Kaplan–Meier survival curves of AF-free survival after the ablation for patients with additional ablation or non-additional ablation and with PWD ≤120 ms and PWD >120 ms in lead I. AF, atrial fibrillation; PWD, p-wave duration
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohguchi, S., Inden, Y., Yanagisawa, S. et al. Long P-wave duration immediately after pulmonary vein isolation on radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation predicts clinical recurrence: correlation with atrial remodeling in persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart Vessels 37, 476–488 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01932-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01932-w