Abstract
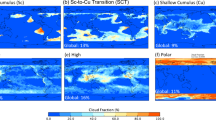
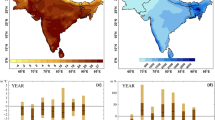
High spatiotemporal resolution radiances from the advanced imagers onboard the new generation of geostationary weather satellites provide a unique opportunity to evaluate the abilities of various reanalysis datasets to depict multilayer tropospheric water vapor (WV), thereby enhancing our understanding of the deficiencies of WV in reanalysis datasets. Based on daily measurements from the Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) onboard the Himawari-8 satellite in 2016, the bias features of multilayer WV from six reanalysis datasets over East Asia are thoroughly evaluated. The assessments show that wet biases exist in the upper troposphere in all six reanalysis datasets; in particular, these biases are much larger in summer. Overall, we find better depictions of WV in the middle troposphere than in the upper troposphere. The accuracy of WV in the ERA5 dataset is the highest, in terms of the bias magnitude, dispersion, and pattern similarity. The characteristics of the WV bias over the Tibetan Plateau are significantly different from those over other parts of East Asia. In addition, the reanalysis datasets all capture the shift of the subtropical high very well, with ERA5 performing better overall.
摘 要
新一代静止气象卫星所携带的先进成像仪能够提供高时空分辨率的辐射观测, 这为检验评估当前各类再分析资料对对流层不同层结水汽的描述能力提供了独特的机会, 有利于增强我们对不同再分析水汽资料不足的理解和认识. 本文利用2016年日本葵花8号静止卫星搭载的成像仪获取的水汽辐射观测资料, 全面评估了六套再分析资料对不同高度层结的水汽在东亚区域的再现能力. 结果表明, 在对流层上层, 六套再分析资料都表现出明显的湿偏差, 尤其是夏季, 湿偏差最大. 整体而言, 再分析资料在对流层中层对水汽的描述能力比对流层上层好. ERA5水汽资料与观测最为接近, 说明其精度最高. 再分析水汽资料在青藏高原区域的精度明显低于东亚其他区域; 此外, 六套再分析资料均能较好地再现副热带高压的移动, 其中ERA5表现最好.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, R. P., and M. A. Ringer, 2003: Inconsistencies between satellite estimates of longwave cloud forcing and dynamical fields from reanalyses. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30(9), 1491, https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL017019.
Bessho, K., and Coauthors, 2016: An introduction to Himawari-8/9-Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satellites. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 94, 151–183, https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2016-009.
Chahine, M. T., and Coauthors, 2006: AIRS: Improving weather forecasting and providing new data on greenhouse gases. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 87, 911–926, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-87-7-911.
Chu, Q. C., Q. G. Wang, G. L. Feng, Z. K. Jia, and G. Liu, 2021: Roles of water vapor sources and transport in the intraseasonal and interannual variation in the peak monsoon rainfall over East China. Climate Dyn., 57(7–8), 2153–2170, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05799-5.
Chung, E.-S., B.-J. Sohn, and J. Schmetz, 2009: Diurnal variation of outgoing longwave radiation associated with high cloud and UTH changes from Meteosat-5 measurements. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys., 105, 109–119, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-009-0041-8.
Chung, E. S., B. J. Sohn, J. Schmetz, and M. Koenig, 2007: Diurnal variation of upper tropospheric humidity and its relations to convective activities over tropical Africa. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 7, 2489–2502, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-2489-2007.
Chung, E.-S., B. J. Soden, B.-J. Sohn, and J. Schmetz, 2011: Model-simulated humidity bias in the upper troposphere and its relation to the large-scale circulation. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 116, D10110, https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JD015609.
Clough, S. A., F. X. Kneizys, and R. W. Davies, 1989: Line shape and the water vapor continuum. Atmospheric Research, 23, 229–241, https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-8095(89)90020-3.
Clough, S. A., M. J. Iacono, and J. L. Moncet, 1992: Line-by-line calculations of atmospheric fluxes and cooling rates: Application to water vapor. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 97, 15761–15785, https://doi.org/10.1029/92JD01419.
Clough, S. A., F. X. Kneizys, L. S. Rothman, and W. O. Gallery, 1981: Atmospheric spectral transmittance and radiance: FAS-COD1 B. Proc. Volume 0277, Atmospheric Transmission, Washington, D.C., United States, SPIE, 152–166, https://doi.org/10.1117/12.931914.
Clough, S. A., M. W. Shephard, E. J. Mlawer, J. S. Delamere, M. J. Iacono, K. Cady-Pereira, S. Boukabara, and P. D. Brown, 2005: Atmospheric radiative transfer modeling: A summary of the AER codes. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 91, 233–244, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2004.05.058.
Davis, S. M., and Coauthors, 2017: Assessment of upper tropospheric and stratospheric water vapor and ozone in reanalyses as part of S-RIP. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 12743–12778, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-12743-2017.
Dee, D. P., and Coauthors, 2011: The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 137, 553–597, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.828.
Di, D., Y. F. Ai, J. Li, W. J. Shi, and N. M. Lu, 2016: Geostationary satellite-based 6.7 µm band best water vapor information layer analysis over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 121, 4600–4613, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JD024867.
Di, D., J. Li, W. Han, W. G. Bai, C. Q. Wu, and W. P. Menzel, 2018: Enhancing the fast radiative transfer model for FengYun-4 GIIRS by using local training profiles. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 123, 12583–12596, https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029089.
Erying, V., T. Shepherd, and D. Waugh, 2010: SPARC: Chemistry-Climate Model Validation, edited by: WCRP-30, WMO/TD-No. 40, SPARC Report No. 5, Toronto, Canada.
Eyre, J., 1991: A fast radiative transfer model for satellite sounding systems. ECMWF Tech. Memo. 176, https://doi.org/10.21957/xsg8d92y3.
Fujiwara, M., S. Polavarapu, and D. Jackson, 2012: A proposal of the SPARC reanalysis/analysis intercomparison project. SPARC Newsletter, 38, 14–17.
Fujiwara, M., and Coauthors, 2017: Introduction to the SPARC Reanalysis Intercomparison Project (S-RIP) and overview of the reanalysis systems. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 1417–1452, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-1417-2017.
Gelaro, R., and Coauthors, 2017: The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Climate, 30, 5419–5454, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0758.1.
Guo, Y. J., S. Q. Zhang, J. H. Yan, Z. Chen, and X. Ruan, 2016: A comparison of atmospheric temperature over China between radiosonde observations and multiple reanalysis datasets. J. Meteor. Res., 30, 242–257, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-016-5169-0.
Held, I. M., and B. J. Soden, 2000: Water vapor feedback and global warming. Annual Review of Energy and the Environment, 25, 441–475, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.energy.25.1.441.
Held, I. M., and B. J. Soden, 2006: Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J. Climate, 19, 5686–5699, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI3990.1.
Hersbach, H., and Coauthors, 2020: The ERA5 global reanalysis. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 146, 1999–2049, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3803.
Hewison, T. J., X. Q. Wu, F. F. Yu, Y. Tahara, X. Q. Hu, D. Kim, and M. Koenig, 2013: GSICS inter-calibration of infrared channels of geostationary imagers using Metop/IASI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 51, 1160–1170, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2013.2238544.
Hólm, E. V., 2002: Revision of the ECMWF humidity analysis: Construction of a Gaussian control variable. Preprints, Proceedings of the ECMWF/GEWEX Workshop on Humidity Analysis, Shinfield Park, Reading, ECMWF.
Holmlund, K., and Coauthors, 2021: Meteosat Third Generation (MTG): Continuation and innovation of observations from geostationary orbit. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 102, E990–E1015, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-19-0304.1.
Jiang, J. H., H. Su, C. X. Zhai, L. T. Wu, K. Minschwaner, A. M. Molod, and A. M. Tompkins, 2015: An assessment of upper troposphere and lower stratosphere water vapor in MERRA, MERRA2, and ECMWF reanalyses using Aura MLS observations. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 120, 11468–11485, https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD023752.
John, V. O., G. Holl, R. P. Allan, S. A. Buehler, D. E. Parker, and B. J. Soden, 2011: Clear-sky biases in satellite infrared estimates of upper tropospheric humidity and its trends. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 116(D14), D14108, https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD015355.
Kobayashi, S., and Coauthors, 2015: The JRA-55 reanalysis: General specifications and basic characteristics. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 93, 5–48, https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2015-001.
Krishnamurti, T. N., and H. N. Bhalme, 1976: Oscillations of a monsoon system. Part I. Observational aspects. J. Atmos. Sci., 33, 1937–1954, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1976)033<1937:OOAMSP>2.0.CO;2.
Lanzante, J. R., and G. E. Gahrs, 2000: The “clear-sky bias” of TOVS upper-tropospheric humidity. J. Climate, 13, 4034–4041, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<4034:TCSBOT>2.0.CO;2.
Li, C. F., and M. Yanai, 1996: The onset and interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon in relation to land-sea thermal contrast. J. Climate, 9, 358–375, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<0358:TOAIVO>2.0.CO;2.
Lin, S. J., 2004: A “vertically Lagrangian” finite-volume dynamical core for global models. Mon. Wea. Rev., 132(10), 2293–2307, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132<2293:AVLFDC>2.0.CO;2.
Lin, Y. L., W. H. Dong, M. H. Zhang, Y. Y. Xie, W. Xue, J. B. Huang, and Y. Luo, 2017: Causes of model dry and warm bias over central U.S. and impact on climate projections. Nature Communications, 8, 881, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01040-2.
Liu, Z. Q., and Coauthors, 2017: CMA global reanalysis (CRA-40): Status and plans. Proc. 5th Int. Conf. on Reanalysis, Rome, Italy.
Machenhauer, B., 1979: The spectral method. Numerical Methods used in Atmospheric Models, Vol. II, GARP Publication Series No. 17, A. Kasahara, Ed., World Meteorological Organization, 121–275.
Mao, J. F., X. Y. Shi, L. J. Ma, D. P. Kaiser, Q. X. Li, and P. E. Thornton, 2010: Assessment of reanalysis daily extreme temperatures with China’s homogenized historical dataset during 1979–2001 using probability density functions. J. Climate, 23, 6605–6623, https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JCLI3581.1.
Min, M., and Coauthors, 2017: Developing the science product algorithm testbed for Chinese next-generation geostationary meteorological satellites: Fengyun-4 series. J. Meteor. Res., 31, 708–719, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-017-6161-z.
Molod, A., L. Takacs, M. Suarez, and J. Bacmeister, 2015: Development of the GEOS-5 atmospheric general circulation model: Evolution from MERRA to MERRA2. Geoscientific Model Development, 8, 1339–1356, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-8-1339-2015.
Oki, T., and S. Kanae, 2006: Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science, 313, 1068–1072, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1128845.
Pierce, D. W., T. P. Barnett, E. J. Fetzer, and P. J. Gleckler, 2006: Three-dimensional tropospheric water vapor in coupled climate models compared with observations from the AIRS satellite system. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L21701, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL027060.
Polavarapu, S., and M. Pulido, 2017: Stratospheric and mesospheric data assimilation: The role of middle atmospheric dynamics. Data Assimilation for Atmospheric, Oceanic and Hydrologic Applications (Vol. III), S. K. Park and L. Xu, Eds., Springer, 429–454, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-43415-5_19.
Randel, W., and Coauthors, 2004: The SPARC intercomparison of middle-atmosphere climatologies. J. Climate, 17, 986–1003, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0986:TSIOMC>2.0.CO;2.
Randel, W. J., and Coauthors, 2009: An update of observed stratospheric temperature trends. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 114, D02107, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010421.
Saha, S., and Coauthors, 2010: The ncep climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 91, 1015–1058, https://doi.org/10.1175/2010BAMS3001.1.
Santer, B. D., and Coauthors, 2003: Behavior of tropopause height and atmospheric temperature in models, reanalyses, and observations: Decadal changes. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 108(D1), 4002, https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002258.
Saunders, R., M. Matricardi, and P. Brunel, 1999: An improved fast radiative transfer model for assimilation of satellite radiance observations. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 125, 1407–1425, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.1999.49712555615.
Schmetz, J., and L. van de Berg, 1994: Upper tropospheric humidity observations from Meteosat compared with short-term forecast fields. Geophys. Res. Lett., 21, 573–576, https://doi.org/10.1029/94GL00376.
Schmit, T. J., M. M. Gunshor, W. P. Menzel, J. J. Gurka, J. Li, and A. S. Bachmeier, 2005: Introducing the next-generation Advanced Baseline Imager on GEOS-R. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 86, 1079–1096, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-86-8-1079.
Schmit, T. J., J. Li, S. A. Ackerman, and J. J. Gurka, 2009: High-spectral- and high-temporal-resolution infrared measurements from geostationary orbit. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 26, 2273–2292, https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JTECHA1248.1.
Seemann, S. W., E. E. Borbas, R. O. Knuteson, G. R. Stephenson, and H.-L. Huang, 2008: Development of a global infrared land surface emissivity database for application to clear sky sounding retrievals from multispectral satellite radiance measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol., 47, 108–123, https://doi.org/10.1175/2007JAMC1590.1.
Shi, L., C. J. Schreck III, V. O. John, E.-S. Chung, T. Lang, S. A. Buehler, and B. J. Soden, 2022: Assessing the consistency of satellite-derived upper tropospheric humidity measurements. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 15(33), 6949–6963, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-15-6949-2022.
Soden, B. J., 2000: The diurnal cycle of convection, clouds, and water vapor in the tropical upper troposphere. Geophys. Res. Lett., 27, 2173–2176, https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL011436.
Soden, B. J., and F. P. Bretherton, 1994: Evaluation of water vapor distribution in general circulation models using satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 99(D1), 1187–1210, https://doi.org/10.1029/93JD02912.
Soden, B. J., and F. P. Bretherton, 1996: Interpretation of TOVS water vapor radiances in terms of layer-average relative humidities: Method and climatology for the upper, middle, and lower troposphere. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 101, 9333–9343, https://doi.org/10.1029/96JD00280.
Sohn, B.-J., J. Schmetz, R. Stuhlmann, and J.-Y. Lee, 2006: Dry bias in satellite-derived clear-sky water vapor and its contribution to longwave cloud radiative forcing. J. Climate, 9(21), 5570–5580, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI3948.1.
Stevens, B., H. Brogniez, C. Kiemle, J.-L. Lacour, C. Crevoisier, and J. Kiliani, 2017: Structure and dynamical influence of water vapor in the lower tropical troposphere. Surveys in Geophysics, 38, 1371–1397, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-017-9420-8.
Takahashi, H., H. Su, and J. H. Jiang, 2016: Error analysis of upper tropospheric water vapor in CMIP5 models using “A-Train” satellite observations and reanalysis data. Climate Dyn., 46(9–10), 2787–2803, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2732-9.
Tian, B. J., B. J. Soden, and X. Q. Wu, 2004: Diurnal cycle of convection, clouds, and water vapor in the tropical upper troposphere: Satellites versus a general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 109, D10101, https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JD004117.
Tompkins, A. M., K. Gierens, and G. Rädel, 2007: Ice supersaturation in the ECMWF integrated forecast system. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 133, 53–63, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.14.
Trenberth, K. E., J. T. Fasullo, and J. Kiehl, 2009: Earth’s global energy budget. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 90, 311–324, https://doi.org/10.1175/2008BAMS2634.1.
Trenberth, K. E., J. T. Fasullo, and J. Mackaro, 2011: Atmospheric moisture transports from ocean to land and global energy flows in reanalyses. J. Climate, 24, 4907–4924, https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JCLI4171.1.
Trenberth, K. E., D. P. Stepaniak, J. W. Hurrell, and M. Fiorino, 2001: Quality of reanalyses in the tropics. J. Climate, 14(7), 1499–1510, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<1499:QORITT>2.0.CO;2.
Wang, X., M. Min, F. Wang, J. P. Guo, B. Li, and S. H. Tang, 2019: Intercomparisons of cloud mask products among Fengyun-4A, Himawari-8, and MODIS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 57, 8827–8839, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923247.
Xu, J., and A. M. Powell Jr., 2011: Uncertainty of the stratospheric/tropospheric temperature trends in 1979–2008: Multiple satellite MSU, radiosonde, and reanalysis datasets. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11, 10727–10732, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-10727-2011.
Xue, Y. H., J. Li, Z. L. Li, M. M. Gunshor, and T. J. Schmit, 2020b: Evaluation of the diurnal variation of upper tropospheric humidity in reanalysis using homogenized observed radiances from international geostationary weather satellites. Remote Sensing, 12, 1628, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101628.
Xue, Y. H., J. Li, Z. L. Li, R. Y. Lu, M. M. Gunshor, S. L. Moeller, D. Di, and T. J. Schmit, 2020a: Assessment of upper tropospheric water vapor monthly variation in reanalyses with near-global homogenized 6.5-µm radiances from geostationary satellites. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 125, e2020JD032695, https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JD032695.
Yanai, M., C. F. Li, and Z. S. Song, 1992: Seasonal heating of the Tibetan Plateau and its effects on the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 70, 319–351, https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj1965.70.1B_319.
Yang, J., Z. Q. Zhang, C. Y. Wei, F. Lu, and Q. Guo, 2017: Introducing the new generation of Chinese geostationary weather satellites, Fengyun-4. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 98, 1637–1658, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0065.1.
Zhang, P., J. Li, E. Olson, T. J. Schmit, J. Li, and W. P. Menzel, 2006: Impact of point spread function on infrared radiances from geostationary satellites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 44, 2176–2183, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2006.872096.
Zhou, T.-J., and R. C. Yu, 2005: Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with typical anomalous summer rainfall patterns in China. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 110(D8), D08104, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JD005413.
Zhu, L. R., R. L. Zhou, D. Di, W. G. Bai, and Z. J. Liu, 2023: Retrieval of atmospheric water vapor content in the environment from AHI/H8 using both physical and random forest methods—A case study for Typhoon Maria (201808). Remote Sensing, 15, 498, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020498.
Acknowledgements
This study was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41975020 and 41975031) (Jun LI). The surface IR emissivity data are from the UW-Madison Baseline Fit Emissivity database (available at ftp://ftp.ssec.wisc.edu/pub/g_emis/). CMA is thanked for providing the CRA reanalysis dataset. The other reanalysis datasets can be downloaded (https://reanalyses.org/atmosphere/overview-current-atmospheric-reanalyses#). We thank W. P. MENZEL for useful input to the discussion and conclusions related to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Article Highlights
• A wet bias in the upper troposphere over East Asia is found for all reanalyses, while the mid-tropospheric moisture bias is inconsistent.
• Water vapor biases in the reanalyses are smaller in the mid than upper troposphere. ERA5 performs best when compared with observations.
• The bias over the Tibetan Plateau is the largest and most inconsistent among the reanalysis datasets.
• Overall, the reanalysis datasets capture the shift of the subtropical high very well, with ERA5 performing better than the others.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di, D., Li, J., Xue, Y. et al. Consistency of Tropospheric Water Vapor between Reanalyses and Himawari-8/AHI Measurements over East Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 41, 19–38 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-023-2332-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-023-2332-2