Abstract
Methanotrophy of arable soils is affected by N fertilization, but the knowledge about the effect of oxygen level is poorly understood; soil aeration can fluctuate and zones of low oxygen are widespread in soil. We monitored CH4 oxidation in three mineral soils (Eutric Cambisol, Haplic Podzol, Mollic Gleysol) under laboratory conditions by varying the O2 level (from 20 to 2% O2), with or without NH4+ (100 mg N kg−1). In controls (without NH4+), CH4 was oxidized completely in the O2 range from oxia (20% O2) to high hypoxia (5% O2), while the process was inhibited under microoxia (2% O2). Ammonium application decreased CH4 consumption in all soils. This negative effect was stronger at 20% and 2% O2 than under hypoxia. The highest CH4 oxidation rates and the shortest initial (lag) phases in both control and NH4+-amended soils were observed under high (5% O2) and low (10% O2) hypoxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
As a greenhouse gas, methane (CH4) has an important role in global warming. Its concentration has doubled since the industrial age (Kirschke et al. 2013). Soil is a large and dynamic reservoir of C (Amundson 2015) and this ecosystem has great importance in the CH4 budget. In non-aerated zones, methanogens produce CH4 (Dubey et al. 2014) but soil has a natural ability to oxidize it due to the activity of aerobic methanotrophic bacteria (Tate 2015). Due to the participation of CH4 in the global climate change and the mitigating role of methanotrophy in soil, studies on processes responsible for the CH4 budget are important. In this context, it is particularly important to understand all mechanisms regulating the circulation of CH4 in soil. Arable soils are generally well aerated (Oenema 2001); therefore, they can be biological sinks for CH4. However, the methanotrophic activity of soils is controlled by a wide range of factors: CH4 and O2 as substrates (Bussmann et al. 2006; Henckel et al. 2000; Hernandez et al. 2015; Li et al. 2015; Mohanty et al. 2016), soil properties and conditions such as organic C content and N availability and moisture, pH and temperature (Einola et al. 2007; Huang et al. 2016; Jäckel et al. 2001; Kravchenko et al. 2005), and human activities, such as grazing, deforestation, and fertilization (Bodelier 2011; Castillo et al. 2017; Chen-rui et al. 2003; Ho et al. 2015; Köster et al. 2017; Trimpler et al. 2016).
Molecular oxygen (O2) is necessary for cell respiration and plays an important role in several chemical and biochemical processes, including CH4 oxidation. Since the gas diffusion coefficient declines in water, O2 availability is influenced by changing soil moisture (Chojnicki et al. 2010; Lamorski et al. 2013). Therefore, it is an important biological driver of greenhouse gas fluxes (Jarecke et al. 2016). Besides, composition of soil air usually differs from that of atmospheric air due to the activity of roots and microorganisms. The average O2 concentration in soil may be close to the atmospheric value (9.1 mmol O2 l−1, corresponding to 21% v/v) (Šantrůčková and Šimek 1994) but hypoxic or anoxic conditions may occur. Therefore, soil aeration usually ranges from 20 to 10% v/v and can even reach zero (Stępniewski et al. 2005). Especially, microoxic zones with a reduced O2 concentration between the oxic and anoxic layers are widespread in soil and are natural habitats of bacteria (Morris and Schmidt 2013). Moreover, bacteria with potential for microaerobic metabolism are common in nature due to the widespread occurrence of microoxic zones in many environments. However, there is insufficient knowledge about microbial activity in microoxic soil environments (Morris and Schmidt 2013).
Next to O2, nitrogen (N) is also an important regulator of the activity of methanotrophic bacteria (Gärdenäs et al. 2011), especially in cultivated soil. The contribution of agricultural soils to the total terrestrial area and the increasing use of N fertilizers (Amundson et al. 2015) suggest that the interaction between CH4 and N becomes important globally in the context of climate change (Bodelier and Steenbergh 2014). Recent studies emphasize that its environmental consequences are not fully recognized. Ammonium can competitively inhibit CH4 oxidation (Alam and Jia 2012; Bender and Conrad 1995; Dunfield and Knowles 1995; Saari et al. 2004; Steinkamp et al. 2001; Wang and Ineson 2003; Xu and Inubushi 2004; Zheng et al. 2013), but also can stimulate the oxidation (Bodelier et al. 2000; Hu and Lu 2015; Krüger and Frenzel 2003; Rigler and Zechmeister-Boltenstern 1999) or have no effect (Bender and Conrad 1995; Liu et al. 2016). Mineral N turnover is strongly affected by O2 availability (e.g., nitrification in aerobic conditions, denitrification in anaerobic conditions) (Stępniewski and Stępniewska 2009) and affects the concentrations of soluble N forms (NH4+, NO3+, NO2−) which may affect CH4 oxidation in soil (Bodelier and Steenbergh 2014). While the effect of NH4+ on soil CH4 oxidation was the focus of previous studies (Bodelier et al. 2000; Saari et al. 2004; Schnell and King 1994), little is known about the effect of O2, and even less about the effects of the soil type. We hypothesize that the soil O2 level may be one of the key factors explaining the contrasting results concerning the NH4+ effect on methanotrophic activity.
Taking into account the abundance of O2-deficient zones in soil, we have hypothesized that CH4 consumption in soil is affected by the O2 concentration as a result of (1) a direct effect on methanotrophic activity and (2) indirectly, as a consequence of the oxygen-driven microbial transformations, which result in changes in concentrations of soluble N forms (NH4+, NO3+, NO2−). Therefore, our aim was to study methane oxidation in mineral soils under different oxygen levels with or without addition of NH4+.
Materials and methods
Soil characteristics
The agricultural soils were Eutric Cambisol, Haplic Podzol, and Mollic Gleysol. Cambisols are the most widespread soil in all EU regions, contributing to about 27% of the land cover area (more than 1.1 mln km2, including the Eutric Cambisol—about 340,000 km2) (Tóth et al. 2008). The Haplic Podzol is the most common Podzol (about 401,000 km2) covering about 14% of the EU area (Tóth et al. 2008). Gleysols represent about 5.3% of the EU soil resources, with the Mollic Gleysol covering about 15,000 km2 of the land area (Tóth et al. 2008).
The selected soils were characterized by similar particle size distribution, which is important for studies concerning gases diffusion in different soils (Bieganowski et al. 2013; Prajapati and Jacinthe 2014), but differed in the contents of organic C and mineral N forms, and kinetic parameters of CH4 oxidation assayed under oxic conditions (Table 1). The soils were collected from the surface (0–20 cm), air-dried, sieved to < 2 mm, and stored in shade under dry conditions, at room temperature.
Description of the experiment
In the experiment, CH4 (1% v/v) consumption was measured during incubation of the triplicate soil samples (10 g of dry mass in 120-ml glass bottles). The initial oxygen levels were oxia (20% O2 v/v), low hypoxia (10% O2 v/v), high hypoxia (5% O2 v/v), and microoxia (2% O2 v/v). Under oxia, we used the atmospheric O2 concentration; to obtain lower O2 levels, the headspace of each sample was diluted with pure N2 and excess air was removed to equilibrate the initial pressure (Walkiewicz et al. 2016). A solution of NH4Cl was added as a source of NH4+ ions (100 mg N kg−1). Samples without NH4+ application but with different initial O2 concentrations were considered as the controls; they were moistened with distilled water. The investigations were carried out at controlled temperature (25 ± 2 °C, Xu and Inubushi 2009; cooled incubator ST4, Pol-Eko-Aparatura) and at 13–14% w/w soil moisture corresponding to the field water capacity (pF 2.2) (Walczak et al. 2002). We measured changes in the CH4 and O2 concentrations during the 21-day incubation of soil samples.
Gas concentration measurements and soil analysis
The headspace gas was sampled (200 μl), and CH4 and O2 consumptions were measured by a gas chromatograph (Shimadzu GC-14A) equipped with a thermal conductivity detector (TCD; temperature 60 °C) and with two columns (3.2-mm diameter), one packed with Porapak Q (for CH4) and the second packed with Molecular Sieve 5A (for O2); He was the carrier gas flowing at a rate of 40 cm−3 min−1. The temperature of the column was 40 °C (Walkiewicz et al. 2012). The detection limit for CH4 was 0.002% v/v and 0.40% v/v for O2. The detector responses were calibrated using certified gas standard containing 1% CH4, 20.9% O2, 0.5% N2O, and 77.6% N2 (Air Products).
Main soil properties were measured in air-dried soils. Organic C (Corg) was determined using a TOC-VCPH analyzer (Shimadzu, Japan) (Szarlip et al. 2014), the soil pH level was measured potentiometrically by adding 1 M KCl (1:2.5 w/w) to soil and after 24-h stabilization at room temperature, and N forms (ammonium, nitrate, nitrite) were analyzed in 0.01 M CaCl2 extracts by flow injection analysis (FIA Star 5000 auto-analyzer, FOSS Tecator). Particle size distribution (PSD) was determined using the laser diffraction method (Dobrowolski et al. 2012) by Mastersizer 2000 (Malvern, UK) with a Hydro G dispersion unit (Sochan et al. 2012). Phosphorus and potassium concentrations were determined by the Egner-Riehm (DL) method, while magnesium concentration was determined by the atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) (Tkaczyk et al. 2017).
Calculations and statistics
The obtained data include changes in the CH4 concentration during the incubation. Depending on the initial O2 concentration, the CH4 depletion curve could be divided into two phases due to different CH4 oxidation rates (Bender and Conrad 1992, 1995; Steenbergh et al. 2010): lag phase I (initial) and phase II (induced, final). The CH4 concentration was expressed as milligram CH4-C kg−1 dry soil. It was corrected for solubility in water using the Bunsen solubility coefficient (α = 0.029 dm3 dm−3 at 25 °C). The CH4 density of 0.657 mg cm−3 was used for calculating the gas mass (Gliński and Stępniewski 1985). Based on the CH4 changes (C—the final, and C0—the initial CH4 concentration) during time (t), the average rates of CH4 oxidation were calculated for all incubation periods using the following equation: CH4 oxidation rate = (C-C0) / t (Wnuk et al. 2017). The equation C = C0e−kt, where k is the first-order kinetic constant (Mohanty et al. 2016), was used for calculating the half-life value (t1/2) expressed as days.
The data were subjected to analysis of variance. To compare the effect of O2 on CH4 oxidation rates; we used one-way ANOVA in particular variants and multi-factor MANOVA considering the significance of three factors: (1) soil properties; (2) O2 level; and (3) NH4+ addition (post hoc Tukey test; STATISTICA 10.0 program, StatSoft Inc.).
Results
Methane oxidation in control soils under different oxygen levels
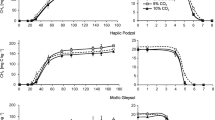
All soils incubated without NH4+ addition (controls) consumed CH4 within 4–9 days under hypoxic (5% and 10% O2) and within 5–11 days under oxic (20% O2) conditions with a biphasic pattern. In contrast, strong inhibition and no distinct phases were observed under microoxic conditions (2% O2) (Fig. 1).
Decrease in the CH4 concentration with the time in the headspace of controls (without NH4+) of Eutric Cambisol, Haplic Podzol, and Mollic Gleysol (without NH4+) incubated with CH4 (1% v/v). Soil samples were incubated under different O2 levels (20%, 10%, 5%, 2% O2 v/v). Points are averages of three replicates; bars indicate the standard deviations. 20% O2—open circles; 10% O2—gray rhombus; 5% O2—black triangle; 2% O2—black square
The length of the initial (lag) phase of CH4 oxidation was affected by soil properties. As a result, the average CH4 oxidation rate (Fig. 3) ranked as Eutric Cambisol < Haplic Podzol < Mollic Gleysol. The highest values (6 to 15 mg CH4-C kg−1 day−1) were achieved at 5% and 10% O2 in all tested soils (p < 0.05). Under oxia (20% O2), the CH4 oxidation was slower, ranging from about 5 to 12 mg CH4-C kg−1 day−1 (p < 0.05). The lowest values (0.351 to 1.382 mg CH4 kg−1 day−1) were observed under microoxia (2% O2) in all soils. Therefore, the half-life (t1/2) values were also the lowest under such aeration (Fig. 3(A)).
The control soils differed in the duration of the lag phase (Fig. 1), and therefore, the CH4 uptake started at a different O2 concentration (see Table 2) as a result of microbial respiration. In all control soils incubated under oxia (20% O2), the CH4 uptake started when the O2 content ranged from ~ 18.3 to 19.2% v/v, and the O2 concentration at the end of incubation did not drop below ~ 17% v/v. Under hypoxia, methanotrophy was initiated at the O2 concentration ranging from 9.70 to 6.84% v/v (under 10% O2) and from 4.47 to 2.72% v/v (under 5% O2), and finally it did not decline below 5.5 and ~ 1% v/v O2, respectively, on the day of the complete CH4 uptake. Under microoxia conditions (2% O2), slight CH4 consumption started at the O2 concentration ranging from ~ 0.4 to 1.44% v/v, and O2 was completely consumed in this treatment at the end of incubation.
Methane oxidation in soils with ammonium and under different oxygen levels
The NH4+ addition changed the CH4 uptake in all tested soils (Fig. 2) and influenced the duration of both phases depending on the O2 level. Moreover, we observed different curve shapes of the induced phase. Generally, the CH4 consumption started earlier in the ammonium-amended soils than that in the controls, but next the process slowed down or was even stopped.
Decrease in the CH4 concentration with the time in the headspace of Eutric Cambisol, Haplic Podzol, and Mollic Gleysol incubated with CH4 (1% v/v) and with NH4+ (100 mg N kg−1) addition. Soil samples were incubated under different O2 levels (20%, 10%, 5%, 2% O2 v/v). Points are averages of three replicates; bars indicate the standard deviations. Open circles for 20% O2; gray rhombus for 10% O2; black triangle for 5% O2; black square for 2% O2
In the Eutric Cambisol, strong inhibition by NH4+ was observed in all O2 levels (Fig. 2(A)). Apparently, there was no (or a very slight) induction of the process at both 20 and 2% O2. A short-term CH4 consumption occurred at high (5% O2) and low (10% O2) hypoxia already after 1-day incubation. This means that, under moderate O2 deficiency (hypoxia), CH4 consumption in this ammonium-amended soil initiated much earlier than that in the control without NH4+ (see Fig. 2(A)). However, this stimulation was short-lived and finally only approx. 30% of the added CH4 was consumed.
In the case of the Haplic Podzol (Fig. 2(B)), strong inhibition by NH4+ was observed under oxia (20% O2), while hypoxia (5% O2 and 10% O2) resulted in the faster initiation of the CH4 uptake. However, in contrast to the Eutric Cambisol, all added CH4 was consumed under hypoxia in the ammonium-amended Haplic Podzol, although it lasted much longer than in the non-amended control (i.e., 14–16 days vs. 6 days). Microoxic conditions (2% O2) strongly inhibited methanotrophy in the Haplic Podzol, like in the control.
After NH4+ addition to the Mollic Gleysol, the CH4 uptake started almost immediately (on the first incubation day) at 20%, 10%, and 5% O2 (Fig. 2(C)). In this soil, the highest CH4 oxidation rate was observed under low hypoxia (10% O2) with complete CH4 oxidation within 14 days. At higher O2 availability, 10% and 20% O2, 87% and 96% of added CH4 was consumed, respectively. Under microoxia (2% O2), the CH4 uptake started in this soil after a short 1-day lag period and proceeded for 9 days; finally, 65% of the added CH4 was consumed.
The CH4 oxidation rates calculated for the ammonium-treated soils were lower and the t1/2 values were much higher than for controls (Fig. 3(A, B)). However, under microoxia (2% O2), as revealed by the analysis of variance, the NH4+ application increased the CH4 oxidation rate in the Mollic Gleysol (by ca. 30%, p < 0.05). In all ammonium-amended soils, the highest methanotrophic activity was observed under hypoxia (5% or 10% O2) (p < 0.05) with the rate values ranging from about 0.9 mg CH4-C kg−1 day−1 (Eutric Cambisol) to about 4 mg CH4-C kg−1 day−1 (Haplic Podzol and Mollic Gleysol). Therefore, the lowest half-life values were recorded under hypoxia in all tested soils (Fig. 3(B)).
Average CH4 oxidation rates (avg ± SD, n = 3) and half-life value in Eutric Cambisol, Haplic Podzol, and Mollic Gleysol enriched with CH4 (1% v/v) and without (control) or with NH4+ (100 mg N kg−1). Soil samples were incubated under different O2 levels (20%, 10%, 5%, 2% O2 v/v). The same letters above the columns indicate no statistically significant differences among the rates (one-way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc test, p < 0.05, calculated separately for each soil)
The NH4+ addition to the tested soils reduced the duration of the lag phase (Fig. 2) in comparison to controls (Fig. 1). Therefore, methanotrophy was initiated at higher O2 concentrations than in the controls (Table 2). In ammonium-amended soils incubated under oxia (20% O2), the CH4 uptake started when O2 ranged from 20.3 to 19.5% v/v, and did not drop below 12.2% v/v O2. Under hypoxia, CH4 uptake started at once at the initial O2 concentrations of 10% and ~ 5% v/v O2 and did not decline below 4.8% and 2.8% under high and low hypoxia, respectively. Under microoxic conditions (2% O2), the consumption started at the O2 concentration ranging from 0.41 to 1.80% v/v O2 (Table 2). As in the controls, oxygen was completely consumed at the end of incubation.
Discussion
Our experiment confirms the great importance of the soil oxygen level during the studies on CH4 oxidation. We simulated field soil conditions and processes that occur in the soil agroecosystems. Our laboratory incubation experiment may be useful in understanding the environmental consequences of C and N interactions.
Oxygen effect on methane oxidation in soils
Oxygen is an electron acceptor for methane oxidation (He et al. 2011) and the major limiting factor in aerobic methanotrophy (Chowdhury and Dick 2013; Wilshusen et al. 2004). O2 is needed in the first step of aerobic methane oxidation for the conversion of methane to methanol (He et al. 2011), and this reaction is catalyzed by methane monooxygenase (MMO) (Hanson and Hanson 1996). We have hypothesized that CH4 consumption at the different oxygen levels may depend on the sensitivity of MMO to O2; some methanotrophs may adapt to low oxygen conditions via specific metabolic strategies (Henckel et al. 2000; Hernandez et al. 2015; Kalyuzhnaya et al. 2013, Ward et al. 2004). Our experiment showed that the O2 level differentiated the CH4 consumption in three mineral soils. Probably, O2 as a substrate for MMO should increase CH4 oxidation as suggested by Chi et al. (2012) and Pawłowska et al. (2011). In our experiment, the methanotrophic activity did not decrease at the lower O2 concentration. Generally, the tested soils (not amended with NH4+) oxidized all added CH4 in the O2 range from oxia (20% O2) to high hypoxia (5% O2) (Fig. 1). However, low (10% O2) and high (5% O2) hypoxia levels were usually more favorable than oxia for methanotrophic activity (Fig. 3). Similarly, Wnuk et al. (2017) reported enhanced CH4 oxidation rate in the same Eutric Cambisol, at higher than in lower moisture. Despite the tested soils samples were characterized by the same initial O2 concentration and the same O2 diffusion due to similar texture, they differed in the duration of the lag phase due to the specific soil properties. Therefore, the real O2 concentrations varied at the beginning of CH4 consumption (Table 2), which did not reach the values at the next O2 level. Our results directly confirmed higher methanotrophic activity under low O2 concentration, whose value depends on soil water content. Oxygen at the level ≤ 5% was reported by Duan et al. (2017) as critical O2 concentration below which CH4 oxidation (1%) was reduced in slurry surface crusts. Our microoxic conditions (2% O2) inhibited or retarded CH4 oxidation, likely due to the effect of the O2 depletion during incubation. Such an O2 concentration (Table 2) could be too low for methanotrophs inhabiting the tested soils due to its complete consumption during incubation. However, Wilshusen et al. (2004) showed slightly higher and more stable activity for leaf compost at 1.5% O2 than 10.5% O2. Czepiel et al. (1996) demonstrated that the methanotrophic activity in a landfill spoil layer decreased at an O2 level below 3% O2, but was not sensitive to higher O2 concentrations.
Biphasic kinetics of CH4 consumption was observed in the control soil samples (without NH4+ addition) incubated at O2 in the range from 20 to 5% O2. Such a curve shape was reported previously by Bender and Conrad (1992, 1995) and Steenbergh et al. (2010). The process was initially slow, but next, the rate increased in the induced phase. The proposed mechanisms explaining the nonlinear CH4 consumption include (1) growth of methanotroph populations (Bender and Conrad 1992, 1995; Cai and Yan 1999; Henckel et al. 2000); (2) increased cell activity (Gilbert and Frenzel 1998; Henckel et al. 1999); (3) combinations of growth and increased cell activity (Steenbergh et al. 2010); (4) a low percentage participation of active methanotrophs in the lag phase (Steenbergh et al. 2010); and (5) changes in the specific activity of methanotrophs, the number of bacteria, and the CH4 concentration (Cai and Yan 1999). The period of low CH4 oxidation (lag phase) can last up to several days (Syamsul Arif et al. 1996) and in long-term fertilized soil even up to 2–3 weeks (Hütsch 2001). In our experiment, the initial phase was shorter under hypoxia than under oxic conditions, which may suggest that reduced O2 availability in non-fertilized soil creates better conditions for activity and growth of methanotrophs. The next phase of the rapid CH4 depletion took the same time for both oxic and hypoxic conditions (2–4 days).
In our study, the CH4 consumption rate ranked as Eutric Cambisol < Haplic Podzol < Mollic Gleysol, likely depending on the presence of different species of methanotrophic bacteria and for different properties of the used soils. The Mollic Gleysol was characterized by relatively high organic C content (Corg 3.93%, Table 1), which may have created better conditions for microbial activity, including that of methanotrophy. In this soil, the half-life values were lower than those in Cambisol and Podzol (even at 2% O2; Fig. 3), which confirmed its high methanotrophic activity.
Ammonium effect on methane oxidation in soils under different O2 levels
The O2 status may have a direct impact on methanotrophic bacteria as well as it can act indirectly by affecting N transformation. Application of both mineral and organic N fertilizers may induce several processes, including denitrification and nitrification (Trimpler et al. 2016). Therefore, not only the O2 level alone, but the combined effect of soil aeration and N (entering the soil through the high N fertilizers input) may have important environmental consequences. Interactions between O2 and the availability of NH4+ can control the rate of nitrification (Caffrey et al. 2003). Since nitrification under reduced O2 concentration has been observed (Goreau et al. 1980; Sliekers et al. 2005), we suppose that nitrifying bacteria, besides methanotrophs, may also consume CH4 (Mohanty et al. 2016; Xu and Inubushi 2004) under hypoxia in our study. However, the intermediate products of NH4+ oxidation, e.g., hydroxylamine and nitrite (NO2−), can be toxic to methanotrophic bacteria and thus may inhibit CH4 consumption (Alam and Jia 2012; Dunfield and Knowles 1995; Schnell and King 1994; Zheng et al. 2013).
In our experiment, after NH4+ application, the highest reduction of CH4 oxidation in all soils was observed under oxia (20% O2) (Figs. 2 and 3). Under 2% O2 and with NH4+ application, the CH4 oxidation rate and half-life value were only slightly changed in comparison to the soil samples without NH4+ addition, especially in the Cambisol and Podzol. Moreover, in the ammonium-amended Mollic Gleysol, about a half of CH4 (32 mg CH4-C kg−1) was consumed until the eighth incubation day under microoxia, i.e., even more than in the control. In the ammonium-amended Eutric Cambisol, low CH4 consumption occurred under hypoxia (5% and 10% O2) and it was stopped after few days. The application of NH4+ to Haplic Podzol strongly delayed methanotrophic activity and CH4 was completely oxidized only under hypoxia (5% and 10% O2) (Fig. 2).
Interestingly, the NH4+ addition reduced the lag phase to 1 day under high (5% O2) and low (10% O2) hypoxia in Eutric Cambisol and Haplic Podzol and in the next day inhibition or slowdown (respectively) occurred (Fig. 2). In the ammonium-amended Mollic Gleysol, the process began immediately except for microoxia, and this resulted in the lowest half-life values. However, the average CH4 oxidation rate was significantly lower than that in the soil without NH4+ (Fig. 3), probably due to accumulation of NO2− and/or other nitrification intermediates. We hypothesize that the NH4+ addition relieved N limitation initially and reduced the lag phase. Bodelier et al. (2000) also showed the initiation of CH4 oxidation without a delay phase in an ammonium-amended rice field soil probably due to the use of NH4+ as a N source. The rate of CH4 oxidation is usually constant over time (Steenbergh et al. 2010). However, in the ammonium-amended soils, we observed periods with a higher and lower rates, especially in more active Mollic Gleysol, probably due to the interference of nitrification products. In the ammonium-amended Mollic Gleysol and Haplic Podzol, methane oxidation rates were even higher under 5% O2 than under 10% O2 (p < 0.05), contrarily to the controls showing slightly higher rates under 10% O2 than under 5% O2 (Fig. 3).
Other mechanisms have been proposed to explain the effects of N forms on CH4 oxidation in soil. High concentration of NH4+ salt can affect the CH4 oxidation by the nonspecific effect of the salt (osmotic stress) (Rigler and Zechmeister-Boltenstern 1999; Saari et al. 2004; Whalen 2000). Competitive inhibition by NH4+ ions is a mechanism often proposed in different soils (Alam and Jia 2012; Bender and Conrad 1995; Bronson and Mosier 1994; Dunfield and Knowles 1995; Schnell and King 1994; Zheng et al. 2013). Both methanotrophs and nitrifiers have several enzymes in common, in particular ammonia monooxygenase vs. particulate methane monooxygenase (MMO). A short-term decline in methanotrophic activity can be due to the competitive inhibition of MMO by NH4+ due to structural similarity of ammonium and methane molecules. Even though the affinity of MMO for methane is 600–1300-fold higher than that for NH4+, high concentrations of NH4+ can inhibit methanotrophic activity (Bèdard and Knowles 1989). The different responses of soils in our study to NH4+ under a different O2 status can be due to dominance of different species of methanotrophic bacteria (which should be confirmed by microbial analyses).
However, the addition of NH4+ can also stimulate methanotrophic activity by changing the C:N ratio (Rigler and Zechmeister-Boltenstern 1999). Methanotrophic bacteria have a relatively high N demand for growth and protein synthesis, as for each mole of assimilated CH4-C, they need 0.25 mol of N (Anthony 1982). Indeed, the size and activity of a methanotrophic population in a rice rhizosphere increased after the addition of urea or (NH4)2PO4 (Bodelier et al. 2000). Stimulation of CH4 uptake on fertilized paddy fields was observed under both field and laboratory conditions (Dan et al. 2001; Krüger and Frenzel 2003), whereas He et al. (2011) reported that the process in landfill cover soil was higher under an ambient O2 concentration than under 3% O2. Our results showed the environmental effects of different O2 levels and N fertilization on methane oxidation. Mineral N form content and O2 level are not constant in soil and their changes can affect soil microbial activity. The tested soils were characterized by similar particle size distribution and, hence, similar air-water conditions; however, they differed in the organic C content (Table 1). Considering soil type, it should be pointed that sandy loam soil (Cambisol) inhibited CH4 consumption in the presence of NH4+, whereas the opposite occurred in the loamy sand (Gleysol). The multi-factor analysis of variance showed that, generally, the methanotrophic activity was significantly influenced by the factors in the following order: NH4+ concentration (p = 0.000, F = 28.97) > O2 level (p = 0.008, F = 4.15) > soil properties (p = 0.031, F = 3.58).
In conclusion, our experiment showed that the methanotrophic activity ranked as Eutric Cambisol < Haplic Podzol < Mollic Gleysol. However, all soil samples without NH4+ addition completely oxidized the added CH4 under oxia (20% O2) to high hypoxia (5% O2) and high reduction of the process occurred under microoxia (2% O2). Hypoxia was usually more favorable than oxia for CH4 oxidation. The addition of NH4+ reduced the lag period, with a decrease or even inhibition of CH4 oxidation, which can be explained by (1) competitive inhibition and (2) an effect of the intermediate products (such as NO2−) of nitrification. Under high hypoxia (5% O2), the negative influence of NH4+ on methanotrophic activity decreased. The methane oxidation rate was significantly (p < 0.001) affected by NH4+ and O2 in all the tested soils; however, the NH4+ effect was stronger than that of O2. The reported contrasting results of NH4+ on soil CH4 oxidation may be partly explained by the O2 level. Further studies should focus on methanotrophy in other soil types under different O2 levels. Moreover, both microbial tests and determination of the activity of isolated MMO under different O2 concentrations would be useful for better understanding the mechanisms underlying our results.
References
Alam MS, Jia Z (2012) Inhibition of methane oxidation by nitrogenous fertilizers in a paddy soil. Front Microbiol 3:1–13
Amundson R, Berhe AA, Hopmans JW, Olson C, Sztein AE, Sparks DL (2015) Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 348:1261071-1-1261071-6
Anthony C (1982) The biochemistry of methylotrophs. Academic Press INC, London
Bèdard C, Knowles R (1989) Physiology, biochemistry, and specific inhibitors of CH4, NH4 +, and CO oxidation by methanotrophs and nitrifiers. Microbiol Rev 53:68–84
Bender M, Conrad R (1992) Kinetics of CH4 oxidation in oxic soils exposed to ambient air or high CH4 mixing ratios. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 101:261–270
Bender M, Conrad R (1995) Effect of CH4 concentrations and soil conditions on the induction of CH4 oxidation activity. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1517–1527
Bieganowski A, Witkowska-Walczak B, Gliński J, Sokołowska Z, Sławiński C, Brzezińska M, Włodarczyk T (2013) Database of Polish arable mineral soils: a review. Int Agrophys 27:335–350
Bodelier PLE (2011) Interactions between nitrogenous fertilizers and methane cycling in wetland and upland soils. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 3:379–388
Bodelier PLE, Steenbergh AK (2014) Interactions between methane and the nitrogen cycle in light of climate change. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 9-10:26–36
Bodelier PL, Roslev P, Henckel T, Frenzel P (2000) Stimulation by ammonium-based fertilizers of methane oxidation in soil around rice roots. Nature 403:421–424
Bronson KF, Mosier AR (1994) Suppression of methane oxidation in aerobic soil by nitrogen fertilizers, nitrification inhibitors, and urease inhibitors. Biol Fert Soils 17:263–268
Bussmann I, Rahalkar M, Schink B (2006) Cultivation of methanotrophic bacteria in opposing gradients of methane and oxygen. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 56:331–344
Caffrey JM, Harrington N, Solem I, Ward BB (2003) Biogeochemical processes in a small California estuary. 2. Nitrification activity, community structure and role in nitrogen budgets. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 248:27–40
Cai Z, Yan X (1999) Kinetic model for methane oxidation by paddy soil as affected by temperature, moisture and N addition. Soil Biol Biochem 31:715–725
Castillo JAA, Apan AA, Maraseni TN, Salmo SG (2017) Soil greenhouse gas fluxes in tropical mangrove forests and in land uses on deforested mangrove lands. Catena 159:60–69
Chen-rui W, Shi Y, Xiao-ming Y, Wu J, Yue J (2003) Advances of study on atmospheric methane oxidation (consumption) in forest soil. J Forestry Res 14:230–238
Chi ZF, Lu WJ, Li H, Wang HT (2012) Dynamics of CH4 oxidation in landfill biocover soil: effect of O2/CH4 ratio on CH4 metabolism. Environ Pollut 170:8–14
Chojnicki BH, Michalak M, Acosta M, Juszczak R, Augustin J, Drösler M, Olejnik J (2010) Measurements of carbon dioxide fluxes by chamber method at the Rzecin wetland ecosystem, Poland. Pol J Environ Stud 19:283–229
Chowdhury TR, Dick RP (2013) Ecology of aerobic methanotrophs in controlling methane fluxes from wetlands. Appl Soil Ecol 65:8–22
Czepiel PM, Mosher B, Crill PM, Harriss RC (1996) Quantifying the effect of oxidation on landfill methane emissions. J Geophys Res 101D:16721–16729
Dan J, Krüger M, Frenzel P, Conrad R (2001) Effect of a late season urea fertilization on methane emission from a rice field in Italy. Agric Ecosyst Environ 83:191–199
Dobrowolski R, Bieganowski A, Mroczek P, Ryżak M (2012) Role of periglacial processes in Epikarst morphogenesis: a case study from Chełm Chalk Quarry, Lublin Upland, Eastern Poland. Permafrost Periglac 23:251–266
Duan YF, Reinsch S, Ambus P, Elsgaard L, Petersen SO (2017) Activity of type I methanotrophs dominates under high methane concentration: methanotrophic activity in slurry surface crusts as influenced by methane, oxygen, and inorganic nitrogen. J Environ Qual 46:767–775
Dubey SK, Singh A, Watanabe T, Asakawa S, Singla A, Arai H, Inubushi K (2014) Methane production potential and methanogenic archaeal community structure in tropical irrigated Indian paddy soils. Biol Fertil Soils 50:369–379
Dunfield P, Knowles R (1995) Kinetics of inhibition of methane oxidation by nitrate, nitrite and ammonium in a humisol. Appl Environ Microb 61:3129–3135
Einola J-KM, Kettunen RH, Rintala JA (2007) Responses of methane oxidation to temperature and water content in cover soil of a boreal landfill. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1156–1164
Gärdenäs IA, Ågren GI, Bird JA, Clarholm M, Hallin S, Ineson P, Kätterer T, Knicker H, Nilsson IS, Näsholmi T, Ogle S, Paustian K, Persson T, Stendahl J (2011) Knowledge gaps in soil carbon and nitrogen interactions - from molecular to global scale. Soil Biol Biochem 43:702–717
Gilbert B, Frenzel P (1998) Rice roots and CH4 oxidation: the activity of bacteria, their distribution and the microenvironment. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1903–1916
Gliński J, Stępniewski W (1985) Soil aeration and its role for plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Goreau TJ, Kaplan WA, Wofsy SC, McElroy MB, Valois FW, Watson SW (1980) Production of NO2 - and N2O by nitrifying bacteria at reduced concentrations of oxygen. Appl Environ Microb 40:526–532
Hanson RS, Hanson TE (1996) Methanotrophic bacteria. Microbiol Rev 60:439–471
He P, Yang N, Fang W, Lü F, Shao L (2011) Interaction and independence on methane oxidation of landfill cover soil among three impact factors: water, oxygen and ammonium. Front Environ Sci Eng China 5:175–185
Henckel T, Friedrich M, Conrad R (1999) Molecular analyses of the methane-oxidizing microbial community in rice field soil by targeting the genes of the 16S rRNA, particulate methane monooxygenase, and methanol dehydrogenase. Appl Environ Microb 65:1980–1990
Henckel T, Roslev P, Conrad R (2000) Effects of O2 and CH4 on presence and activity of the indigenous methanotrophic community in rice field soil. Environ Microbiol 2:666–679
Hernandez ME, Beck DAC, Lidstrom ME, Chistoserdova L (2015) Oxygen availability is a major factor in determining the composition of microbial communities involved in methane oxidation. PeerJ 3:801–814
Ho A, Reim A, Kim SY, Meima-Franke M, Termorshuizen A, de Boer W, van der Putten WH, Bodelier PL (2015) Unexpected stimulation of soil methane uptake as emergent property of agricultural soils following bio-based residue application. Glob Chang Biol 21:3864–3879
Hu A, Lu Y (2015) The differential effects of ammonium and nitrate on methanotrophs in rice field soil. Soil Biol Biochem 85:31–38
Huang S, Sun Y, Yu X, Zhang W (2016) Interactive effects of temperature and moisture on CO2 and CH4 production in a paddy soil under long-term different fertilization regimes. Biol Fertil Soils 52:285–294
Hütsch BW (2001) Methane oxidation in non-flooded soils as affected by crop production - invited paper. Eur J Agron 14:237–260
Jäckel U, Schnell S, Conrad R (2001) Effect of moisture, texture and aggregate size of paddy soil on production and consumption of CH4. Soil Biol Biochem 33:965–971
Jarecke KM, Loecke TD, Burgin A (2016) Coupled soil oxygen and greenhouse gas dynamics under variable hydrology. Soil Biol Biochem 95:164–172
Kalyuzhnaya MG, Yang S, Rozova ON, Smalley NE, Clubb J, Lamb A, Nagana Gowda GA, Raftery D, Fu Y, Bringel F, Vuilleumier S, Beck DAC, Trotsenko YA, Khmelenina VN, Lidstrom ME (2013) Highly efficient methane biocatalysis revealed in a methanotrophic bacterium. Nat Commun 4:2785
Kirschke S, Bousquet P, Ciais P, Saunois M, Canadell JG, Dlugokencky EJ, Bergamaschi P, Bergmann D, Blake DR, Bruhwiler L, Cameron-Smith P, Castaldi S, Chevallier F, Feng L, Fraser A, Heimann M, Hodson EL, Houweling S, Josse B, Fraser PJ, Krumme PB, Lamarque J-F, Langenfelds RL, Quéré CL, Naik V, O’Doherty S, Palmer PI, Pison I, Plummer D, Poulter B, Prinn RG, Rigby M, Ringeval B, Santini M, Schmidt M, Shindell DT, Simpson IJ, Spahni R, Steele LP, Strode SA, Sudo S, Szopa S, van der Werf GR, Voulgarakis A, van Weele M, Weiss RF, Williams JE, Zeng G (2013) Three decades of global methane sources and sinks. Nat Geosci 6:813–823
Köster K, Köster E, Kulmala L, Berninger F, Pumpanen J (2017) Are the climatic factors combined with reindeer grazing affecting the soil CO2 emissions in subarctic boreal pine forest? Catena 149:616–622
Kravchenko IK, Semenov VM, Kuznetsova TV, Bykova SA, Dulov LE, Pardini D, Gispert M, Boeckx P, Van Cleemput O, Gal’chenko VF (2005) Physicochemical and biological factors affecting atmospheric methane oxidation in gray forest soils. Microbiology 74:255–260
Krüger M, Frenzel P (2003) Effects of N-fertilisation on CH4 oxidation and production, and consequences for CH4 emissions from microcosms and rice fields. Glob Chang Biol 9:773–784
Lamorski K, Pastuszka T, Krzyszczak J, Sławiński C, Witkowska-Walczak B (2013) Soil water dynamic modeling using the physical and support vector machine methods. Vadose Zone J 12. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2013.05.0085
Li Y, Dong S, Liu S, Zhou H, Gao Q, Cao G, Wang X, Su X, Zhang Y, Tang L, Zhao H, Wu X (2015) Seasonal changes of CO2, CH4 and N2O fluxes in different types of alpine grassland in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. Soil Biol Biochem 80:306–314
Liu J, Chen X, Zhan A, Luo S, Chen H, Jiang H, Huang X, Li S (2016) Methane uptake in semiarid farmland subjected to different mulching and nitrogen fertilization regimes. Biol Fertil Soils 52:941–950
Mohanty SR, Tiwari S, Dubey G, Ahirwar U, Kollah B (2016) How methane feedback response influence redox processes in a tropical vertisol. Biol Fertil Soils 52:479–490
Morris RL, Schmidt TM (2013) Shallow breathing: bacterial life at low O2. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:205–212
Oenema O (2001) Technical and policy aspects of strategies to decrease greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 60:301–315
Pawłowska M, Rożej A, Stępniewski W (2011) The effect of bed properties on methane removal in an aerated biofilter - model studies. Waste Manag 31:903–913
Prajapati P, Jacinthe PA (2014) Methane oxidation kinetics and diffusivity in soils under conventional tillage and long-term no-till. Geoderma 230–231:161–170
Rigler E, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S (1999) Oxidation of ethylene and methane in forest soils - effect of CO2 and mineral nitrogen. Geoderma 90:147–159
Saari A, Rinnan R, Martikainen PJ (2004) Methane oxidation in boreal forest soils: kinetics and sensitivity to pH and ammonium. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1037–1046
Šantrůčková H, Šimek M (1994) Soil microorganisms at different CO2 and O2 tensions. Folia Microbiol 39:62225–62230
Schnell S, King GM (1994) Mechanistic analysis of ammonium inhibition of atmospheric methane consumption in forest soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:3514–3521
Sliekers OA, Haaijer SCM, Stafsnes MH, Kuenen JG, Jetten MMS (2005) Competition and coexistence of aerobic ammonium- and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria at low oxygen concentrations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:808–817
Sochan A, Bieganowski A, Ryżak M, Dobrowolski R, Bartmiński P (2012) Comparison of soil texture determined by two dispersion units of Mastersizer 2000. Int Agrophys 26:99–102
Steenbergh AK, Meima MM, Kamst M, Bodelier PLE (2010) Biphasic kinetics of a methanotrophic community is a combination of growth and increased activity per cell. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 71:12–22
Steinkamp R, Butterbach-Bahl K, Papen H (2001) Methane oxidation by soils of an N limited and N fertilized spruce forest in the Black Forest, Germany. Soil Biol Biochem 3:145–153
Stępniewski W, Stępniewska Z (2009) Selected oxygen-dependent process - response to soil management and tillage. Soil Tillage Res 102:193–200
Stępniewski W, Stępniewska Z, Bennicelli RP, Gliński J (2005) Oxygenology in outline. Institute of Agrophysics Polish Academy of Sciences, Lublin
Syamsul Arif MA, Houwen F, Verstraete W (1996) Agricultural factors affecting methane oxidation in arable soil. Biol Fertil Soils 21:95–102
Szarlip P, Stelmach W, Jaromin-Gleń K, Bieganowski A, Brzezińska M, Trembaczowski A, Hałas S, Łagód G (2014) Comparison of the dynamics of natural biodegradation of petrol and diesel oil in soil. Desalin Water Treat 52:3690–3697
Tate KR (2015) Soil methane oxidation and land-use change - from process to mitigation. Soil Biol Biochem 80:260–272
Tkaczyk P, Bednarek W, Dresler S, Krzyszczak J, Baranowski P, Sławiński C (2017) Relationship between assimilable-nutrient content and physicochemical properties of topsoil. Int Agrophys 31:551–562
Tóth G, Montanarella L, Stolbovoy V, Máté F, Bódis K, Jones A, Panagos P, Van Liedekierke M (2008) Soils of the European Union. JRC Sci Tech Rep European Communities. https://doi.org/10.2788/87029
Trimpler K, Stockfisch N, Märländer B (2016) The relevance of N fertilization for the amount of total greenhouse gas emissions in sugar beet cultivation. Eur J Agron 81:64–71
Walczak R, Ostrowski J, Witkowska-Walczak B, Sławiński C (2002) Spatial characteristic of hydro-physical properties in arable mineral soils in Poland as illustrated by field water capacity (FWC). Int Agrophys 16:151–159
Walkiewicz A, Bulak P, Brzezińska M, Włodarczyk T, Polakowski C (2012) Kinetics of methane oxidation in selected mineral soils. Int Agrophys 26:401–406
Walkiewicz A, Bulak P, Brzezińska M, Wnuk E, Bieganowski A (2016) Methane oxidation in heavy metal contaminated Mollic Gleysol under oxic and hypoxic conditions. Environ Pollut 213:403–411
Wang ZP, Ineson P (2003) Methane oxidation in a temperate coniferous forest soil: effects of inorganic N. Soil Biol Biochem 35:427–433
Ward N, Larsen Ø, Sakwa J, Bruseth L, Khouri H, Durkin AS, Dimitrov G, Jiang L, Scanlan D, Kang KH, Lewis M, Nelson KE, Methè B, Wu M, Heidelberg JF, Paulsen IT, Fouts D, Ravel J, Tettelin H, Ren Q, Read T, DeBoy RT, Seshadri R, Salzberg SL, Jensen HB, Kåre Birkeland N, Nelson WC, Dodson RJ, Grindhaug SH, Holt I, Eidhammer I, Jonasen I, Vanaken S, Utterback T, Feldblyum TV, Fraser CM, Lillehaug JR, Eisen JA (2004) Genomic insights into methanotrophy: the complete genome sequence of Methylococcus capsulatus (Bath). PLoS Biol 10:1616–1628
Whalen SC (2000) Influence of N and non-N salts on atmospheric methane oxidation by upland boreal forest and tundra soils. Biol Fertil Soils 31:279–287
Wilshusen JH, Hettiaratchi JPA, De Visscher A, Saint-Fort R (2004) Methane oxidation and formation of EPS in compost: effect of oxygen concentration. Environ Pollut 129:305–314
Wnuk E, Walkiewicz A, Bieganowski A (2017) Methane oxidation in lead-contaminated mineral soils under different moisture levels. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:25346–25354
Xu X, Inubushi K (2004) Effects of N sources and methane concentrations on methane uptake potential of a typical coniferous forest and its adjacent orchard soil. Biol Fertil Soils 40:215–221
Xu X, Inubushi K (2009) Responses of ethylene and methane consumption to temperature and pH in temperate volcanic forest soils. Eur J Soil Sci 60:489–498
Zheng Y, Zhang LM, He JZ (2013) Immediate effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium amendments on the methanotrophic activity and abundance in a Chinese paddy soil under short-term incubation experiment. J Soils Sediments 13:189–196
Funding
This paper was partly financed from the funds of the National Science Centre, Poland (decision no. DEC-2013/11/N/NZ9/04725).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Walkiewicz, A., Brzezińska, M. & Bieganowski, A. Methanotrophs are favored under hypoxia in ammonium-fertilized soils. Biol Fertil Soils 54, 861–870 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1302-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1302-9