Abstract
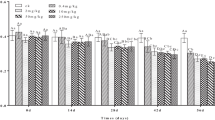
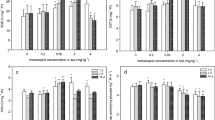
Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) is a cyclic heptapeptide toxin produced by cyanobacteria in eutrophic water. It can be transferred into soil–crop systems via irrigation and cyanobacterial paste fertilization. No studies have examined the potential toxicity of MC-LR to soil animals. Therefore, in the present study, the toxicological effects of MC-LR on earthworm (Eisenia fetida), including survival, growth, reproduction, oxidative stress, and cell viability, were investigated. The LC50 of MC-LR was 0.149 μg cm−2 at 72 h based on a filter paper test and 0.460 mg kg−1 at 14 days based on an acute soil test. MC-LR seriously affected the reproduction of earthworms. Based on hatchability, the EC50 of MC-LR was 0.268 mg kg−1, similar to environmentally relevant concentrations of microcystins. The changes in activities of superoxide dismutase, guaiacol peroxidase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, together with the levels of glutathione and malondialdehyde, indicated that oxidative damage and lipid peroxidation played significant roles in MC-LR toxicity. In addition, the toxicity of MC-LR in earthworms increased despite degradation of MC-LR in soil over time, possibly due to the formation of toxic metabolites of MC-LR or the bioaccumulation of MC-LR in earthworms. A reduction in the neutral red retention time along with an increase in coelomocyte apoptosis with increasing MC-LR concentrations indicated a severe damage to viability. These results suggest that environmentally relevant MC-LR concentrations in agricultural soil may cause reproductive, biochemical, and cellular toxicity to Eisenia fetida. This information can be used in ecological risk assessments on MC-LR in soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amado LL, Monserrat JM (2010) Oxidative stress generation by microcystins in aquatic animals: why and how. Environ Int 36:226–235
An ZH, Sun LS, Wang P (2015) Acute toxicity and accumulation of microcystin-leucine-arginine in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852). Crustaceana 88:397–404
Andriuzzi WS, Ngo P, Geisen S, Keith AM, Dumack K, Bolger T, Bonkowski M, Brussaard L, Faber JH, Chabbi A, Rumpel C, Schmidt O (2016) Organic matter composition and the protist and nematode communities around anecic earthworm burrows. Biol Fertil Soils 52:91–100
Bartsch H, Nair J (2000) Ultrasensitive and specific detection methods for exocylicDNA adducts: markers for lipid peroxidation and oxidativestress. Toxicology 153:105–114
Capowiez Y, Rault M, Costagliola G, Mazzia C (2005) Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on two earthworm species (Aporrectodea nocturna and Allolobophora icterica). Biol Fertil Soils 41:135–143
Carmichael WW (2001) Health effects of toxin-producing cyanobacteria: “the cyanoHABs”. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 7:1393–1407
Chen T, Wang QS, Cui J, Yang W, Shi Q, Hua ZC, Ji JG, Shen PP (2005) Induction of apoptosis in mouse liver by microcystin-LR: a combined transcriptomic, proteomic, and simulation strategy. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:958–974
Chen W, Song LR, Gan NQ, Li L (2006) Sorption, degradation and mobility of microcystins in Chinese agriculture soils: risk assessment for groundwater protection. Environ Pollut 144:752–758
Chen W, Jia YL, Li EH, Zhao S, Zhou QC, Liu LM, Song LR (2012) Soil-based treatments of mechanically collected cyanobacterial blooms from Lake Taihu: efficiencies and potential risks. Environ Sci Technol 46:13370–13376
Chen L, Chen J, Zhang XZ, Xie P (2016) A review of reproductive toxicity of microcystins. J Hazard Mater 301:381–399
Cook CM, Vardaka E, Lanaras T (2004) Toxic cyanobacteria in Greek freshwaters, 1987—2000: occurrence, toxicity, and impacts in the mediterranean region. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 32:107–124
Corbel S, Bouaïcha N, Mougin C (2014) Dynamics of the toxic cyanobacterial microcystin-leucine-arginine peptide in agricultural soil. Environ Chem Lett 12:535–541
Corbel S, Mougin C, Nélieu S, Delarue G, Bouaïcha N (2016) Evaluation of the transfer and the accumulation of microcystins in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum cultivar MicroTom) tissues using a cyanobacterial extract containing microcystins and the radiolabeled microcystin-LR (14C-MC-LR). Sci Total Environ 541:1052–1058
Du L, Li GD, Liu MM, Li YQ, Yin SZ, Zhao J, Zhang XY (2015) Evaluation of DNA damage and antioxidant system induced by di-n-butyl phthalates exposure in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 115:75–82
Duan X, Xu L, Song J, Jiao J, Liu M, Li H (2015) Effects of benzo [a] pyrene on growth, the antioxidant system, and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in 2 different soil types under laboratory conditions. Environ Toxicol Chem 34(2):283–290
Eyambe GS, Goven AJ, Fitzpatrick L, Venables BJ, Cooper EL (1991) A non-invasive technique for sequential collection of earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) leukocytes during subchronic immunotoxicity studies. Lab Anim 25(1):61–67
Falconer IR (2005) Is there a human health hazard from microcystins in the drinking water supply? Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 33:64–71
GB/T (2014) Test guildlines on environmental safety assessment for chemical pesticides [S] 31270
Gomes SIL, Hansen D, Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Amorim MJB (2015) Effects of silver nanoparticles to soil invertebrates: oxidative stress biomarkers in Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 199:49–55
Greig-Smith PW, Becker H, Edwards PJ, Heimbach F (1992) Eco-toxicology of earthworms. Tntercept, Andover
Gupta N, Pant SC, Vijayaraghavan R, Rao PVL (2003) Comparative toxicity evaluation of cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin variants (LR, RR, YR) in mice. Toxicology 188:285–296
Hoang DT, Pausch J, Razavi BS, Kuzyakova I, Banfield CC, Kuzyakov Y (2016) Hotspots of microbial activity induced by earthworm burrows, old root channels, and their combination in subsoil. Biol Fertil Soils 52:1105–1119
Huan ZB, Luo JH, Xu Z, Xie DF (2016) Acute toxicity and genotoxicity of carbendazim, main impurities and metabolite to earthworms (Eisenia foetida). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96:62–69
Li L, Xie P, Guo LG (2010a) Antioxidant response in liver of the phytoplanktivorous bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) intraperitoneally-injected with extracted microcystins. Fish Physiol Biochem 36:165–172
Li XY, Luo YR, Yun MX, Wang J, Wang JJ (2010b) Effects of 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium bromide on the anti-oxidant system of earthworm. Chemosphere 78:853–858
Li YW (2015) Occurrence and phytoxicity of typical microcystins in soil-vegetable system. A PhD dissertation in Jinan University, GuangZhou
Li YW, Huang XP, Wu XL, Xiang L, Zhan XJ, Li ZJ, Wen HF, Zhong FL, Mo CH, Hong AH (2013) Stimultaneous extraction and determination of three microcystins from soil using solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chin J Anal Chem 41:88–92
Li YW, Zhan XJ, Xiang L, Deng ZS, Huang BH, Wen HF, Sun TF, Cai QY, Li H, Mo CH (2014) Analysis of trace microcystins in vegetables using solid-phase extraction followed by high performance liquid chromatography triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 62:11831–11839
Lin DS, Zhou QX, Xie XJ, Liu Y (2010) Potential biochemical and genetic toxicity of triclosan as an emerging pollutant on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 81:1328–1333
Liu S, Zhou QX, Wang YY (2011) Ecotoxicological responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to soil contaminated with HHCB. Chemosphere 83:1080–1086
Lu RS (2000) Methods of agricultural chemical analysis in soil. China Agriculture Science and Technique Press, Beijing
Ma TT, Chen LK, Wu LH, Zhang HB, Luo YM (2016) Oxidative stress, cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in earthworm Eisenia fetida at different di-n-butyl phthalate exposure levels. PLoS One 10:1371
Markad VL, Kodam KM, Gholo VS (2012) Effect of fly ash on biochemical responses and DNA damage in earthworm, Dichogaster curgensis. J Hazard Mater 215-216:191–198
Merel S, Walker D, Chicana R, Snyder S, Baurès E, Thomas O (2013) State of knowledge and concerns on cyanobacterial blooms and cyanotoxins. Environ Int 59:303–327
OECD (1984) Guidelines for testing of chemicals. Test 207: earthworm acute toxicity tests. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
OECD (2004) Guidelines for testing of chemicals. Test 222: earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei). Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Papadimitriou T, Kagalou I, Stalikas C, Pilidis G, Leonardos ID (2012) Assessment of microcystin distribution and biomagnification in tissues of aquatic food web compartments from a shallow lake and evaluation of potential risks to public health. Ecotoxicology 21:1155–1166
Pflugmacher S, Wiegand C, Oberemm A, Beattie KA, Krause E, Codd GA, Steinberg CEW (1998) Identification of an enzymatically formed glutathione conjugate of thecyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR: the first step of detoxication. Biochim Biophys Acta 1425:527–533
Puddick J, Prinsep MR, Wood SA, Kaufononga SAF, Cary SC, Hamilton DP (2014) High levels of structural diversity observed in microcystins from microcystis CAWBG11 and characterization of six new microcystin congeners. Mar Drugs 12:5372–5395
Radi R, Beckman JS, Bush KM, Freeman BA (1991) Peroxynitrite-induced membrane lipid peroxidation: the cytotoxic potential of superoxide and nitric oxide. Arch Biochem Biophys 288:481–487
Roberts BL, Dorough HW (1984) Relative toxicities of chemicals to the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Environ Toxicol Chem 3:67–78
Saint-Denis M, Narbonne JF, Arnaud C, Thybaud E, Ribera D (1999) Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil: effects of benzo(a)pyrene. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1837–1846
Shi YJ, Shi YJ, Wang X, Lu YL, Yan SF (2007) Comparative effects of lindane and deltamethrin on mortality, growth, and cellulase activity in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Pestic Biochem Physiol 89:31–38
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41:905–909
Song YF, Kai JR, Song XY, Zhang W, Li LL (2015) Long-term toxic effects of deltamethrin and fenvalerante in soil. J Hazard Mater 289:158–164
Svendsen C, Spurgeon D, Hankard P, Weeks J (2004) A review of lysosomal membrane stability measured by neutral red retention: is it a workable earthworm biomarker ? Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 57(1):20–29
Van Groenigen JW, Lubbers IM, Vos HMJ, Brown GG, De Deyn GB, Van Groenigen KJ (2014) Earthworms increase plant production: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 4:6365
Velki M, Hackenberger BK (2013) Inhibition and recovery of molecular biomarkers of earthworm Eisenia andrei after exposure to organophosphate dimethoate. Soil Biol Biochem 57:100–108
Wang QL, Zhu L, Huang BJ, Li Y (2007) Toxicity effects of lead in polluted soil on earthworm coelomocyte lysosome. J Agro-Environ Sci 26(5):1874–1878
Wang LH, Wang XT, Geng ZR, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Wu J, Han XD (2013) Distribution of microcystin-LR to testis of male Sprague-Dawley rats. Ecotoxicology 22:1555–1563
Wang K, Pang S, Mu XY, Qi SZ, Li DZ, Cui F, Wang CJ (2015) Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia fetida, to five neonicotinoid insecticides. Chemosphere 132:120–126
Weeks JM, Svendsen C (1996) Neutral red retention by lysosomes from earthworm (Lumbricus rubellus) coelomocytes: a simple biomarker of exposure to soil copper. Environ Toxicol Chem 15(10):1801–1805
Wood SA, Holland PT, Stirling DJ, Briggs LR, Sprosen J, Ruck JG, Wear RG (2006) Survey of cyanotoxins in New Zealand water bodies between 2001 and 2004. N Z J Mar Fresh 40:585–597
Xu DM, Wen YZ, Wang KX (2010) Effect of chiral differences of metolachlor and its (S)-isomer on their toxicity to earthworms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1925–1931
Xu DM, Li CD, Wen YZ, Liu WP (2013) Antioxidant defense system responses and DNA damage of earthworms exposed to Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Environ Pollut 174:121–127
Xu XB, Shi YJ, Lu YL, Zheng XQ, Ritchie RJ (2015) Growth inhibition and altered gene transcript levels in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 69:1–7
Zhan XJ, Xing L, Li YW, Mo CH, Huang XP, Wu XL, Yuan Y, Liu Y, Li ZJ (2013) Influences of microcystin-LR and chromium on seed germination of Chinese cabbage. J Agro-Environ Sci 1672-2043: 01-0203-02
Zhang HJ, Cai CC, Fang WD, Wang J, Zhang Y, Liu JY, Jia XY (2013a) Qxidative damage and apoptosis induced by microcystin-LR in the liver of Rana nigromaculata in vivo. Aquat Toxicol 140-141:11–18
Zhang HJ, Cai CC, Wu YZ, Shao DD, Ye BH, Zhang Y, Liu JY, Wang J, Jia XY (2013b) Mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum pathways involved in microcystin-LR-induced apoptosis of the testes of male frog (Rana nigromaculata) in vivo. J Hazard Mater 252-253:382–389
Zhang QM, Zhang GL, Yin PJ, Lv YZ, Yuan S, Chen JQ, Wei BB, Wang CX (2015) Toxicological effects of soil contaminated with spirotetramat to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 139:138–145
Zhao YY, Xie LQ, Yan YJ (2015) Microcystin-LR impairs zebrafish reproduction by affecting oogenesis and endocrine system. Chemosphere 120:115–122
Zhou WS, Liang HL, Xie P, Zhang XZ (2012) Toxic effects of microcystin-LR on mice erythrocytes in vitro. Fresenius Environ Bull 21:2274–2281
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NSFC-Guangdong Joint Fund (U1501233), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41301337, 41573093), the Research Team Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2016A030312009), the Project on the Integration of Industry, Education and Research of Guangdong Province (2015B090903070 and 2013B090600143), the Program of the Guangdong Science and Technology Department (2016B020242005, 2015B020235008), Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou (201704020074), 2017 Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou Water Resources Bureau. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, HF., Li, YW., Xiang, L. et al. Toxicological effects of microcystin-LR on earthworm (Eisenia fetida) in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 53, 849–860 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1225-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1225-x