Abstract
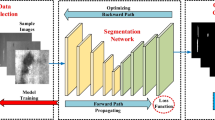
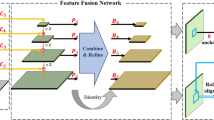
The strip steel is a common metallic material with a wide range of applications in various industries. However, the issue of surface defects that possess high concealment and low discrimination, which arises during the process of inspecting the quality of strip steel, imposes limitations on the overall quality of strip steel products. The challenging task of industrial quality inspection stems from the difficulty and inefficiency of detecting these defects. This paper addresses the aforementioned challenges by introducing a fast segmentation network model called the feature reused network (FR-Net), which aims to improve the detection of small defects and enhance real-time detection performance in the strip steel surface quality inspection process. In FR-Net, a feature fusion module is used to construct a feature reused fusion bypass to improve the segmentation accuracy of small defects. In addition, a lightweight feature refinement module is proposed to enhance the expression capability of the feature extraction network without increasing the computational effort. Finally, an atrous spatial pyramid pooling module with residual connectivity is proposed to fuse deep features of different scales and enhance the perception of objects of different scales. Experiments on the publicly available datasets showed that the proposed FR-Net achieved the mean intersection over union (mIoU) for NEU-Seg and SD-Saliency-900 datasets were 84.53% and 87.24%, respectively. Meanwhile, the detection speed on a single GPU was 58 FPS. Finally, the size of the proposed FR-Net model is only 45 MB, achieving a good trade-off between accuracy, speed, and model size, thus, providing a new solution for network model deployment on industrial equipment.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The NEU-Seg dataset is published by Northeastern University, the URL is: https://github.com/DHW-Master/NEU_Seg
References
Hao, R., Lu, B., Cheng, Y., Li, X., Huang, B.: A steel surface defect inspection approach towards smart industrial monitoring. J. Intell. Manuf. 32(7), 1833–1843 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01670-2
Zhou, X., Fang, H., Fei, X., Shi, R., Zhang, J.: Edge-aware multi-level interactive network for salient object detection of strip steel surface defects. IEEE Access 9, 149465–149476 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3124814
Zhou, X., Fang, H., Liu, Z., Zheng, B., Sun, Y., Zhang, J., Yan, C.: Dense attention-guided cascaded network for salient object detection of strip steel surface defects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71, 1–14 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2021.3132082
Song, G., Song, K., Yan, Y.: EDRNet: encoder–decoder residual network for salient object detection of strip steel surface defects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 69(12), 9709–9719 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2020.3002277
Lee, S.Y., Tama, B.A., Moon, S.J., Lee, S.: Steel surface defect diagnostics using deep convolutional neural network and class activation map. Appl. Sci. 9, 9245449 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245449
Huang, Z., Wu, J., Xie, F.: Automatic surface defect segmentation for hot-rolled steel strip using depth-wise separable U-shape network. Mater. Lett. 301, 130271 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130271
Zhang, J., Wang, H., Tian, Y., Liu, K.: An accurate fuzzy measure-based detection method for various types of defects on strip steel surfaces. Comput. Ind. 122, 103231 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2020.103231
Cao, J., Yang, G., Yang, X.: A pixel-level segmentation convolutional neural network based on deep feature fusion for surface defect detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2020.3033726
Ma, Z., Li, Y., Huang, M., Huang, Q., Cheng, J., Tang, S.: Automated real-time detection of surface defects in manufacturing processes of aluminum alloy strip using a lightweight network architecture. J. Intell. Manuf. 34(5), 2431–2447 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-022-01930-3
Singh, S.A., Desai, K.A.: Automated surface defect detection framework using machine vision and convolutional neural networks. J. Intell. Manuf. 34(4), 1995–2011 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-021-01878-w
Zhang, D., Song, K., Xu, J., He, Y., Niu, M., Yan, Y.: MCnet: multiple context information segmentation network of no-service rail surface defects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2020.3040890
Sun, J., Yan, S., Song, X.: QCNet: query context network for salient object detection of automatic surface inspection. Vis. Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02597-w
Cui, L., Jiang, X., Xu, M., Li, W., Lv, P., Zhou, B.: SDDNet: a fast and accurate network for surface defect detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2021.3056744
Guan, S., Lei, M., Lu, H.: A steel surface defect recognition algorithm based on improved deep learning network model using feature visualization and quality evaluation. IEEE Access. 8, 49885–49895 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2979755
Konovalenko, I., Maruschak, P., Brezinová, J., Viňáš, J., Brezina, J.: Steel surface defect classification using deep residual neural network. Metals. 10(6), 10060846 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060846
Wu, W., Li, Q.: Machine vision inspection of electrical connectors based on improved Yolo v3. IEEE Access 8, 166184–166196 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3022405
Liu, Y., Yuan, Y., Balta, C., Liu, J.: A light-weight deep-learning model with multi-scale features for steel surface defect classification. Materials (Basel) 13, 4629 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204629
Bao, Y., Song, K., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Yan, Y., Yu, H., Li, X.: Triplet-graph reasoning network for few-shot metal generic surface defect segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2021.3083561
Zhang, S., Zhang, Q., Gu, J., Su, L., Li, K., Pecht, M.: Visual inspection of steel surface defects based on domain adaptation and adaptive convolutional neural network. Mech. Syst. Sign. Proce. 153, 107541 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.107541
He, D., Xu, K., Zhou, P.: Defect detection of hot rolled steels with a new object detection framework called classification priority network. Comput. & Ind. Eng. 128, 290–297 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2018.12.043
Ma, Z., Li, Y., Huang, M., Huang, Q., Cheng, J., Tang, S.: A lightweight detector based on attention mechanism for aluminum strip surface defect detection. Comput. Ind. 136, 103585 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2021.103585
Tian, R., Jia, M.: DCC-CenterNet: a rapid detection method for steel surface defects. Meas. 187, 110211 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110211
Lv, X., Duan, F., Jiang, J.-J., Fu, X., Gan, L.: Deep metallic surface defect detection: the new benchmark and detection network. Sensors. 20(6), 61562 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061562
He, Y., Song, K., Meng, Q., Yan, Y.: An end-to-end steel surface defect detection approach via fusing multiple hierarchical features. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 69(4), 1493–1504 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2019.2915404
Choi, W., Cha, Y.-J.: SDDNet: real-time crack segmentation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Elect. 67(9), 8016–8025 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2019.2945265
Antwi-Bekoe, E., Liu, G., Ainam, J.-P., Sun, G., Xie, X.: A deep learning approach for insulator instance segmentation and defect detection. Neur. Comput. Appl. 34(9), 7253–7269 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06792-z
Kang, D., Han, Y., Zhu, J., Lai, J.: An axially decomposed self-attention network for the precise segmentation of surface defects on printed circuit boards. Neur. Comput. Appl. 34(16), 13697–13712 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07192-7
Song, L., Lin, W., Yang, Y.-G., Zhu, X., Guo, Q., Xi, J.: Weak micro-scratch detection based on deep convolutional neural network. IEEE Access. 7, 27547–27554 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2894863
Luo, Q., He, Y.: A cost-effective and automatic surface defect inspection system for hot-rolled flat steel. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 38, 16–30 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2015.09.008
Liu, P., Song, Y., Chai, M., Han, Z., Zhang, Y.: Swin-UNet++: a nested swin transformer architecture for location identification and morphology segmentation of dimples on 2.25Cr1Mo0.25V fractured surface. Materials (Basel). 14(24), 7504 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247504
Üzen, H., Turkoglu, M., Aslan, M., Hanbay, D.: Depth-wise squeeze and excitation block-based efficient-unet model for surface defect detection. Visual Comput. 39, 1745–1764 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02442-0
Dong, H., Song, K., He, Y., Xu, J., Yan, Y., Meng, Q.: PGA-Net: pyramid feature fusion and global context attention network for automated surface defect detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 16(12), 7448–7458 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tii.2019.2958826
Song, G., Song, K., Yan, Y.: Saliency detection for strip steel surface defects using multiple constraints and improved texture features. Opt. Las. Eng. 128, 106000 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.106000
Wang, Y., Song, K., Liu, J., Dong, H., Yan, Y., Jiang, P.: RENet: Rectangular convolution pyramid and edge enhancement network for salient object detection of pavement cracks. Meas. 170, 108698 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108698
Wan, C., Ma, S., Song, K.: TSSTNet: a two-stream swin transformer network for salient object detection of no-service rail surface defects. Coatings 12(11), 1730 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12111730
Cao, J., Yang, G., Yang, X.: TAFFNet: two-stage attention-based feature fusion network for surface defect detection. J. Sign. Pro. Syst. 94(12), 1531–1544 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-022-01801-3
Ding, T., Li, G., Liu, Z., Wang, Y.: Cross-scale edge purification network for salient object detection of steel defect images. Meas 199, 111429 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111429
Mordia, R., Kumar, V.A.: Visual techniques for defects detection in steel products: a comparative study. Eng. Failure Anal. 134, 106047 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106047
Kaddah, W., Elbouz, M., Ouerhani, Y., Baltazart, V., Desthieux, M., Alfalou, A.: Optimized minimal path selection (OMPS) method for automatic and unsupervised crack segmentation within two-dimensional pavement images. Vis. Comput. 35(9), 1293–1309 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1515-9
Roth K., Pemula L., Zepeda J., Schölkopf B., Brox T., and Gehler P.: Towards Total Recall in Industrial Anomaly Detection. In: Procedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 14298–14308. IEEE (2022). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01392.
Wei, C., Liang, J., Liu, H., Hou, Z., Huan, Z.: Multi-stage unsupervised fabric defect detection based on DCGAN. Vis. Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02754-1
Schlegl, T., Seeböck, P., Waldstein, S.M., Langs, G., Schmidt-Erfurth, U.: f-AnoGAN: Fast unsupervised anomaly detection with generative adversarial networks. Med. Image Anal. 54, 30–44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.01.010
He K., Zhang X., Ren S., and Sun J.: Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In : Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp, 770–778. IEEE (2016).
Shelhamer, E., Long, J., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 39, 640–651 (2017)
Simonyan K. and Zisserman A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014).
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2481–2495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
Elhassan M. A. M., Yang C., Huang C., and Legesse Munea T.: SPFNet:Subspace Pyramid Fusion Network for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv e-prints, arXiv:2204.01278 (2022).
Cheng, X., Yu, J.: RetinaNet with difference channel attention and adaptively spatial feature fusion for steel surface defect detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2020.3040485
Yu F. and Koltun V.: Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions. arXiv e-prints, arXiv:1511.07122.
Chen L.-C., Zhu Y., Papandreou G., Schroff F., and Adam H.: Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In: Proceddings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 833–851. Springer International Publishing (2018) .
Zhao H., Shi J., Qi X., Wang X., and Jia J.: Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In: Procedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6230–6239. IEEE (2017). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.660.
Lin G., Milan A., Shen C., and Reid I.: RefineNet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In: Procedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 5168–5177. IEEE (2017). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.549.
Yu C., Wang J., Peng C., Gao C., Yu G., and Sang N.: BiSeNet: bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In: Proceddings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp. 334–349. Springer International Publishing (2017).
Fu, J., Liu, J., Tian, H., Li, Y., Bao, Y., Fang, Z., & Lu, H.: Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. In: proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 3141–3149. IEEE (2019). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00326.
Lu Y., Chen Y., Zhao D., and Chen J.: Graph-FCN for Image Semantic Segmentation. In: advances in neural networks – ISNN 2019, pp. 97–105. Springer International Publishing (2019).
Huang G., Liu Z., Van Der Maaten L., and Weinberger K. Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 4700–4708. IEEE (2017).
Zhang X., Zhou X., Lin M., and Sun J.: Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 6848–6856. IEEE (2018).
Funding
No Funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QF performed software, conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, and writing-original draft preparation. FL and JF did conceptualization, writing—review, and editing. HL provided supervision, project administration, writing—review, and editing. XL done supervision, project administration. CL, SX, and QY contributed formal analysis and investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Q., Li, F., Li, H. et al. Feature reused network: a fast segmentation network model for strip steel surfaces defects based on feature reused. Vis Comput 40, 3633–3648 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03056-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03056-w