Abstract
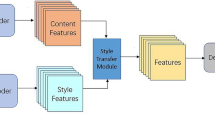
Arbitrary style transfer is an interesting and challenging technique. In the testing phase, it needs to adaptively fuse content images and style images not seen in the training phase. Users judge the model performance by the image quality alone. Simply put, the image quality is mainly concerned with two points, content consistency and style consistency. In this paper, we propose two contrastive losses to preserve content and fuse style. It is worth noting that our style consistency focuses on the fact that the style between different patches in the generated image is consistent and cannot have the style of the original content image patches, but this does not help the style of the generated images and the reference images to be consistent. Therefore, a simple and effective feature fusion method, Covariance Attention Network (CovAttN), is designed to encourage the generated image style to gradually approach the reference image style. It aligns content features and style features from both channel-wise correlation and spatial distribution to form a two-stage style injection. Compared with state-of-the-art models and ablation experiments demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method on arbitrary style transfer.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The datasets that support the findings of this study are openly available in MS-COCO at http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/train2014.zip and WikiArt at https://www.kaggle.com/c/painter-by-numbers.
References
Gatys, L.A., Ecker, A.S., Bethge, M.: Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2414–2423 (2016)
Lin, T., Ma, Z., Li, F., He, D., Li, X., Ding, E., Wang, N., Li, J., Gao, X.: Drafting and revision: Laplacian pyramid network for fast high-quality artistic style transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5141–5150 (2021)
Ma, Z., Lin, T., Li, X., Li, F., He, D., Ding, E., Wang, N., Gao, X.: Dual-affinity style embedding network for semantic-aligned image style transfer. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3143356
Jing, Y., Yang, Y., Feng, Z., Ye, J., Yu, Y., Song, M.: Neural style transfer: a review. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 26(11), 3365–3385 (2019)
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., Fei-Fei, L.: Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 694–711. Springer (2016)
Ulyanov, D., Lebedev, V., Vedaldi, A., Lempitsky, V.: Texture networks: feed-forward synthesis of textures and stylized images. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.03417 (2016)
Ulyanov, D., Vedaldi, A., Lempitsky, V.: Improved texture networks: maximizing quality and diversity in feed-forward stylization and texture synthesis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6924–6932 (2017)
Chen, D., Yuan, L., Liao, J., Yu, N., Hua, G.: Stylebank: an explicit representation for neural image style transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1897–1906 (2017)
Dumoulin, V., Shlens, J., Kudlur, M.: A learned representation for artistic style. arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.07629 (2016)
Zhang, H., Dana, K.: Multi-style generative network for real-time transfer. In: European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (2018)
Li, Y., Fang, C., Yang, J., Wang, Z., Lu, X., Yang, M.-H.: Diversified texture synthesis with feed-forward networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3920–3928 (2017)
Chen, T.Q., Schmidt, M.: Fast patch-based style transfer of arbitrary style. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.04337 (2016)
Yao, Y., Ren, J., Xie, X., Liu, W., Liu, Y.-J., Wang, J.: Attention-aware multi-stroke style transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1467–1475 (2019)
Liu, S., Zhu, T.: Structure-guided arbitrary style transfer for artistic image and video. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 24, 1299–1312 (2021)
Wang, Z., Zhao, L., Chen, H., Qiu, L., Mo, Q., Lin, S., Xing, W., Lu, D.: Diversified arbitrary style transfer via deep feature perturbation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7789–7798 (2020)
Wu, Z., Zhu, Z., Du, J., Bai, X.: Ccpl: contrastive coherence preserving loss for versatile style transfer. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 189–206. Springer (2022)
Li, X., Liu, S., Kautz, J., Yang, M.-H.: Learning linear transformations for fast image and video style transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3809–3817 (2019)
Deng, Y., Tang, F., Dong, W., Huang, H., Ma, C., Xu, C.: Arbitrary video style transfer via multi-channel correlation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 1210–1217 (2021)
Park, D.Y., Lee, K.H.: Arbitrary style transfer with style-attentional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5880–5888 (2019)
Deng, Y., Tang, F., Dong, W., Sun, W., Huang, F., Xu, C.: Arbitrary style transfer via multi-adaptation network. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 2719–2727 (2020)
Huang, X., Belongie, S.: Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1501–1510 (2017)
Li, Y., Fang, C., Yang, J., Wang, Z., Lu, X., Yang, M.-H.: Universal style transfer via feature transforms. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Sheng, L., Lin, Z., Shao, J., Wang, X.: Avatar-net: multi-scale zero-shot style transfer by feature decoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8242–8250 (2018)
Chen, H., Wang, Z., Zhang, H., Zuo, Z., Li, A., Xing, W., Lu, D., et al.: Artistic style transfer with internal–external learning and contrastive learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 26561–26573 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Tang, F., Dong, W., Huang, H., Ma, C., Lee, T.-Y., Xu, C.: Domain enhanced arbitrary image style transfer via contrastive learning. In: ACM SIGGRAPH (2022)
Jing, Y., Liu, X., Ding, Y., Wang, X., Ding, E., Song, M., Wen, S.: Dynamic instance normalization for arbitrary style transfer. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 4369–4376 (2020)
Xu, W., Long, C., Wang, R., Wang, G.: Drb-gan: a dynamic resblock generative adversarial network for artistic style transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6383–6392 (2021)
Zhang, M., Wang, N., Li, Y., Gao, X.: Neural probabilistic graphical model for face sketch synthesis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(7), 2623–2637 (2019)
Zhang, M., Li, J., Wang, N., Gao, X.: Compositional model-based sketch generator in facial entertainment. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 48(3), 904–915 (2017)
Zhang, M., Wang, N., Li, Y., Gao, X.: Deep latent low-rank representation for face sketch synthesis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(10), 3109–3123 (2019)
Park, T., Efros, A.A., Zhang, R., Zhu, J.-Y.: Contrastive learning for unpaired image-to-image translation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 319–345. Springer (2020)
Lee, H., Seol, J., Lee, S.: Contrastive learning for unsupervised image-to-image translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.03117 (2021)
Jeong, J., Shin, J.: Training gans with stronger augmentations via contrastive discriminator. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2020)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, pp. 1597–1607 (2020)
Kolkin, N., Salavon, J., Shakhnarovich, G.: Style transfer by relaxed optimal transport and self-similarity. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10051–10060 (2019)
Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Dollár, P., Zitnick, C.L.: Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 740–755. Springer (2014)
Phillips, F., Mackintosh, B.: Wiki art gallery, inc.: A case for critical thinking. Account. Educ. 26(3), 593–608 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Zhou, G. Arbitrary style transfer via content consistency and style consistency. Vis Comput 40, 1369–1382 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02855-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02855-5