Abstract
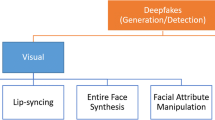
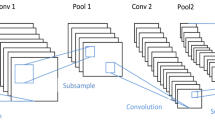
Development in artificial intelligence has brought a new revolution to technologies and approaches that have been employed for malicious purposes specifically after the introduction of generative adversarial networks (GANs) in 2014. GANs are empowered of generating fake visual samples with high realism. Several refined ML-based methods can produce highly realistic deepfakes videos that can be employed for harassing and blackmailing people. Moreover, deepfakes have introduced political stress by navigating disinformation which can result in societal, and political encounters. The prevailing situation has induced a severe danger to the privacy of humans and thus, urged for the introduction of automated approaches to identify deepfakes. In the presented approach, we have used deep learning (DL)-based approach namely ResNet-Swish-Dense54 for reliable and accurate detection of deepfakes. Initially, human faces are extracted from input video frames. Then, the extracted faces are passed to the ResNet-Swish-Dense54 model to perform the content classification as being real or manipulated. We have evaluated our model over the challenging datasets namely DFDC, FaceForensic++, and CelebDF datasets, and confirmed the robustness of the proposed approach through experimentation. Moreover, we have evaluated our approach for adversarial attacks and proved the explainability power of the ResNet-Swish-Dense54 model by generating heatmaps and performing cross-dataset validation. Both the quantitative and qualitative results demonstrated the effectiveness of our approach for visual manipulation detection.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan, A.R., Doosti, F., Karimi, M., Harouni, M., Tariq, U., Fati, S.M., Ali Bahaj, S.: Authentication through gender classification from iris images using support vector machine. Micosc. Res. Tech. 84(11), 2666–2676 (2021)
Palotás, Á.B., Rainey, L.C., Feldermann, C.J., Sarofim, A.F., Vander Sande, J.B.: Soot morphology: an application of image analysis in high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 33(3), 266–278 (1996)
Mahmood, M.T., Choi, W.J., Choi, T.S.: PCA-based method for 3D shape recovery of microscopic objects from image focus using discrete cosine transform. Microsc. Res. Tech. 71(12), 897–907 (2008)
Nawaz, M., Mehmood, Z., Bilal, M., Munshi, A.M., Rashid, M., Yousaf, R.M., Rehman, A., Saba, T.: Single and multiple regions duplication detections in digital images with applications in image forensic. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 40(6), 10351–10371 (2021)
Nazir, T., Irtaza, A., Javed, A., Malik, H., Mehmood, A., Nawaz, M.: Digital image forensic analysis using hybrid features. In: 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ICAI), 2021, pp. 33–36. IEEE
Vinolin, V., Sucharitha, M.: Dual adaptive deep convolutional neural network for video forgery detection in 3D lighting environment. Vis. Comput. 37(8), 2369–2390 (2021)
Yang, G., Xu, K., Fang, X., Zhang, J.: Video face forgery detection via facial motion-assisted capturing dense optical flow truncation. Vis. Comput. 1–20 (2022)
Masood, M., Nawaz, M., Malik, K.M., Javed, A., Irtaza, A.: Deepfakes Generation and Detection: State-of-the-art, open challenges, countermeasures, and way forward. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.00484 (2021)
He, D., He, X., Yuan, R., Li, Y., Shen, C.: Lightweight network-based multi-modal feature fusion for face anti-spoofing. Vis. Comput. 1–13 (2022)
Tyagi, S., Yadav, D.: A detailed analysis of image and video forgery detection techniques. Vis. Comput. 1–21 (2022)
Ballester, P., Araujo, R.M.: On the performance of GoogLeNet and AlexNet applied to sketches. In: Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2016)
(September 11, 2020). Reface App. Available: https://reface.app/
Schroff, F., Kalenichenko, D., Philbin, J.: Facenet: a unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 815–823 (2015)
Setiaji, H., Paputungan, I.V.: Design of telegram bots for campus information sharing. In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 325, no. 1, p. 012005. Institute of Physics Publishing (2018)
(January 11, 2021). Sound Forge. Available: https://www.magix.com/gb/music/sound-forge/
Boylan, J.F.: Will deep-fake technology destroy democracy? The New York Times, Oct, vol. 17, 2018.
Harwell, D.: Scarlett Johansson on fake AI-generated sex videos: ‘nothing can stop someone from cutting and pasting my image. Washington Post (2018)
Chan, C., Ginosar, S., Zhou, T., Efros, A.A.: Everybody dance now. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5933–5942 (2019)
Nawaz, M., Mehmood, Z., Nazir, T., Masood, M., Tariq, U., Munshi, A.M., Mehmood, A., Rashid, M.: Image authenticity detection using DWT and circular block-based LTrP features. CMC Comput. Mater. Contin. 69(2), 1927–1944 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Zheng, L., Thing, V.L: Automated face swapping and its detection. In: 2017 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), pp. 15–19. IEEE
Yang, X., Li, Y., Lyu, S.: Exposing deep fakes using inconsistent head poses. In: ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 8261–8265. IEEE (2019)
Güera, D., Baireddy, S., Bestagini, P., Tubaro, S., Delp, E.J.: We need no pixels: video manipulation detection using stream descriptors. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.08743 (2019)
Jack, K.: Chapter 13-MPEG-2. In: Video Demystified: A Handbook for the Digital Engineer, pp. 577–737
Ciftci, U.A., Demir, I.: FakeCatcher: detection of synthetic portrait videos using biological signals. In: IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2020)
Jung, T., Kim, S., Kim, K.: DeepVision: deepfakes detection using human eye blinking pattern. IEEE Access 8, 83144–83154 (2020)
Ranjan, R., Patel, V.M., Chellappa, R.: Hyperface: a deep multi-task learning framework for face detection, landmark localization, pose estimation, and gender recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(1), 121–135 (2017)
Soukupova, T., Cech, J.: Eye blink detection using facial landmarks. In: 21st computer vision winter workshop, Rimske Toplice, Slovenia (2016)
Gupta, S., Thakur, K., Kumar, M.: 2D-human face recognition using SIFT and SURF descriptors of face’s feature regions. Vis. Comput. 37(3), 447–456 (2021)
Zhou, D., Liu, Y., Li, X., Zhang, C.: Single-image super-resolution based on local biquadratic spline with edge constraints and adaptive optimization in transform domain. Vis. Comput. 1–16 (2020)
Zhu, X., Chen, Z.: Dual-modality spatiotemporal feature learning for spontaneous facial expression recognition in e-learning using hybrid deep neural network. Vis. Comput. 36(4), 743–755 (2020)
Couillaud, J., Ziou, D.: Light field variational estimation using a light field formation model. Vis. Comput. 36(2), 237–251 (2020)
Xu, Y., Raja, K., Pedersen, M.: Supervised contrastive learning for generalizable and explainable DeepFakes detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 379–389 (2022)
Kolagati, S., Priyadharshini, T., Rajam, V.M.A.: Exposing deepfakes using a deep multilayer perceptron–convolutional neural network model. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2(1), 100054 (2022)
Roy, R., Joshi, I., Das, A., Dantcheva, A.: 3D CNN Architectures and attention mechanisms for deepfake detection. (2022)
Sun, Z., Han, Y., Hua, Z., Ruan, N., Jia, W.: Improving the efficiency and robustness of deepfakes detection through precise geometric features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3609–3618 (2021)
Chen, Z., Xie, L., Pang, S., He, Y., Zhang, B.: MagDR: mask-guided detection and reconstruction for defending deepfakes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9014–9023 (2021)
Mehta, V., Gupta, P., Subramanian, R., Dhall, A.: FakeBuster: a DeepFakes detection tool for video conferencing scenarios. In: 26th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, pp. 61–63 (2021)
Masood, M., Nawaz, M., Javed, A., Nazir, T., Mehmood, A., Mahum, R.: Classification of Deepfake videos using pre-trained convolutional neural networks. In: 2021 International Conference on Digital Futures and Transformative Technologies (ICoDT2), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2021)
Baltrušaitis, T., Robinson, P., Morency, L.-P.: Openface: an open source facial behavior analysis toolkit. In: 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 1–10. IEEE (2016)
Fydanaki, A., Geradts, Z.: Evaluating OpenFace: an open-source automatic facial comparison algorithm for forensics. Forensic Sci. Res. 3(3), 202–209 (2018)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Patwardhan, N., Ingalhalikar, M., Walambe, R.: ARiA: utilizing Richard's curve for controlling the non-monotonicity of the activation function in deep neural nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.08878 (2018)
Dolhansky, B., Bitton, J.,. Pflaum, B., Lu, J., Howes, R., Wang, M., Ferrer, C.C.: The DeepFake detection challenge dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.07397 (2020)
Rossler, A., Cozzolino, D., Verdoliva, L., Riess, C., Thies, J., Nießner, M.: Faceforensics++: learning to detect manipulated facial images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1–11 (2019)
(2018, 14 March 2022). Deepfakes github. Available: http://github.com/deepfakes/faceswap
Thies, J., Zollhofer, M., Stamminger, M., Theobalt, C., Nießner, M.: Face2face: real-time face capture and reenactment of rgb videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2387–2395 (2016)
Thies, J., Zollhöfer, M., Nießner, M.: Deferred neural rendering: image synthesis using neural textures. ACM Trans. Graph. 38(4), 1–12 (2019)
Gandhi, A., Jain, S.: Adversarial perturbations fool deepfake detectors. In: 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2020)
Carlini, N., Farid, H.: Evading deepfake-image detectors with white-and black-box attacks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 658–659 (2020)
Hussain, S., Neekhara, P., Dolhansky, B., Bitton, J., Ferrer, C.C., McAuley, J., Koushanfar, F.: Exposing vulnerabilities of deepfake detection systems with robust attacks. Digit. Threats Res. Pract. (2021)
Hussain, S., Neekhara, P., Jere, M., Koushanfar, F., McAuley, J.: Adversarial deepfakes: evaluating vulnerability of deepfake detectors to adversarial examples. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 3348–3357 (2021)
Nawaz, M., Masood, M., Javed, A., Iqbal, J., Nazir, T., Mehmood, A., Ashraf, R.: Melanoma localization and classification through faster region-based convolutional neural network and SVM. Multimed. Tools Appl. 1–22 (2021)
Carvalho, T., De Rezende, E.R., Alves, M.T., Balieiro, F.K., Sovat, R.B.: Exposing computer generated images by eye’s region classification via transfer learning of VGG19 CNN. In: 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), pp. 866–870. IEEE (2017)
Theckedath, D., Sedamkar, R.: Detecting affect states using VGG16, ResNet50 and SE-ResNet50 networks. SN Comput. Sci. 1(2), 1–7 (2020)
Xia, X., Xu, C., Nan, B.: Inception-v3 for flower classification. In: 2017 2nd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), pp. 783–787. IEEE (2017)
Ferreira, C.A., Melo, T., Sousa, P., Meyer, M.I., Shakibapour, E., Costa, P., Campilho, A.: Classification of breast cancer histology images through transfer learning using a pre-trained inception resnet v2. In: International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, pp. 763–770. Springer, Berlin (2018)
Kusniadi, I., Setyanto, A.: Fake video detection using modified XceptionNet. In: 2021 4th International Conference on Information and Communications Technology (ICOIACT), pp. 104–107. IEEE (2021)
Krešo, I., Oršić, M., Bevandić, P., Šegvić, S.: Robust semantic segmentation with ladder-densenet models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.03465 (2018)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.-C.: Mobilenetv2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Marques, G., Agarwal, D., de la Torre Díez, I.: Automated medical diagnosis of COVID-19 through EfficientNet convolutional neural network. Appl. Soft Comput. 96, 106691 (2020)
Saxen, F. Werner, P., Handrich, S., Othman, E., Dinges, L., Al-Hamadi, A.: Face attribute detection with mobilenetv2 and nasnet-mobile. In: 2019 11th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis (ISPA), pp. 176–180. IEEE (2019)
Amerini, I., Galteri, L., Caldelli, R., Del Bimbo, A.: Deepfake video detection through optical flow based cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (2019)
Koonce, B.: ResNet 34. In: Convolutional Neural Networks with Swift for Tensorflow, pp. 51–61. Springer, Berlin (2021)
Wang, C., Chen, D., Hao, L., Liu, X., Zeng, Y., Chen, J., Zhang, G.: Pulmonary image classification based on inception-v3 transfer learning model. IEEE Access 7, 146533–146541 (2019)
Ranjan, P., Patil, S., Kazi, F.: Improved generalizability of deep-fakes detection using transfer learning based CNN framework. In: 2020 3rd International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies (ICICT), pp. 86–90. IEEE (2020)
Chintha, A., Rao, A., Sohrawardi, S., Bhatt, K., Wright, M., Ptucha, R.: Leveraging edges and optical flow on faces for deepfake detection. In: 2020 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), pp. 1–10. IEEE (2020)
Trinh, L., Tsang, M., Rambhatla, S., Liu, Y.: Interpretable and trustworthy deepfake detection via dynamic prototypes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 1973–1983 (2021)
Ganguly, S., Ganguly, A., Mohiuddin, S., Malakar, S., Sarkar, R.: ViXNet: vision transformer with xception network for deepfakes based video and image forgery detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 118423 (2022)
Hernandez-Ortega, J., Tolosana, R., Fierrez, J., Morales, A.: DeepFakesON-Phys: DeepFakes detection based on heart rate estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.00400 (2020)
Afchar, D., Nozick, V., Yamagishi, J., Echizen, I.: Mesonet: a compact facial video forgery detection network. In: 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2018)
Li, Y., Lyu, S.: Exposing deepfake videos by detecting face warping artifacts. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.00656 (2018)
Nguyen, H.H., Yamagishi, J., Echizen, I.: Capsule-forensics: using capsule networks to detect forged images and videos. In: ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2307–2311. IEEE (2019)
Pan, Z., Ren, Y., Zhang, X.: Low-complexity fake face detection based on forensic similarity. Multimed. Syst. 27(3), 353–361 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grant of the Punjab Higher Education Commission (PHEC) of Pakistan via Award No. (PHEC/ARA/PIRCA/20527/21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest between them.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nawaz, M., Javed, A. & Irtaza, A. ResNet-Swish-Dense54: a deep learning approach for deepfakes detection. Vis Comput 39, 6323–6344 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02732-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02732-7