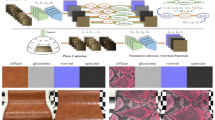
Abstract
The surface of a large number of objects in the real world shows the characteristics of stationary material. These appearances usually frequently exhibit the same or similar reflectance properties in different locations, while recent methods based on deep learning can estimate the surface reflectance properties from one or multiple photographs. For stationary materials, these lightweight methods do not use the potential reflectance information to recover plausible material properties from fewer images or produce better results from the same number of images. Moreover, directly using high-resolution images to optimize models greatly increases GPU consumption. In this paper, we present a pipeline capable of reconstructing high-resolution material properties from two images taken with the flash turned on or turned off. To reduce the number of captures to two, we utilize the stationary feature to generate multiple observations of the same small region. The new observations and original observation are used to estimate the higher-quality reflectance properties of this area. We then map the estimated reflectance properties to the high-resolution appearance parameters. Optimizing the model using only small area images reduces GPU consumption. Furthermore, we use a high-resolution flash image to estimate initial high-resolution reflectance parameter maps, crop the same location area from the initial results to initialize the auto-encoder. In addition, we leverage the jump rearrangement to reduce artifacts of high-resolution results. For reconstruction, two refinements that can reintroduce details are indispensable. We demonstrate and evaluate our method on the synthetic and real data.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aittala, M., Aila, T., Lehtinen, J.: Reflectance modeling by neural texture synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 35(4), 1–13 (2016)
Aittala, M., Weyrich, T., Lehtinen, J., et al.: Two-shot SVBRDF capture for stationary materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 34(4), 110–1 (2015)
Asselin, L.P., Laurendeau, D., Lalonde, J.F.: Deep SVBRDF estimation on real materials. In: 2020 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 1157–1166. IEEE (2020)
Dana, K.J., Van Ginneken, B., Nayar, S.K., Koenderink, J.J.: Reflectance and texture of real-world surfaces. ACM Trans. Graph. 18(1), 1–34 (1999)
da Silva Nunes, M., Melo Nascimento, F., Miranda, F., Jr., Trinchão Andrade, B., et al.: Techniques for BRDF evaluation. Vis. Comput. 38, 1–17 (2021)
Deschaintre, V., Aittala, M., Durand, F., Drettakis, G., Bousseau, A.: Single-image SVBRDF capture with a rendering-aware deep network. ACM Trans. Graph. 37(4), 1–15 (2018)
Deschaintre, V., Aittala, M., Durand, F., Drettakis, G., Bousseau, A.: Flexible SVBRDF capture with a multi-image deep network. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 38, pp. 1–13. Wiley Online Library (2019)
Deschaintre, V., Drettakis, G., Bousseau, A.: Guided fine-tuning for large-scale material transfer. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 39, pp. 91–105. Wiley Online Library (2020)
Dong, Y.: Deep appearance modeling: a survey. Vis. Inf. 3(2), 59–68 (2019)
Dong, Y., Chen, G., Peers, P., Zhang, J., Tong, X.: Appearance-from-motion: recovering spatially varying surface reflectance under unknown lighting. ACM Trans. Graph. 33(6), 1–12 (2014)
Gao, D., Li, X., Dong, Y., Peers, P., Xu, K., Tong, X.: Deep inverse rendering for high-resolution SVBRDF estimation from an arbitrary number of images. ACM Trans. Graph. 38(4), 1–15 (2019)
Gatys, L., Ecker, A.S., Bethge, M.: Texture synthesis using convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 28, 262–270 (2015)
Goldman, D.B., Curless, B., Hertzmann, A., Seitz, S.M.: Shape and spatially-varying BRDFS from photometric stereo. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(6), 1060–1071 (2009)
Guo, Y., Smith, C., Hašan, M., Sunkavalli, K., Zhao, S.: Materialgan: reflectance capture using a generative SVBRDF model. ACM Trans. Graph 39(6), 254:1-254:13 (2020)
Karis, B., Games, E.: Real shading in unreal engine 4. Proc. Phys. Based Shading Theory Pract. 4(3), 1 (2013)
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aittala, M., Hellsten, J., Lehtinen, J., Aila, T.: Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8110–8119 (2020)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) (2015)
Lawrence, J., Ben-Artzi, A., DeCoro, C., Matusik, W., Pfister, H., Ramamoorthi, R., Rusinkiewicz, S.: Inverse shade trees for non-parametric material representation and editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 25(3), 735–745 (2006)
Li, X., Dong, Y., Peers, P., Tong, X.: Modeling surface appearance from a single photograph using self-augmented convolutional neural networks. ACM Trans. Graph. 36(4), 1–11 (2017)
Li, Z., Shafiei, M., Ramamoorthi, R., Sunkavalli, K., Chandraker, M.: Inverse rendering for complex indoor scenes: Shape, spatially-varying lighting and SVBRDF from a single image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2475–2484 (2020)
Li, Z., Sunkavalli, K., Chandraker, M.: Materials for masses: SVBRDF acquisition with a single mobile phone image. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 72–87 (2018)
Li, Z., Xu, Z., Ramamoorthi, R., Sunkavalli, K., Chandraker, M.: Learning to reconstruct shape and spatially-varying reflectance from a single image. ACM Trans. Graph. 37(6), 1–11 (2018)
Matusik, W.: A data-driven reflectance model. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2003)
Nicodemus, F.E., Richmond, J.C., Hsia, J.J., Ginsberg, I., Limperis, T.: Geometrical Considerations and Nomenclature for Reflectance, vol. 160. US Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC (1977)
Palma, G., Callieri, M., Dellepiane, M., Scopigno, R.: A statistical method for SVBRDF approximation from video sequences in general lighting conditions. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 31, pp. 1491–1500. Wiley Online Library (2012)
Riviere, J., Peers, P., Ghosh, A.: Mobile surface reflectometry. In: Computer Graphics Forum, 35, pp. 191–202. Wiley Online Library (2016)
Schlick, C.: An inexpensive BRDF model for physically-based rendering. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 13, pp. 233–246. Wiley Online Library (1994)
Sole, A., Guarnera, G.C., Farup, I., Nussbaum, P.: Measurement and rendering of complex non-diffuse and goniochromatic packaging materials. Vis. Comput. 37(8), 2207–2220 (2021)
Trowbridge, T., Reitz, K.P.: Average irregularity representation of a rough surface for ray reflection. JOSA 65(5), 531–536 (1975)
Walter, B., Marschner, S.R., Li, H., Torrance, K.E.: Microfacet models for refraction through rough surfaces. Rendering techniques 2007, 18th (2007)
Ye, W., Li, X., Dong, Y., Peers, P., Tong, X.: Single image surface appearance modeling with self-augmented CNNS and inexact supervision. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 37, pp. 201–211. Wiley Online Library (2018)
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A., Shechtman, E., Wang, O.: The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 586–595 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Beihang University Yunnan Innovation Institute Yunding Technology Plan (2021) of Yunnan Provincial Key R &D Program (No. 202103AN080001-003) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U19A2063)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Shen, X., Hu, Y. et al. High-resolution SVBRDF estimation based on deep inverse rendering from two-shot images. Vis Comput 39, 4609–4622 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02612-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02612-0