Abstract
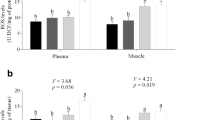
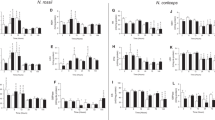
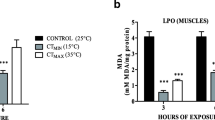
For a comprehensive understanding of fish responses to increasing thermal stress in marine environments, we investigated tissue energetics, antioxidant levels, inflammatory and cell death responses in Sparus aurata (gilthead seabream) red muscle during exposure to elevated temperatures (24 °C, 26 °C, 30 °C) compared to the control temperature of 18 °C. Energetic aspects were assessed by determining lactate, glucose and lipids levels in blood plasma, ATP, ADP and AMP levels, and AMPK phosphorylation as an indicator of regulatory changes in energy metabolism, in tissue extracts. Oxidative defence was assessed by determining superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione reductase maximum activities. Moreover, xanthine levels were determined as an indicator of purine conversion to xanthine and associated ROS production. In the context of inflammatory response and cell death due to oxidative stress, pro-inflammatory cytokines (IkBα phosphorylation, IL-6 and TNFα) levels, and LC3 II/I ratio and SQSTM1/p62 as indicators of autophagic-lysosomal pathway were also determined. A recovery in the efficacy of ATP production after a marked decrease during the 1st day of exposure to 24 °C is observed. This biphasic pattern is paralleled by antioxidant enzymes’ activities and inflammatory and autophagy responses, indicating a close correlation between ATP turnover and stress responses, which may benefit tissue function and survival. However, exposure beyond 24 °C caused tissue’s antioxidant capacity loss, triggering the inflammatory and cell death response, leading to increased fish mortality. The results of the present study set the thermal limits of the gilthead seabream at 22–24 °C and establish the used cellular and metabolic indicators as tools for the definition of the extreme thermal limits in marine organisms.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abele D, Puntarulo S (2004) Formation of reactive species and induction of antioxidant defence systems in polar and temperate marine invertebrates and fish. Comp Biochem Physiol A 138:405–415
Abele D, Heise K, Pörtner HO, Puntarulo S (2002) Temperature dependence of mitochondrial function and production of reactive oxygen species in the intertidal mud clam Mya arenaria. J Exp Biol 205:1831–1841
Adam H (1963) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, HU Bergmeyer, New York
Barsotti C, Ipata PL (2004) Metabolic regulation of ATP breakdown and of adenosine production in rat brain extracts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2214–2225
Bauchot M-L, Hureau J-C (1990) Sparidae. In: Quero JC, Hureau JC, Karrer C, Post A, Saldanha L (eds) Check-list of the fishes of the eastern tropical Atlantic (CLOFETA), vol 2. JNICT, SEI, UNESCO, Paris, pp 790–812
Baudry N, Laemmel E, Vicaut E (2008) In vivo reactive oxygen species production induced by ischemia in muscle arterioles of mice: involvement of xanthine oxidase and mitochondria. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294:H821–H828
Becker LB, vanden Hoek TL, Shao ZH, Li CQ, Schumacker PT (1999) Generation of superoxide in cardiomyocytes during ischemia before reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 277:H2240–H2246
Bennett WA, Judd FW (1992) Comparison of methods for determining low temperature tolerance: experiments with pinfish, Lagodon rhomboids. Copeia 4:1059–1065
Bennett W, Currier RJ, Beitinger TL (1997) Cold tolerance and potential overwinter of red-bellied piranha, Pygocentrus nattereri, in the United States. Trans Am Fish Soc 126(5):841–849
Bethoux JP, Gentili B, Raunet J, Tailliez D (1990) Warming trend in the western Mediterranean deep water. Nature 347:660–662
Boueiz A, Damarla M, Hassoun PM (2008) Xanthine oxidoreductase in respiratory and cardiovascular disorders. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294:L830–L840
Bowden TJ, Thompson KD, Morgan AL, Gratacap RML, Nikoskelainen S (2007) Seasonal variation and the immune response: a fish perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol 22:695–706
Burton BA (2002) Stress in fishes: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr Comp Biol 42(3):517–525
Calvo N, Marsh DR (2011) The combined effects of ENSO and the 11 year solar cycle on the Northern Hemisphere polar stratosphere. J Geophys Res 16:15226
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1985) Glutathione reductase assay. Methods Enzymol 113:484–495
Chandra J, Samali A, Orrenius S (2000) Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 29:323–333
Christen F, Desrosiers V, Dupont-Cyr BA, Vandenberg GW, Le François NR, Tardif J-C, Dufresne F, Lamarre SG, Blier PU (2018) Thermal tolerance and thermal sensitivity of heart mitochondria: Mitochondrial integrity and ROS production. Free Radic Biol Med 116:11–18
Chung DJ, Schulte PM (2015) Mechanisms and costs of mitochondrial thermal acclimation in a eurythermal killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus). J Exp Biol 218:1621–1631
Cohen G, Dembiec D, Marcus J (1970) Measurement of catalase activity in tissue extracts. Anal Biochem 34(1):30–38
Davies KJA (1987) Protein damage and degradation by oxygen radicals I. Gen Asp Biol Chem 262:9895–9901
Dodson M, Darley-Usmar V, Zhang J (2013) Cellular metabolic and autophagic pathways: traffic control by redox signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 63:207–221
Farthing DE, Farthing CA, Xi L (2015) Inosine and hypoxanthine as novel biomarkers for cardiac ischemia: from bench to point-of-care. Exp Biol Med 240:821–831
Feidantsis K, Pörtner HO, Lazou A, Michaelidis B (2009) Metabolic and molecular stress responses of the gilthead seabream Sparus aurata during long-term exposure to increasing temperatures. Mar Biol 156:797–809
Feidantsis K, Antonopoulou E, Lazou A, Pörtner HO, Michaelidis B (2013) Seasonal variations of cellular stress response of the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). J Comp Physiol B 183:625–639
Feidantsis K, Pörtner HO, Antonopoulou E, Michaelidis B (2015) Synergistic effects of acute warming and low pH on cellular stress responses of the gilthead seabream Sparus aurata. J Comp Physiol B 185:185–205
Feidantsis K, Pörtner HO, Vlachonikola E, Antonopoulou E, Michaelidis B (2018) Seasonal changes in metabolism and cellular stress phenomena in the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Physiol Biochem Zool 91(3):878–895
Forrester SJ, Kikuchi DS, Hernandes MS, Xu Q, Griendling KK (2018) Reactive oxygen species in metabolic and inflammatory signaling. Circ Res 122:877–902
Fridovich I (1986) Biological effects of the superoxide radical. Arch Biochem Biophys 247:1–11
Gambaiani DD, Mayol P, Isaac SJ, Simmonds MP (2009) Potential impacts of climate change and greenhouse gas emissions on Mediterranean marine ecosystems and cetaceans. J Mar Biol Assoc 89(1):179–201
Garcia-Castillo J, Pelegrin P, Mulero V, Meseguer J (2002) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of tumor necrosis factor α from a marine fish reveal its constitutive expression and ubiquitous nature. Immunogenetics 54:200–207
Hakim J (1993) Reactive oxygen species and inflammation. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil 187(3):286–295
Hardewig I, Peck LS, Pörtner HO (1999) Thermal sensitivity of mitochondrial function in the Antarctic Notothenioid Lepidonotothen nudifrons. J Comp Physiol B 169:597–604
Hardie DG (2004) The AMP-activated protein kinase pathway–new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci 117(23):5479–5487
Hardie G, Sakamoto K (2006) AMPK: a key sensor of fuel and energy status in skeletal muscle. Physiology 21:48–60
Hardie G, Schaffer B, Brunet A (2016) AMPK: an energy-sensing pathway with multiple inputs and outputs. Trends Cell Biol 26:190–201
Heise K, Puntarulo S, Nikinmaa M, Abele D, Pörtner HO (2006) Oxidative stress during stressful heat exposure and recovery in the North Sea eelpout (Zoarces viviparus). J Exp Biol 209:353–363
Iftikar FI, Hickey AJR (2013) Do mitochondria limit hot fish hearts? Understanding the role of mitochondrial function with heat stress in Notolabrus celidotus. PLoS One 8:e64120
Iftikar FI, Morash AJ, Cook DG, Herbert NA, Hickey AJR (2015) Temperature acclimation of mitochondria function from the hearts of a temperate wrasse (Notolabrus celidotus). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 184:46–55
Imlay JA, Linn S (1988) DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science 240:1302–1309
Iwama GK (1999) Stress in fish. Stress of life: from molecules to man. Ann NY Acad Sci 851:304–310
Jayasundara N, Somero GN (2013) Physiological plasticity of cardiorespiratory function in a eurythermal marine teleost, the longjaw mudsucker Gillichthys mirabilis. J Exp Biol 216(11):2111–2121
Jayasundara N, Gardner LD, Block BA (2013) Effects of temperature acclimation on Pacific bluefin tuna (Thunnus orientalis) cardiac transcriptome. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 305:R1010–R1020
Jayasundara N, Tomanek L, Dowd WW, Somero GN (2015) Proteomic analysis of cardiac response to thermal acclimation in the eurythermal goby fish Gillichthys mirabilis. J Exp Biol 218:1359–1372
Jeffries KM, Hinch SG, Sierocinski T, Pavlidis P, Miller KM (2014) Transcriptomic responses to high water temperature in two species of Pacific salmon. Evol Appl 7:286–300
Jeffries KM, Connon RE, Davis BE, Komoroske LM, Britton MT, Sommer T, Todgham AE, Fangue NA (2016) Effects of high temperatures on threatened estuarine fishes during periods of extreme drought. J Exp Biol 219:1705–1716
Khan JR, Iftikar FI, Herbert NA, Gnaiger E, Hickey AJR (2014) Thermal plasticity of skeletal muscle mitochondrial activity and whole animal respiration in a common intertidal triplefin fish, Forsterygion lapillum (Family: Tripterygiidae). J Comp Physiol B 184:991–1001
Kraffe E, Marty Y, Guderley H (2007) Changes in mitochondrial oxidative capacities during thermal acclimation of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: roles of membrane proteins, phospholipids and their fatty acid compositions. J Exp Biol 210:149–165
Kregel KC (2002) Heat shock proteins: modifying factors in physiological stress response and acquired thermotolerance. J Appl Physiol 92:2177–2186
Kültz D (2005) Molecular and evolutionary basis of the cellular stress response. Annu Rev Physiol 67:225–257
Laing KJ, Wang T, Zou J, Holland J, Hong S, Bols N, Hirono I, Aoki T, Secombes CJ (2001) Cloning and expression analysis of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss tumor nekrosis factor-α. Eur J Biochem 268:1315–1322
Lamprecht W, Trautschold I (1963) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, HU Bergmeyer, New York
Lewis JM, Hori TS, Rise ML, Walsh PJ, Currie S (2010) Transcriptome responses to heat stress in the nucleated red blood cells of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Physiol Genom 42:361–373
Li AJ, Leung PTY, Bao VWW, Lui GCS, Leung KMY (2014) Temperature-dependent physiological and biochemical responses of the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma with consideration of both low and high thermal extremes. J Therm Biol 36:116–123
Logan CA, Somero GN (2010) Transcriptional responses to thermal acclimationin the eurythermal fish Gillichthys mirabilis (Cooper 1864). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299:R843–R852
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101:13–30
Madeira DL, Narciso HN, Cabral C, Vinagre MS (2013) Influence of temperature in thermal and oxidative stress responses in estuarine fish. Comp Biochem Physiol A 166:237–243
Madeira D, Vinagre C, Costa PM, Diniz MS (2014) Histopathological alterations, physiological limits, and molecular changes of juvenile Sparus aurata in response to thermal stress. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 505:253–266
Madeira D, Vinagre C, Diniz MS (2016) Are fish in hot water? Effects of warming on oxidative stress metabolism in the commercial species Sparus aurata. Ecol Indic 63:324–331
McEwen BS, Wingfield JC (2003) Response to commentaries on the concept of allostasis. Horm Behav 43(1):28–30
Nicholls RJ, Hoozemans FMJ (1996) The Mediterranean: vulnerability to coastal implication of climate change. Ocean Coast Manag 31(2–3):105–132
Paoletti F, Mocali A (1990) Determination of Superoxide dismutase activity by purely chemical system based on NAD(P)H oxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:209–220
Pörtner HO (2001) Climate change and temperature dependent biogeography: oxygen limitation of thermal tolerance in animals. Naturwissenschaften 88:137–146
Pörtner HO (2002a) Climate variations and the physiological basis of temperature dependent biogeography: systemic to molecular hierarchy of thermal tolerance in animals. Comp Biochem Physiol A 132:739–761
Pörtner HO (2002b) Physiological basis of temperature-dependent biogeography: trade-offs in muscle design and performance in polar ectotherms. J Exp Biol 205:2217–2230
Pörtner HO (2010) Oxygen- and capacity-limitation of thermal tolerance: a matrix for integrating climate-related stressor effects in marine ecosystems. J Exp Biol 213(6):881–893
Pörtner HO (2012) Integrating climate-related stressor effects on marine organisms: unifying principles linking molecule to ecosystem-level changes. MEPS 470:273–290
Pörtner HO, Farrell AP (2008) Ecology: physiology and climate change. Science 322:690–692
Pörtner HO, Knust R (2007) Climate change affects marine fishes through the oxygen limitation of thermal tolerance. Science 315:95–97
Portt L, Norman G, Clapp C, Greenwood M, Michael T, Greenwood T (2011) Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: a review. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:238–259
Sadovy de Mitcheson Y, Liu M (2008) Functional hermaphroditism in teleosts. Fish Fish 9(1):1–43
Salach JI (1978) Preparation of monoamine oxidase from beef liver mitochondria. Methods Enzymol 53:495–501
Schulte MP (2014) What is environmental stress? Insights from fish living in a variable environment. J Exp Biol 217:23–34
Shin MK, Park HR, Yeo WJ, Han KN (2018) Effects of thermal stress on the mRNA expression of SOD, HSP90, and HSP70 in the Spotted Sea Bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Ocean Sci J 53(1):43–52
Smith LS, Bell GR (1964) A technique for prolonged blood sampling in free-swimming salmon. J Fish Res Board Can 21(4):711
Sokolova IM, Frederich M, Bagwe R, Lannig G, Sukhotin AA (2012) Energy homeostasis as an integrative tool for assessing limits of environmental stress tolerance in aquatic invertebrates. Mar Environ Res 79:1–15
Somero GN (2010) The physiology of climate change: how potentials for acclimatization and genetic adaptation will determine ‘winners’ and ‘losers’. J Exp Biol 213:912–920
Thorne MAS, Burns G, Fraser KPP, Hillyard G, Clark MS (2010) Transcriptional profiling of acute temperature stress in the Antarctic plunderfish Harpagifer antarcticus. Mar Genom 3:35–44
Tomalty KMH, Meek MH, Stephens MR, Rincón G, Fangue NA, May BP, Baerwald MR (2015) Transcriptional response to acute thermal exposure in Juvenile Chinook Salmon determined by RNAseq. Genes Genom Genet 5(7):1335–1349
Tornatore L, Thotakura AK, Bennett J, Moretti M, Franzoso G (2012) The nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway: integrating metabolism with inflammation. Trends Cell Biol 22:557–566
Vanden Hoek TL, Li C, Shao Z, Schumacker PT, Becker LB (1997) Significant levels of oxidants are generated by isolated cardiomyocytes during ischemia prior to reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol 29:2571–2583
Vargas-Chacoff L, Arjona FJ, Polakof S, Martín del Río MP, Soengas JL, Mancera JM (2009) Interactive effects of environmental salinity and temperature on metabolic responses of gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata. Comp Biochem Physiol A 154:417–424
Weinstein RB, Somero GN (1998) Effects of temperature on mitochondrial function in the Antarctic fish Trematomus bernachii. J Comp Physiol 168B:190–196
Windisch HS, Frickenhaus S, John U, Knust R, Pörtner HO, Lucassen M (2014) Stress response or beneficial temperature acclimation: transcriptomic signatures in Antarctic fish (Pachycara brachycephalum). Mol Ecol 23:3469–3482
Zajączkowski S, Ziółkowski W, Badtke P, Zajączkowski MA, Flis DJ, Figarski A, Smolińska-Bylańska M, Wierzba TH (2018) Promising effects of xanthine oxidase inhibition by allopurinol on autonomic heart regulation estimated by heart rate variability (HRV) analysis in rats exposed to hypoxia and hyperoxia. PLoS One 13(2):e0192781
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Animals received proper care in compliance with the “Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” published by US National Institutes of Health (NIH publication No 85–23, revised 1996) and the “Principles of laboratory animal care” published by the Greek Government (160/1991) based on EU regulations (86/609). The protocol as well as surgery and sacrifice were approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of the Directorate of Veterinary Services of Prefecture of Thessaloniki under the license number EL 54 BIO 05.
Additional information
Communicated by Bernd Pelster.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feidantsis, K., Georgoulis, I., Zachariou, A. et al. Energetic, antioxidant, inflammatory and cell death responses in the red muscle of thermally stressed Sparus aurata. J Comp Physiol B 190, 403–418 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-020-01278-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-020-01278-1