Abstract
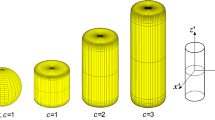
In this study, an experimental analysis is conducted on the settling of straight and curved cylindrical rods, which are used to replicate a Reynolds number range applicable to atmospheric settling of microplastic fibres. The rods are dropped in a chamber filled with a quiescent water–glycerin mixture, and their settling velocity is determined from the images of two cameras arranged with perpendicular views. It is shown that a curved cylindrical rod settles faster than a straight cylindrical rod with the same diameter and length. As the rod radius of curvature decreases, the terminal velocity increases, and the corresponding drag coefficient decreases. The maximum difference in the terminal velocity between the straight and curved rods depends on the rod aspect ratio, curvature index, and Reynolds number. A new semi-empirical model is also developed to estimate the drag coefficient and terminal velocity of both straight and curved cylindrical rods studied in this research. The results of the new model are significantly more consistent with the experimental data compared to the previous models, with a low RMS error of 6.8%. This novel model has been utilized to predict the terminal velocity of realistic fibres in the atmosphere.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request to the authors.
References
Allen S, Allen D, Phoenix V et al (2019) Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nat Geosci 12(5):339–344
Allen S, Allen D, Baladima F et al (2021) Evidence of free tropospheric and long-range transport of microplastic at pic du midi observatory. Nat Commun 12(1):7242
Bagheri G, Bonadonna C (2016) On the drag of freely falling non-spherical particles. Powder Technol 301:526–544
Banaei AA, Rahmani M, Martinez DM et al (2020) Inertial settling of flexible fiber suspensions. Phys Rev Fluids 5(2):024301
Bergmann M, Mützel SM, Primpke S et al (2019) White and wonderful? Microplastics prevail in snow from the alps to the arctic. Sci Adv 5(8):eaxx1157
Bergmann M, Collard F, Fabres J et al (2022) Plastic pollution in the Arctic. Nat Rev Earth Environ 3(5):323–337
Brenner H (1962) Effect of finite boundaries on the stokes resistance of an arbitrary particle. J Fluid Mech 12(1):35–48
Cai L, Wang J, Peng J et al (2017) Characteristic of microplastics in the atmospheric fallout from dongguan city, china: preliminary research and first evidence. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24928–24935
Candelier F, Mehlig B (2016) Settling of an asymmetric dumbbell in a quiescent fluid. J Fluid Mech 802:174–185
Cheng N (2008) Formula for the viscosity of a glycerol- water mixture. Indust Eng Chem Res 47(9):3285–3288
Chow A, Adams E (2011) Prediction of drag coefficient and secondary motion of free-falling rigid cylindrical particles with and without curvature at moderate reynolds number. J Hydraul Eng 137(11):1406–1414
Clift R, Grace JR, Weber ME (1978) Bubbles. Academic Press, New York, Drops and Particles
Cox R (1970) The motion of long slender bodies in a viscous fluid part 1 general theory. J Fluid Mech 44(4):791–810
Dehghani S, Moore F, Akhbarizadeh R (2017) Microplastic pollution in deposited urban dust, Tehran metropolis, Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:20360–20371
Dris R, Gasperi JMS et al (2016) Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: a source of microplastics in the environment? Marine Pollut Bull 104(1):290–293
Du Roure O, Lindner A, Nazockdast EN et al (2019) Dynamics of flexible fibers in viscous flows and fluids. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 51:539–572
Evangeliou N, Tichy O, Eckhardt S et al (2022) Sources and fate of atmospheric microplastics revealed from inverse and dispersion modelling: from global emissions to deposition. J Hazard Mater 432:128585
Finnegan AMD, Süsserott R, Gabbott SE et al (2022) Man-made natural and regenerated cellulosic fibres greatly outnumber microplastic fibres in the atmosphere. Environ Pollut 310:119808
Fintzi N, Gamet L, Pierson JL (2023) Inertial loads on a finite-length cylinder embedded in a steady uniform flow. Phys Rev Fluids 8(4):044302
Ganser G (1993) A rational approach to drag prediction of spherical and nonspherical particles. Powder Technol 77(2):143–152
Goral KD, Guler H, Larsen BE et al (2023) Settling velocity of microplastic particles having regular and irregular shapes. Environ Res 228:115783
Haider A, Levenspiel O (1989) Drag coefficient and terminal velocity of spherical and nonspherical particles. Powder Technol 58(1):63–70
Henn A (1996) Calculation of the stokes and aerodynamic equivalent diameters of a short reinforcing fiber. Particle Syst Charact 13(4):249–253
Huner B, Hussey R (1977) Cylinder drag at low reynolds number. Phys Fluids 20(8):1211–1218
Jayaweera KOLF, Mason BJ (1965) The behaviour of freely falling cylinders and cones in a viscous fluid. J Fluid Mech 22:709–720
Kaimal JC, Finnigan JJ (1994) Atmospheric boundary layer flows: their structure and measurement. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Khalili A, Liu B (2017) Stokes’ paradox: creeping flow past a two-dimensional cylinder in an infinite domain. J Fluid Mech 817:374–387
Kharrouba M, Pierson JL, Magnaudet J (2021) Flow structure and loads over inclined cylindrical rodlike particles and fibers. Phys Rev Fluids 6(4):044308
Khayat R, Cox R (1989) Inertia effects on the motion of long slender bodies. J Fluid Mech 209:435–462
Liu K, Wu T, Wang X et al (2019) Consistent transport of terrestrial microplastics to the ocean through atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol 53(18):10612–10619
Lopez D, Guazzelli E (2017) Inertial effects on fibers settling in a vortical flow. Phys Rev Fluids 2(2):024306
Marchetti B, Raspa V, Lindner A et al (2018) Deformation of a flexible fiber settling in a quiescent viscous fluid. Phys Rev Fluids 3(10):104102
McNown JS, Malaika J (1950) Effects of particle shape on settling velocity at low reynolds numbers. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 31(1):74–82
Michaelides EE, Feng Z (2023) Review—drag coefficients of non-spherical and irregularly shaped particles. J Fluids Eng 145(6):060801
Napper IE, Parker-Jurd FNF, Wright SL et al (2023) Examining the release of synthetic microfibres to the environment via two major pathways: atmospheric deposition and treated wastewater effluent. Sci Total Environ 857:159317
Nguyen TH, Kieu-Le TC, Tang FH et al (2022) Controlling factors of microplastic fibre settling through a water column. Sci Total Environ 838:156011
O’Brien S, Rauert C, Ribeiro F et al (2023) There’s something in the air: a review of sources, prevalence and behaviour of microplastics in the atmosphere. Sci Total Environ 874:162193
Rong X, Qi D, He G et al (2008) Single curved fiber sedimentation under gravity. Comput Math Appl 55(7):1560–1567
Roy A, Hamati R, Tierney L et al (2019) Inertial torques and a symmetry breaking orientational transition in the sedimentation of slender fibres. J Fluid Mech 875:576–596
Sen S, Mittal S, Biswas G (2009) Steady separated flow past a circular cylinder at low reynolds numbers. J Fluid Mech 620:89–119
Soloff S, Adrian R, Liu Z (1997) Distortion compensation for generalized stereoscopic particle image velocimetry. Meas Sci Technol 8(12):1441
Song X, Xu Z, Li G et al (2017) A new model for predicting drag coefficient and settling velocity of spherical and non-spherical particle in Newtonian fluid. Powder Technol 321:242–250
Stokes G (1851) On the effect of the internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums. Trans Cambridge Philos Soc 9:8–106
Taylor JR, Thompson W (1982) An introduction to error analysis: the study of uncertainties in physical measurements, vol 2. Springer, Cham
Ward E, Gordon M, Hanson R et al (2024) Modelling the effect of shape on atmospheric microplastic transport. Atmos Environ 326:120458
Wright S, Ulke J, Font A et al (2020) Atmospheric microplastic deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport. Environ Int 136:105411
Xu X, Nadim A (1994) Deformation and orientation of an elastic slender body sedimenting in a viscous liquid. Phys Fluids 6(9):2889–2893
Yang X, Wang Y, Li Y et al (2022) Experimental research on the settling property of slender fiber particles under the influence of multiple factors. Powder Technol 405:117543
Yu Z, Yang G, Zhang W (2022) A new model for the terminal settling velocity of microplastics. Mar Pollut Bull 176:113449
Zhang J, Choi CE (2022) Improved settling velocity for microplastic fibers: A new shape-dependent drag model. Environ Sci Technol 56(2):962–973
Zhang Y, Kang S, Allen S et al (2020) Atmospheric microplastics: a review on current status and perspectives. Earth Sci Rev 203:103118
Acknowledgements
This project is funded [in part] by the Northern Contaminants Program (CIRNAC, M-61) and the Government of Canada (ECCC, Grants and Contributions Award GCXE21S030).
Funding
This project is funded [in part] by the Northern Contaminants Program (CIRNAC, M-61) and the Government of Canada (ECCC, Grants and Contributions Award GCXE21S030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hamidi, A., Daramsing, D., Gordon, M.D. et al. Straight and curved cylindrical rods settling in quiescent fluid with application to atmospheric microplastics. Exp Fluids 65, 81 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-024-03819-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-024-03819-8