Abstract
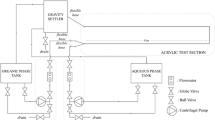
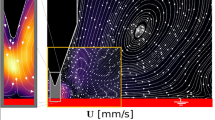
Gas–liquid intermittent flows can be found in many engineering applications, nevertheless a detailed knowledge of this flow pattern is still not fully available. In the present work, an experimental study was conducted with the objective of developing a measurement procedure capable of providing ensemble-averaged three-component velocity fields in the liquid phase of a gas–liquid, intermittent, horizontal flow in a pipe. To this end, a high-frequency stereoscopic particle image velocimetry system (SPIV) was employed, combined with the laser induced fluorescence (LIF) technique to separate the light scattered by the liquid–gas interfaces from that emitted by the fluorescent tracer particles. A set of photogates was used to trigger the SPIV system, allowing for the measurement of velocity fields in the liquid plug, downstream of the elongated bubble, and in the liquid film, upstream of the elongated bubble nose position. The triggered measurements allowed the determination of ensemble-averaged three-component velocity fields at different positions in relation to the bubble nose, obtained from the replication of a sufficiently large number of bubble passage events. Contours of the liquid flow streamwise vorticity component in cross-stream planes upstream and downstream of the bubble nose tip were also obtained from the SPIV measurements. The photogate system was also employed to measure the bubble velocity. This information was used to transform time-based into space-based velocity field data. This allowed the construction of a three-dimensional representation of the ensemble-averaged structure of the gas bubble nose and the associated vortical structures induced in the liquid flow. The three-component velocity information obtained revealed the influence of the gas bubble motion on the liquid flow in the plug and liquid film regions.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed WH (2011) Experimental investigation of air-oil slug flow using capacitance probes, hot-film anemometer, and image processing. Int J Multiph Flow 37:876–887
Baker O (1954) Design of pipelines for simultaneous flow of oil and gas. Oil Gas J 53:185–195
Bertola V (2002) Slug velocity in horizontal gas-liquid flow. Experiments in Fluids Vol 22:722–727
BIPM, IEC, IFCC, ILAC, ISO IUPAC, IUPAP, OIML (2008) Evaluation of measurement data—guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement. JCGM 100:2008
Bjorkquist DC (2002) Stereo PIV calibration verification. In: 11th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, 8–11 July
Carneiro J, Fonseca R Jr, Ortega A, Chucuya R, Nieckele A, Azevedo LFA (2011) Statistical characterization of two-phase slug ow in a horizontal pipe. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 33:251–258
Carpintero-Rogero E (2008) Experimental investigation of transient slug flow. PhD Thesis, Technische Universitat Munchen
Czapp M, Muller C, Fernández PA, Sattelmayer T (2012) High-speed Stereo and 2D PIV measurements of two-phase slug flow in a horizontal pipe. In: 16th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, 9–12 July
De Oliveira WR, de Paula IB, Martins FJWA, Farias PSC, Azevedo LFA (2015) Bubble characterization in horizontal air-water intermittent flow. Int J Multiph Flow 69:18–30
Dukler AE, Hubbard MG (1975) A model for gas-liquid slug flow in horizontal and near horizontal tubes. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 14(4):337–347
Fabre J (1994) Advancements of two-phase slug flow modeling. The University centennial petroleum engineering symposium SPE paper 27961-MS
Fabre J, Peresson LL, Corteville J, Odello R, Bourgeois T (1990) Severe sluggingin pipeline/riser systems. SPE Prod Eng 5(3):299–305
Farias PSC, Martins FJWA, Sampaio LEB, Serfaty R, Azevedo LFA (2012) Liquid film characterization in horizontal, annular, two-phase, gas-liquid flow using time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence. Exp Fluids 52(3):633–645
Febres M, Nieckele A, Fonseca R Jr, Azevedo LFA (2010) Three-dimensional unit slug in a horizontal pipe. In: 7th international conference on multiphase flow, Tampa, 30 May–4 June
Goharzadeh A, Rodgers P (2009) Experimental characterization of slug flow velocity distribution in two phase pipe flow. In: ASME 2009 international mechanical engineering congress and exposition. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Lake Buena Vista, Florida, November 13–19
Kim TW, Aydin TB, Pereyra E, Sarica C (2018) Detailed flow field measurements and analysis in highly viscous slug flow in horizontal pipes. Int J Multiph Flow 106:75–94
Kvernvold O, Vindoy V, Sontvedt T, Saasen A, Selmer-Olsen S (1984) Velocity distribution in horizontal slug flow. Int J Multiph Flow 10:447–457
Lewis S, Fu WL, Kajasoy G (2002) Internal flow structure description of slug flow pattern in a horizontal pipe. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 45:3897–3910
Lindken R, Merzkirch W (2002) A novel technique for measurements in multiphase flow and its application to two-phase bubbly flows. Exp Fluids 33:814–825
Prasad AK (2000) Stereoscopic particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 29:103–116
Raffel M, Willert CE, Scarano F, Kähler CJ, Wereley ST, Kompenhans J (2018) Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide. Springer, New York
Sciacchitano A, Wieneke B (2016) PIV uncertainty propagation. Meas Sci Technol 27(8):084006
Sharma S, Lewis S, Kojasoy G (1998) Local studies in horizontal gas-liquid slug flow. Nucl Eng Des 184:305–318
Siddiqui MI, Muni S, Heikal MR, de Sercey G, Rashid A, Aziz A, Dass SC (2016) Simultaneous velocity measurements and the coupling effect of liquid and gas phases in slug flow using PIV-LIF technique. J Vis 19:103–114
Soloff SM, Adrian RJ, Liu Z-C (1997) Distortion compensation for generalized stereoscopic particle image velocimetry. Meas Sci Technol 8(12):1441–1454
Suzanne C, Ellingsen K, Risso F, Roid V (1998) Local measurements in turbulent bubbly flows. Nucl Eng Des 184:319–327
Wieneke B (2005) Stereo-PIV using self-calibration on particle images. Exp Fluids 39(2):267–280
Acknowledgements
The present work is part of an ongoing research project in two-phase flow carried in the Laboratory of Fluid Engineering, at PUC-Rio, in a partnership with Petrobras. The authors sincerely acknowledge the continuous support from Petrobras. Scholarship support by CAPES, agency from the Brazilian Ministry of Education, CNPq, Brazilian Research Council, and FAPERJ, Research Foundation of the State of Rio de Janeiro, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 1111 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, L.S., Martins, F.J.W.A. & Azevedo, L.F.A. A technique for measuring ensemble-averaged, three-component liquid velocity fields in two-phase, gas–liquid, intermittent pipe flows. Exp Fluids 59, 147 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-018-2601-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-018-2601-5