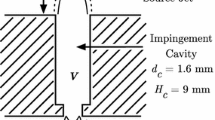
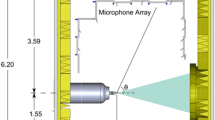
Abstract
For flow control applications requiring high-frequency excitation, very few actuators have sufficient dynamic response and/or control authority to be useful in high-speed flows. Due to this reason, experiments involving high-frequency excitation, attempted in the past, have been limited to either low-frequency actuation with reasonable control authority or moderate-frequency actuation with limited control authority. The current work expands on the previous development of the resonance-enhanced microactuators to design actuators that are capable of producing high-amplitude pulses at much higher frequencies [\(\mathcal {O}\) (10 kHz)]. Using lumped element modeling, two actuators have been designed with nominal frequencies of 20 and 50 kHz. Extensive benchtop characterization using acoustic measurements as well as optical diagnostics using a high-resolution micro-schlieren setup is employed to characterize the dynamic response of these actuators. The actuators performed at a range of frequencies, 20.3–27.8 and 54.8–78.2 kHz, respectively. In addition to providing information on the actuator flow physics and performance at various operating conditions, this study serves to develop easy-to-integrate high-frequency actuators for active control of high-speed jets. Preliminary testing of these actuators is performed by implementing the 20-kHz actuator on a Mach 0.9 free jet flow field for noise reduction. Acoustic measurements in the jet near field demonstrate attenuation of radiated noise at all observation angles.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja K, Blakney D (1985) Tone excited jets, part IV: acoustic measurements. J Sound Vib 102(1):93–117
Alkislar MB, Krothapalli A, Butler G (2007) The effect of streamwise vortices on the aeroacoustics of a mach 0.9 jet. J Fluid Mech 578:139–169
Arakeri V, Krothapalli A, Siddavaram V, Alkislar M, Lourenco L (2003) On the use of microjets to suppress turbulence in a mach 0.9 axisymmetric jet. J Fluid Mech 490:75–98
Armstrong RR, Michalke A, Fuchs HV (1977) Coherent structures in jet turbulence and noise. AIAA J 15(7):1011–1017
Bechert D, Pfizenmaier E (1975) On the amplification of broad band jet noise by a pure tone excitation. J Sound Vib 43(3):581–587
Beutner TJ, Adelgren R, Elliott G (2006) Characterization of schlieren light source using laser-induced optical breakdown in argon. AIAA J 44(2):399–402
Blackstock DT (2000) Fundamentals of physical acoustics. Wiley, London
Cattafesta LN III, Sheplak M (2011) Actuators for active flow control. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 43:247–272
Cavalieri AV, Rodríguez D, Jordan P, Colonius T, Gervais Y (2013) Wavepackets in the velocity field of turbulent jets. J Fluid Mech 730:559–592
Crow SC, Champagne F (1971) Orderly structure in jet turbulence. J Fluid Mech 48(03):547–591
Fuchs HV, Michel U (1978) Experimental evidence of turbulent source coherence affecting jet noise. AIAA J 16(9):871–872
Greska BJ (2005) Supersonic jet noise and its reduction using microjet injection. PhD dissertation, Florida State University, ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 3183064
Hartmann J (1922) On a new method for the generation of sound-waves. Phys Rev 20(6):719
Hussain A, Hasan M (1985) Turbulence suppression in free turbulent shear flows under controlled excitation. Part 2. Jet-noise reduction. J Fluid Mech 150:159–168
Jordan P, Colonius T (2013) Wave packets and turbulent jet noise. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 45:173–195
Kastner J, Samimy M (2002) Development and characterization of Hartmann tube fluidic actuators for high-speed flow control. AIAA J 40(10):1926–1934
Kibens V (1980) Discrete noise spectrum generated by acoustically excited jet. AIAA J 18(4):434–441
Krothapalli A, Venkatakrishnan L, Lourenco L, Greska B, Elavarasan R (2003) Turbulence and noise suppression of a high-speed jet by water injection. J Fluid Mech 491:131–159
Kuo CW, Morris P, McLaughlin DK (2012) Noise reduction in supersonic jets by nozzle fluidic inserts. In: 18th AIAA/CEAS aeroacoustics conference (33rd AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference), American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics
Laurendeau E, Bonnet JP, Jordan P, Delville J et al (2006) Impact of fluidic chevrons on the turbulence structure of a subsonic jet. AIAA Pap 3510:2006
Lou H (2005) Control of supersonic impinging jets using microjets. PhD dissertation, Florida State University, ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 3183086
Michalke A (1977) Instability of a compressible circular free jet with consideration of the influence of the jet boundary layer thickness. NASA-TM-75190
Michalke A (1984) Survey on jet instability theory. Prog Aerosp Sci 21:159–199
Mollo-Christensen E (1963) Measurements of near field pressure of subsonic jets. Tech. rep, DTIC Document
Mollo-Christensen E (1967) Jet noise and shear flow instability seen from an experimenters viewpoint. J Appl Mech 34(1):1–7
Moore C (1977) The role of shear-layer instability waves in jet exhaust noise. J Fluid Mech 80(02):321–367
Morris PJ (2009) A note on noise generation by large scale turbulent structures in subsonic and supersonic jets. Int J Aeroacoust 8(4):301–315
Phalnikar K, Kumar R, Alvi F (2008) Experiments on free and impinging supersonic microjets. Exp Fluids 44(5):819–830
Powell A (1988) The sound-producing oscillations of round underexpanded jets impinging on normal plates. J Acoust Soc Am 83(2):515–533
Powell A (2010) On Prandtl’s formulas for supersonic jet cell length. Int J Aeroacoust 9(1):207–236
Raman G, Srinivasan K (2009) The powered resonance tube: from Hartmann’s discovery to current active flow control applications. Prog Aerosp Sci 45(4):97–123
Raman G, Khanafseh S, Cain A, Kerschen E (2004) Development of high bandwidth powered resonance tube actuators with feedback control. J Sound Vib 269(3):1031–1062
Reba R, Narayanan S, Colonius T (2010) Wave-packet models for large-scale mixing noise. Int J Aeroacoust 9(4–5):533–558
Samimy M, Kim JH, Kastner J, Adamovich I, Utkin Y (2007) Active control of a mach 0.9 jet for noise mitigation using plasma actuators. AIAA J 45(4):890–901
Samimy M, Kim JH, Kearney-Fischer M, Sinha A (2010) Acoustic and flow fields of an excited high Reynolds number axisymmetric supersonic jet. J Fluid Mech 656:507–529
Solomon JT (2010) High-bandwidth unsteady microactuators for active control of high-speed flows. Florida State University
Solomon JT, Foster C, Alvi FS (2012) Design and characterization of high-bandwidth, resonance enhanced pulsed microactuators: a parametric study. AIAA J 51(2):386–396
Tam CK (1998) Jet noise: since 1952. Theoret Comput Fluid Dyn 10(1–4):393–405
Tam CK, Viswanathan K, Ahuja K, Panda J (2008) The sources of jet noise: experimental evidence. J Fluid Mech 615:253–292
Upadhyay P, Valentich G, Alvi FS (2016) Flow and acoustic features of a mach 0.9 jet using high frequency excitation. In: 54th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, p 0527
Uzun A, Hussaini MY (2011) Prediction of noise generated by a round nozzle jet flow using computational aeroacoustics. J Comput Acoust 19(03):291–316
Uzun A, Foster CH, Solomon JT, Oates WS, Hussaini MY, Alvi FS (2011) Simulations of pulsed actuators for high-speed flow control. In: Proceedings of the 17th AIAA/CEAS aeroacoustics conference, Portland, Oregon
Viswanathan K (2002) Analysis of the two similarity components of turbulent mixing noise. AIAA J 40(9):1735–1744
Vlasov E, Ginevskii A, Karavosov R, Makarenko T (1999) Turbulence suppression in subsonic jets by high-frequency acoustic excitation. Fluid Dyn 34(1):23–28
Volpe JA, Settles GS (2006) Laser-induced gas breakdown as a light source for schlieren and shadowgraph particle image velocimetry. Opt Eng 45(8):080509–080509
Wiley AS (2010) Effects of unsteady actuation on resonance-dominated impinging jets. Florida State University
Worden TJ, Upadhyay P, Gustavsson JP, Alvi FS (2014) Studies on microjet control effectiveness in high-temperature supersonic impinging jets. AIAA J 52(8):1757–1769
Zaman K (1985) Far-field noise of a subsonic jet under controlled excitation. J Fluid Mech 152:83–111
Zaman K, Hussain A (1981) Turbulence suppression in free shear flows by controlled excitation. J Fluid Mech 103:133–159
Zhuang N, Alvi FS, Alkislar MB, Shih C (2006) Supersonic cavity flows and their control. AIAA J 44(9):2118–2128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Upadhyay, P., Gustavsson, J.P.R. & Alvi, F.S. Development and characterization of high-frequency resonance-enhanced microjet actuators for control of high-speed jets. Exp Fluids 57, 88 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-016-2164-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-016-2164-2