Abstract
Purpose
Results of a retrospective single-institution study recently suggested improved prognostic outcomes in patients undergoing photodynamic diagnosis (PDD)-assisted transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) prior to radical cystectomy (RC). We sought to validate the prognostic influence of PDD-assisted TURBT on survival after RC by relying on a multi-institutional dataset.
Methods
To provide a homogeneous study population, patients with organ metastasis at the time of RC and/or after neoadjuvant chemotherapy were excluded from analysis, which resulted in overall 549 bladder cancer (BC) patients from 18 centers of the Prospective Multicenter Radical Cystectomy Series 2011 (PROMETRICS 2011). To evaluate the influence of PDD conducted during primary or final TURBT on cancer-specific mortality (CSM) and overall mortality (OM) after RC, bootstrap-corrected multivariate Cox proportional-hazards regression models were applied (median follow-up: 25 months; IQR: 19–30). Sensitivity analyses were performed for both patients with pure urothelial carcinoma and patients undergoing one single TURBT only.
Results
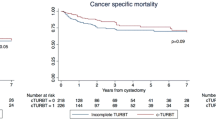
In 88 (16.0 %) and 100 (18.2 %) patients, PDD was used in primary and final TURBTs, respectively. In 335 (61.0 %) patients, a single TURBT was performed prior to RC; in 194 patients (35.3 %), TURBT had been performed in a different center. CSM and OM rates at 3 years were 32 and 40 %, respectively. Use of PDD during primary or final TURBT was no independent predictor of CSM or OM. These results were internally valid and were confirmed in sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions
PDD utilization during TURBT prior to RC does not independently impact the prognosis of BC patients after RC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Witjes JA, Comperat E, Cowan NC, De Santis M, Gakis G, Lebret T et al (2014) EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2013 guidelines. Eur Urol 65:778–792
Babjuk M, Burger M, Zigeuner R, Shariat SF, van Rhijn BW, Comperat E et al (2013) EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2013. Eur Urol 64:639–653
Simone G, Bianchi M, Giannarelli D, Daneshmand S, Papalia R, Ferriero M et al (2015) Development and external validation of nomograms predicting disease-free and cancer-specific survival after radical cystectomy. World J Urol 33:1419–1428
Abdi H, Pourmalek F, Gleave ME, So AI, Black PC (2016) Balancing risk and benefit of extended pelvic lymph node dissection in patients undergoing radical cystectomy. World J Urol 34:41–48
Gakis G, Ngamsri T, Rausch S, Mischinger J, Todenhofer T, Schwentner C et al (2015) Fluorescence-guided bladder tumour resection: impact on survival after radical cystectomy. World J Urol 33:1429–1437
May M, Bastian PJ, Burger M, Bolenz C, Trojan L, Herrmann E et al (2011) Multicenter evaluation of the prognostic value of pT0 stage after radical cystectomy due to urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. BJU Int 108:E278–E283
Faba OR, Palou J, Breda A, Villavicencio H (2012) High-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: update for a better identification and treatment. World J Urol 30:833–840
Authors’ contributions
Matthias May was involved in project development, data analysis and drafting of the manuscript; Hans-Martin Fritsche was involved in project development, data collection and manuscript editing; Malte W. Vetterlein critically revised the manuscript; Patrick J. Bastian was involved in manuscript editing and supervision; Michael Gierth collected the data and edited the manuscript; Philipp Nuhn collected the data and edited the manuscript; Atiqullah Aziz was involved in project development, data collection and manuscript editing; Margit Fisch collected the data and edited the manuscript; Christian G. Stief was involved in data collection and manuscript editing; Markus Hohenfellner collected the data and edited the manuscript; Manfred P. Wirth was involved in data collection and manuscript editing; Vladimir Novotny collected the data and edited the manuscript; Oliver W. Hakenberg was involved in data collection and manuscript editing; Joachim Noldus collected the data and edited the manuscript; Christian Gilfrich edited the manuscript; Christian Bolenz was involved in data collection and manuscript editing; Maximilian Burger was involved in project development, data collection and manuscript editing; Sabine Brookman-May was involved in project development and critical revision of the manuscript; Collaborators were involved in acquisition of data; MS manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We confirm that there are no competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the local ethics board, and all subjects provided written informed consent.
Additional information
Matthias May and Hans-Martin Fritsche have contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
May, M., Fritsche, HM., Vetterlein, M.W. et al. Impact of photodynamic diagnosis-assisted transurethral resection of bladder tumors on the prognostic outcome after radical cystectomy: results from PROMETRICS 2011. World J Urol 35, 245–250 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-016-1877-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-016-1877-4