Abstract
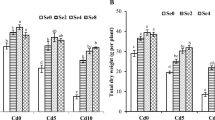
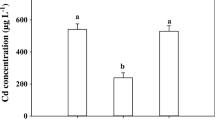
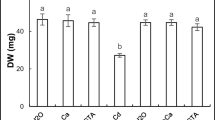
Anthropogenic activities lead to plant exposure to increasing concentrations of heavy metals, including cadmium (Cd). In this regard, alleviation of Cd stress by selenium (Se) addition to pea seeds germination medium was assessed. Different concentrations of Se (0, 5, and 15 µM) were combined with CdCl2 (0 or 300 µM). The addition of Se reversed the detrimental effects of Cd on seedling growth in terms of biomass production. Seedling exposure to Cd stress induced the loss of membrane integrity, as manifested by the increased lipoperoxidation byproduct (malondialdehyde) content and the lipoxygenase activity. The enrichment of germination medium with Se reduced Cd accumulation in the plant tissues (more than 40% in radicles and epicotyls) and counteracted the Cd effects on membrane integrity traits. The Se protective effects on cell membrane were associated with proline over-accumulation in Cd-exposed radicles and epicotyls (32% and 28% increase, respectively). The Se-induced proline accumulation could be a consequence of its increased biosynthesis via Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase upregulation, concomitantly with a decrease of its oxidation by the proline dehydrogenase enzyme. Besides, when supplied in combination with Cd, the highest Se concentration abolished the Cd-triggered decrease of glyoxalase I and glyoxalase II activities, leading to the reduction of methylglyoxal levels. The amelioration of the cellular redox state under the combination of Cd with Se was reflected by the reduction of hydrogen peroxide accumulation. This positive impact was mediated by the stimulation of the Cd-downregulated superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase activities and the reduction of the Cd-stimulated catalase. Overall, the current findings suggest that the enrichment of the seeds germination medium with Se appeared as a suitable option to ameliorate pea seedling tolerance to Cd stress. The present study could be extended to crops grown on the soil to confirm the protecting role of Se against heavy metal pollution.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods in Enzymology. Academic Press, Elseiver, pp 121–126
Ahn SJ, Rengel Z, Matsumoto H (2004) Aluminum-induced plasma membrane surface potential and H+-ATPase activity in near-isogenic wheat lines differing in tolerance to aluminum. New Phytol 162:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01009.x
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren M-X et al (2022) Melatonin mitigates cadmium toxicity by promoting root architecture and mineral homeostasis of tomato genotypes. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:1112–1128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00720-9
Alves LR, Rodrigues dos Reis A, Prado ER et al (2019) New insights into cadmium stressful-conditions: role of ethylene on selenium-mediated antioxidant enzymes. Ecotox Environ Safe 186:109747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109747
Alves LR, Prado ER, de Oliveira R et al (2020) Mechanisms of cadmium-stress avoidance by selenium in tomato plants. Ecotoxicology 29:594–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02208-1
Alyemeni MN, Ahanger MA, Wijaya L et al (2018) Selenium mitigates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants by modulating chlorophyll fluorescence, osmolyte accumulation, and antioxidant system. Protoplasma 255:459–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1162-4
Ardestani MM, van Gestel CAM (2013) Using a toxicokinetics approach to explain the effect of soil pH on cadmium bioavailability to Folsomia candida. Environ Pollut 180:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.05.024
Aslam M, Sulaman M, Saeed S, Shahid S, Shoukat S, Sajjad M, Adnan M, Iqbal M, Sharif MT (2017) Specific role of proline against heavy metals toxicity in plants. Int J Pure Appl Biosci 5(6):27–34. https://doi.org/10.18782/2320-70516032
Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2019) Role of selenium in plants against abiotic stresses: phenological and molecular aspects. In: Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (eds) Molecular plant abiotic stress: biology and biotechnology. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 123–133
Bates LS, Waldren SP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Ben Massoud M, Kharbech O, Sakouhi L et al (2021) Calcium and citrate protect Pisum sativum roots against copper toxicity by regulating the cellular redox status. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00652-4
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chauhan R, Awasthi S, Tripathi P et al (2017) Selenite modulates the level of phenolics and nutrient element to alleviate the toxicity of arsenite in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 138:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.015
Clemens S (2006) Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 88:1707–1719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2006.07.003
Cui J, Liu T, Li Y, Li F (2018) Selenium reduces cadmium uptake into rice suspension cells by regulating the expression of lignin synthesis and cadmium-related genes. Sci Total Environ 644:602–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.002
DalCorso G, Farinati S, Maistri S, Furini A (2008) How plants cope with cadmium: staking all on metabolism and gene expression. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1268–1280. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00737.x
Ding Y, Feng R, Wang R et al (2014) A dual effect of Se on Cd toxicity: evidence from plant growth, root morphology and responses of the antioxidative systems of paddy rice. Plant Soil 375:289–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1966-8
Djanaguiraman M, Devi DD, Shanker AK et al (2005) Selenium—an antioxidative protectant in soybean during senescence. Plant Soil 272:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-4039-1
Dong X, Chang Y, Zheng R et al (2021) Phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated soil: impacts on morphological traits, proline content and stomata parameters of sweet sorghum seedlings. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106:528–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03125-7
Dziubinska H, Filek M, Krol E, Trebacz K (2010) Cadmium and selenium modulate slow vacuolar channels in rape (Brassica napus) vacuoles. J Plant Physiol 167:1566–1570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.06.016
El Rasafi T, Oukarroum A, Haddioui A et al (2020) Cadmium stress in plants: a critical review of the effects, mechanisms, and tolerance strategies. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 52:675–726. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1835435
Feng R, Wang L, Yang J et al (2021) Underlying mechanisms responsible for restriction of uptake and translocation of heavy metals (metalloids) by selenium via root application in plants. J Hazard Mater 402:123570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123570
Fielding JL, Hall JL (1978) A biochemical and cytochemical study of peroxidase activity in roots of Pisum sativum II: distribution of enzymes in relation to root development. J Exp Bot 29:983–991. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/29.4.983
Filek M, Zembala M, Hartikainen H et al (2009) Changes in wheat plastid membrane properties induced by cadmium and selenium in presence/absence of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 96:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-008-9455-0
Godt J, Scheidig F, Grosse-Siestrup et al (2006) The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. J Occup Med Toxicol 1:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6673-1-22
Gratão PL, Monteiro CC, Tezotto T et al (2015) Cadmium stress antioxidant responses and root-to-shoot communication in grafted tomato plants. Biometals 28:803–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-015-9867-3
Gzyl-Malcher B, Filek M, Brezesinski G (2009) Influence of cadmium and selenate on the interactions between hormones and phospholipids. Langmuir 25:13071–13076. https://doi.org/10.1021/la901653y
Haider FU, Liqun C, Coulter JA et al (2021) Cadmium toxicity in plants: impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotox Environ Safe 211:111887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111887
Handa N, Kohli SK, Kaur R et al (2018) Role of compatible solutes in enhancing antioxidative defense in plants exposed to metal toxicity. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Fujita M (eds) Plants Under Metal and Metalloid Stress: Responses, Tolerance and Remediation. Springer, Singapore, pp 207–228
Handa N, Kohli SK, Sharma A et al (2019) Selenium modulates dynamics of antioxidative defence expression, photosynthetic attributes and secondary metabolites to mitigate chromium toxicity in Brassica juncea L. plants. Environ Exp Bot 161:180–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.11.009
Hasanuzzaman M, Hossain MA, Fujita M (2012) Exogenous selenium pretreatment protects rapeseed seedlings from cadmium-induced oxidative stress by upregulating antioxidant defense and methylglyoxal detoxification systems. Biol Trace Elem Res 149:248–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9419-4
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan MHMB, Raza A et al (2020) Selenium in plants: boon or bane? Environ Exp Bot 178:104170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104170
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hong Z, Lakkineni K, Zhang Z, Verma DPS (2000) Removal of feedback inhibition of δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase results in increased proline accumulation and protection of plants from osmotic stress. Plant Physiol 122:1129–1136. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.4.1129
Hoque TS, Hossain MA, Mostofa MG, Burritt DJ, Fujita M, Tran LSP (2016) Methylglyoxal: an emerging signaling molecule in plant abiotic stress responses and tolerance. Front Plant Sci 7:1341. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01341
Huang Q, Xu Y, Liu Y et al (2018) Selenium application alters soil cadmium bioavailability and reduces its accumulation in rice grown in Cd-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:31175–31182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3068-x
Huang H, Li M, Rizwan M et al (2021) Synergistic effect of silicon and selenium on the alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice plants. J Hazard Mater 401:123393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123393
Kaur C, Singla-Pareek SL, Sopory SK (2014) Glyoxalase and methylglyoxal as biomarkers for plant stress tolerance. Crit Rev Plant Sci 33:429–456. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2014.904147
Kaya C, Ashraf M, Alyemeni MN et al (2020) Salicylic acid-induced nitric oxide enhances arsenic toxicity tolerance in maize plants by upregulating the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and glyoxalase system. J Hazar Materials 399:123020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123020
Khan MIR, Nazir F, Mohd A et al (2015) Selenium and sulfur influence ethylene formation and alleviate cadmium-induced oxidative stress by improving proline and glutathione production in wheat. J Plant Physiol 173:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2014.09.011
Kharbech O, Ben Massoud M, Chaoui A, Mur LAJ, Djebali W (2020a) Exogenous nitric oxide confers tolerance to Cr (VI) in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings by modulating endogenous oxido-nitrosative events. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10411-5
Kharbech O, Sakouhi L, Ben Massoud M et al (2020b) Nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide protect plasma membrane integrity and mitigate chromium-induced methylglyoxal toxicity in maize seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 157:244–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.10.017
Kharbech O, Sakouhi L, Mahjoubi Y et al (2022) Nitric oxide donor, sodium nitroprusside modulates hydrogen sulfide metabolism and cysteine homeostasis to aid the alleviation of chromium toxicity in maize seedlings (Zea mays L.). J Hazar Mat 424:127302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127302
Lanza MGDB, dos Reis AR (2021) Roles of selenium in mineral plant nutrition: ROS scavenging responses against abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 164:27–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.04.026
Li HF, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2008) Selenium uptake, translocation and speciation in wheat supplied with selenate or selenite. New Phytol 178(1):92–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02343.x
Lin L, Zhou W, Dai H et al (2012) Selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. J Hazard Mater 235–236:343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.08.012
Liu W, Shang S, Feng X et al (2015) Modulation of exogenous selenium in cadmium-induced changes in antioxidative metabolism, cadmium uptake, and photosynthetic performance in the 2 tobacco genotypes differing in cadmium tolerance. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2760
Luo Y, Wei Y, Sun S et al (2019) Selenium modulates the level of auxin to alleviate the toxicity of cadmium in tobacco. Inter J Mol Sci 20:3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153772
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)45228-9
Mostofa MG, Seraj ZI, Fujita M (2014) Exogenous sodium nitroprusside and glutathione alleviate copper toxicity by reducing copper uptake and oxidative damage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Protoplasma 251(6):1373–1386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0639-7
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a076232
Rady MM, Belal HEE, Gadallah FM, Semida WM (2020) Selenium application in two methods promotes drought tolerance in Solanum lycopersicum plant by inducing the antioxidant defense system. Sci Hortic 266:109290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109290
Rahoui S, Chaoui A, Ben C et al (2015) Effect of cadmium pollution on mobilization of embryo reserves in seedlings of six contrasted Medicago truncatula lines. Phytochemistry 111:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.12.002
Repkina N, Talanova V, Ignatenko A, Titov A (2019) Involvement of proline and non-protein thiols in response to low temperature and cadmium stresses in wheat. Biol Plant 63:70–77. https://doi.org/10.32615/bp.2019.009
Rigby H, Smith SR (2020) The significance of cadmium entering the human food chain via livestock ingestion from the agricultural use of biosolids, with special reference to the UK. Environ Int 143:105844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105844
Saed-Moucheshi A, Shekoofa A, Pessarakli M (2014) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and detoxifying in plants. J Plant Nutr 37:1573–1585. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2013.868483
Sakouhi L, Rahoui S, Ben Massoud M et al (2016) Calcium and EGTA alleviate cadmium toxicity in germinating chickpea seeds. J Plant Growth Regul 35:1064–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9605-2
Sakouhi L, Rahoui S, Gharsallah C et al (2018) Effects of calcium and EGTA on thiol homeostasis and defense-related enzymes in Cd-exposed chickpea roots. Acta Physiol Plant 40:20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2596-1
Sakouhi L, Kharbech O, Massoud MB et al (2021) Calcium and ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid mitigate toxicity and alteration of gene expression associated with cadmium stress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) shoots. Protoplasma 258(4):849–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-020-01605-x
Sakouhi L, Kharbech O, Ben Massoud M et al (2022a) Oxalic acid mitigates cadmium toxicity in Cicer arietinum L. germinating seeds by maintaining the cellular redox homeostasis. J Plant Growth Regul 35:1064–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10334-1
Sakouhi L, Kharbech O, Ben Massoud M et al (2022b) Exogenous oxalic acid protects germinating chickpea seeds against cadmium injury. J Soil Sci Plant Nutri 2:647–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00675-x
Schiavon M, Pittarello M, Pilon-Smits EAH, Wirtz M, Hell R, Malagoli M (2012) Selenate and molybdate alter sulfate transport and assimilation in Brassica juncea L. Czern.: implications for phytoremediation. Environ Exp Bot 75:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2011.08.016
Seppänen M, Turakainen M, Hartikainen H (2003) Selenium effects on oxidative stress in potato. Plant Sci 165:311–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(03)00085-2
Seregin IV, Ivanov VB (2001) Physiological aspects of cadmium and lead toxic effects on higher plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 48:523–544. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016719901147
Sergiev I, Alexieva V, Karanov E (1997) Effect of spermine, atrazine and combination between them on some endogenous protective systems and stress markers in plants. Comt Rend Acad Bulg Sci 51:121–124
Shakeri E, Mozafari AA, Sohrabi F, Saed-Moucheshi A (2019) Role of proline and other osmoregulatory compounds in plant responses to abiotic stresses. In: Pessarakli M (ed) Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Shen H, He LF, Sasaki T et al (2005) Citrate secretion coupled with the modulation of soybean root tip under aluminum stress. up-regulation of transcription, translation, and threonine-oriented phosphorylation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Plant Physiol 138:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.058065
Sieprawska A, Filek M, Kornaś A (2015) Involvement of selenium in protective mechanisms of plants under environmental stress conditions. Acta Biol Crac Bot 57:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1515/abcsb-2015-0014
Singh M, Pratap Singh V, Dubey G, Mohan Prasad S (2015) Exogenous proline application ameliorates toxic effects of arsenate in Solanum melongena L. seedlings. Ecotox Environ Safe 117:164–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.03.021
Thiruvengadam M, Chung IM (2015) Selenium, putrescine, and cadmium influence health-promoting phytochemicals and molecular-level effects on turnip (Brassica rapa ssp. rapa). Food Chem 173:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.012
Trippe RC, Pilon-Smits EAH (2020) Selenium transport and metabolism in plants: phytoremediation and biofortification implications. J Hasard Mater 404:124178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124178
Wild R, Ooi L, Srikanth V, Münch G (2012) A quick, convenient and economical method for the reliable determination of methylglyoxal in millimolar concentrations: the N-acetyl-L-cysteine assay. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:2577–2581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6086-4
Wu Z, Yin X, Bañuelos GS et al (2016) Indications of selenium protection against cadmium and lead toxicity in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Front Plant Sci 7:1875. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01875
Zhang ZW, Dong YY, Feng LY et al (2020) Selenium enhances cadmium accumulation capability in two mustard family species—Brassica napus and B. juncea. Plants 9:904. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070904
Zhao Y, Hu C, Wang X et al (2019) Selenium alleviated chromium stress in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis) by regulating root morphology and metal element uptake. Ecotox Environ Safe 173:314–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.090
Zhou J, Zhang C, Du B et al (2021) Soil and foliar applications of silicon and selenium effects on cadmium accumulation and plant growth by modulation of antioxidant system and Cd translocation: comparison of soft vs durum wheat varieties. J Hazard Mater 402:123546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123546
Zhu YG, Pilon-Smits EAH, Zhao FJ et al (2009) Selenium in higher plants: understanding mechanisms for biofortification and phytoremediation. Trends Plant Sci 14:436–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.06.006
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Tunisian Ministry of High Education and Scientific Research (LR18ES38).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LS Experiments, Writing-Original draft, Software; YM, AL, Experiments; OK Writing, Statistical Analysis; AC Funding acquisition; WD Conceptualization, Supervision. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Vijay Pratap Singh.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sakouhi, L., Mahjoubi, Y., Labben, A. et al. Effects of Cadmium–Selenium Interaction on Glyoxalase and Antioxidant Systems of Pisum sativum Germinating Seeds. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 3084–3099 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10772-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10772-5