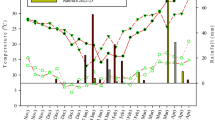
Abstract
Currently, the government of Ethiopia is supplying fertilizers containing N, P, S, Zn & B. However, many researchers argued that N and P are the only yield-limiting nutrients. The current study was conducted to identify yield-limiting nutrients for tef and to assess the inherent nutrient supplying status of Vertisols. The experiments were carried out during the 2020/2021cropping season under screen house, on-station, and on-farm conditions at Yilmana Densa district of Amhara region, Ethiopia. Tef (Quncho variety) was used as a test crop. This trial contained ten treatments including: control, PKSZnB, NKSZnB, NPSZnB, NPKZnB, NPKSB, NPKSZn, NPKSZnB, NP, and NPS. Each pot with a height of 0.185 m and volume of 0.186 m3 was filled with 5 kg of soil which was taken from 0 to 20 cm depth by auger. The pot trial was laid out in a completely randomized design (CRD), while the field trials were laid out in a completely randomized block design (RCBD) with three replications. The gross plot area was 7.5 m2 for field experiments. Yield-limiting nutrients were identified through a nutrient omission trial. The data were analyzed using SAS version 9.0, and significant treatment means were separated by using LSD at P ≤ 0.05. The nutrient contents of the soils determined from the composite samples collected before planting indicated that TN (0.126% on-station and 0.125% on-farm) was low. The Av.P (3.89 mg kg−1on-station and 4.24 mg kg−1 on-farm) content of the soil was also very low. The result revealed that omission of N and P highly significantly (P < 0.01) reduced grain yield, straw yield, and yield components of tef in all experiments. The results were affected by inadequate supply of N and P nutrients. However, the absence of potassium, sulfur, zinc, and boron did not show significant (P < 0.05) yield reduction. The lowest grain and biomass yields (2.2 and 7.9 g/pot under greenhouse), (177.2 and 533.3 kg ha−1 on-station), and (24.9 and 533.3 kg ha−1 on-farm), respectively, were recorded from omission of N. The low yield of tef mainly caused by poor soil fertility. As a result of N and P omissions, grain yield decreased by 81.6% and 80.7% on-station, by 96.5% and 85.2% on-farm, and by 58.0% and 54.2% in the pot experiment, respectively. In addition, omission of P also resulted in significant grain and biomass yields (2.4 and 8.1 g/pot under screenhouse), (191.1 and 1066.7 kg ha−1 on-station), and (106.4 and 533.3 kg ha−1 on-farm), respectively. Application of K, S, Zn, and B did not have any effect on tef yield over the applied NP. The uptake of N, P, K, S, Zn, and B by tef grain and straw was low in N and P nutrient omissions. Based on these results, N and P were identified as the most yield-limiting nutrients. Application of NP is better than K, S, Zn, and B containing fertilizers for tef production.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abebe A, Abera G, Beyene S (2020) Sorption characteristics, growth, and yield response of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to the application of essential nutrients on Nitisol and Vertisol of central highland of Ethiopia. Afr J Plant Sci 14(3):108–120. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJPS2019.1873
Abera Y, Kassa S (2017) Status of soil micronutrients in Ethiopian soils: a review. J Environ Earth Sci 7(4):85–90
Abera Y, Kebede M (2013) Assessment of status of some micronutrients in Vertisols of the central highlands of Ethiopia. Int Res J Agric Sci Soil Sci 3(5):169–173
Abewa A, Adgo E, Alemayehu G, Yitaferu B, Solomon JKQ, Assefa K, Payne W (2020) Genotypes and their growing environments influence on physicochemical qualities of tef grain in the highlands of Ethiopia. Ethiopian J Agric Sci 30(4):1–27. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9060283
Amare T, Bazie Z, Alemu E, Wubet A, Agumas B, Muche M, Fentie D (2018) Crop responses to balanced nutrients in northwestern Ethiopia. Blue Nile J Agric Res 1(1):1–14
Asefa F, Debela A, Mohammed M (2014) Evaluation of tef [Eragrostistef (Zuccagni) Trotter] responses to different rates of NPK along with Zn and B in Didessa District, southwestern Ethiopia. World Appl Sci J 32(11):2245–2249. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2014.32.11.14562
Assefa A, Liban M, Taddese T and Marye A (2006) Determination of optimum rates of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization for tef (Eragrostis tef) production in different agro-ecological areas of northwestern Ethiopia. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 1st annual regional conference on completed crop research activities, Bahirdar
Baissa T, Suwanarit A, Osotsapar Y, Sarobol ED (2003) Status of Mn and Fe in agricultural soils of western Ethiopia: laboratory assessment. Kasetsart J Nat Sci 37(3):296–306
Baye K (2014) Teff nutrient composition and health benefits (Vol. 67): Intl Food Policy Res Inst
Berhe T, Girmay G, Kidanemariam A (2020) Validation of blended NPSB fertilizer rates on yield, yield components of teff [Eragrostis tef (Zuccagni) Trotter] at Vertisols of Hatsebo, Central Tigray, Ethiopia. J Soil Sci Environ Manage 11(2):75–86. https://doi.org/10.5897/JSSEM2019.0795
Bremmer JM and Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen total. Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. Madison WI: Soil science society of America
CSA (2020) The federal democratic republic of Ethiopia central statistical agency agricultural sample survey (Vol. 1). Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Dash A, Singh H, Mahakud T, Pradhan K, Jena D (2015) Interaction effect of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium with sulphur, boron and zinc on yield and nutrient uptake by rice under rice-rice cropping system in inceptisol of coastal Odisha. Int Res J Agric Sci Soil Sci 5:14–21
Demiss M, Mamo T, Beyene S, Kidanu S (2020) Effect of potassium levels on teff (Eragrostis tef (Zucc.) Trotter) growth and yield in central highland Vertisols of Ethiopia. Eurasian J Soil Sci 9(2):105–118. https://doi.org/10.18393/ejss.663486
Dereje G, Alemu D, Adisu T, Anbessa B (2018) Response of yield and yield components of tef [Eragrostis tef (Zucc.) Trotter] to optimum rates of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer rate application in Assosa Zone, Benishangul Gumuz Region. Ethiopian J Agric Sci 28(1):81–94
EMSA (Ethiopia Metrological Service Agency) (2020) Records of weather data from 2010 to 2020 in Northwest Branch. Bahir Dar, Ethiopia
Esayas A, Tafesse D and Ali A (2006) Soils of Adet Agricultural Research Center and its testing sites. National soil research center (NSRC) Soil survey and land evaluation section: Soil survey internal report
Estefan G, Sommer R, Ryan J (2013) Methods of soil, plant, and water analysis. A manual for the west Asia and north Africa region, 3rd edn. International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas, Beirut, pp 65–119
Hailu H, Mamo T, Keskinen R, Karltun E, Gebrekidan H, Bekele T (2015) Soil fertility status and wheat nutrient content in Vertisol cropping systems of central highlands of Ethiopia. Agric Food Secur 4(1):19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40066-015-0038-0
Horneck DA, Sullivan DM, Owen JS and Hart JM (2011) Soil test interpretation guide
Ketema S (1997) Tef [Eragrostis Tef (Zucc.)] (Vol. 12): Bioversity International
Kolawole GO, Eniola O, Oyeyiola YB (2018) Effects of nutrients omission on maize growth and nutrient uptake in three dominant soil types of southwestern Nigeria. J Plant Nutr 41(15):1903–1915. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2018.1482909
Kumar B, Sharma GK, Mishra VN, Chandrakar T, Pradhan A, Singh DP, Thakur AK (2018) Assessment of yield limiting nutrients through response of rice (Oryza sativa L.) to nutrient omission in Inceptisols of Bastar District of Chhattisgarh State in India. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 7(08):3972–3980. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.708.410
Kumar B, Sharma GK, Mishra VN, Chandrakar T, Kumar T (2020) Crop response based assessment of Ssoil fertility through nutrient omission technique in Alfisol of Bastar District of Chhattisgarh State in India. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 9(8):40–50. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2020.908.005
Landon JR (1991) Booker tropical soil manual: a handbook for soil survey and agricultural land evaluation in the tropics and subtropics. Wiley, New York
Metson AJ (1961) Methods of chemical analysis for soil survey samples, soil bureau bulletin 12. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Zealand
Mirutse F, Haile M, Kebede F, Tsegay A, Yamoah C (2009) Response of tef [Eragrostis tef (Trotter)] to phosphorus and nitrogen on vertisol at North Ethiopia. J Drylands 2(1):8–14
MoANR and ATA (2016) Soil fertility status and fertilizer recommendation Atlas of Amhara National Regional State. Ethiopian Soil Information System (EthioSIS). In Shiferaw HTH, Mamo T (Ed.), (Vol. 1). Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Murphy HF (1968) A report on the fertility status and other data on some soils of Ethiopia
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1983) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis: part 2 chemical and microbiological properties. Agronomy Mongraphs, Madison, pp 539–579
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. Agronomy Mongraphs, Madison, pp 403–430
Olsen SR (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate: US Department of Agriculture
Pandey M, Kumar M (2017) Effect of sulfur, manganese, and zinc on yield, quality, and uptake of nutrients by wheat (Triticum aestivum). Ann Plant Soil Res 19(4):403–407
Rawal N, Khatri N, GCChaurasiya CBBP (2018) Determination of indigenous nutrient supplying capacity of soil through omission plot experiment for wheat in western Terai of Nepal. J Inst Agric Animal Sci 35(1):79–87. https://doi.org/10.3126/jiaas.v35i1.22517
Schneider K and Anderson L (2010) Yield gap and productivity potential in Ethiopian agriculture: staple grains and pulses. EPAR brief, 98
Sertsu S and Bekele T (2000) Procedures for soil and plant analysis. Ethiopian Agricultural Research Organization, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Singh V (2016) Productivity, nutrient uptake, and economics of wheat as affected by nutrient omissions in alluvial soil. Ann Plant Soil Res 18(3):219–225
Singh V (2018) Breaking yield barrier in wheat (Triticum aestivum) through site-specific nutrient management. Ann Plant Soil Res 20(1):12–15
Tadese T (1991) Soil, plant, water, fertilizer, animal manure, and compost analysis. Working document No. 13. International Livestock Research Center for Africa, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Tariku S, Fantahun A, Fentahu A (2018) Participatory evaluation and selection of improved tef varieties in a researcher managed trial in western Ethiopia. Int J Emerging Technol Adv Eng 8(5):28–42
Tesfaye Y, Teshome G, Asefa K (2019) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers rate on yield and yield components of tef at Adola District, Guji Zone, in southern Ethiopia. Am J Agric Res. https://doi.org/10.28933/AJAR-2019-03-0705
Wilson M, Sasal MC, Caviglia OP (2013) Critical bulk density for a Mollisol and a Vertisol using least limiting water range. Effect on early wheat growth. Geoderma 192:354–361
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Adet Agricultural Research Center and Amhara Agricultural Research Institute (ARARI) for providing financial support and study grant, Debere Birhan Agricultural Research Center for facilitating laboratory analysis and Bahir Dar University College of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BA Performed conceptualization, conducted the experiment, data collection, formal analysis, writing and original draft preparation. EA did supervision, formal analysis, editing and reviewing. TA assisted in writing, performed conceptualization, supervision, formal analysis, editing and reviewing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Mikihisa Umehara.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alemayehu, B., Adgo, E. & Amare, T. Nutrients Limiting Tef [Eragrostis tef (Zucc.) Trotter] Crop Yield on Vertisols in Yilmana Densa, Upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 2736–2748 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10741-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10741-y