Abstract
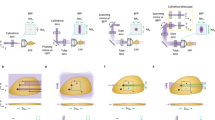
The optical system is designed here, to miniaturize the mechanical scanning and number of phase patterns illumination in lensless microscopy. The random phase mask is positioned in vertical column before the sample, which encoded the sample information and resulted into a final image at the sensor plane. To improve the signal to noise ratio and resolution of final image, the axial direction scanning of sample and sensor (SS) is performed while keeping them mutually immovable. This operation gathered the lost information of sample in between the sample and sensor planes. This axial motion of SS is performed with periodic steps, which would help in the reconstruction process during post processing. The final image has resolution of about 4 µm and field of view of 15 mm2. There are numerous advantages of such type of techniques, including portability and fast processing of data.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Goodman, Introduction to fourier optics (McGraw-Hill, 1968)
X. Zhang, I. Khimji, U.A. Gurkan, U.A.H. Safaee, P.N. Catalano et al., Lab Chip 11, 2535–2540 (2011)
G. Jin, I.-H. Yoo, S.P. Pack, J.-W. Yang, U.-H. Ha et al., Biosens. Bioelectron. 38, 126–131 (2012)
L.M. Lee, X. Cui, C. Yang, Biomed. Microdevices 11, 5 (2009)
A.F. Coskun, T.-W. Su and A. Ozcan: Lab Chip, 10(2010)
B. Khademhosseinieh, G. Biener, I. Sencan, A. Ozcan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 21 (2010)
I. Sencan, A.F. Coskun, U. Sikora, A. Ozcan, Sci. Rep. 4, 3760 (2014)
T.-W. Su, S.O. Isikman, W. Bishara, D. Tseng, A. Erlinger, A. Ozcan, Opt. Exp. 18, 9 (2010)
W. Luo, A. Greenbaum, Y. Zhang, A. Ozcan, Light Sci. Appl. 4, e261 (2015)
W. Bishara, T.-W. Su, A.F. Coskun, A. Ozcan, Opt. Exp 18, 11 (2010)
G. Zheng, S.A. Lee, S. Yang, C. Yan, Lab Chip 10, 22 (2010)
S. Bernet, W. Harm, A. Jesacher, M. Ritsch-Marte: Opt. Exp. 19, 25 (2011)
W. Harm, C. Roider, A. Jesacher, S. Bernet, and M. Ritsch-Marte: Opt. Exp. 22, 18 (2014)
A. Hussain, Y. Li, D. Liu, C. Kuang, X. Liu, Sci. Rep 7, 14768 (2017)
A. Hussain, Y. Li, D. Liu, C. Kuang, X. Liu, J. Biomed. Opt. 22, 11 (2017)
W. Luo, Y. Zhang, Z. Göröcs, A. Feizi, A. Ozcan, Sci. Rep 6, 22738 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFF0101400); National Natural Science Foundation of China (6171101129, 61427818, 61827825, and 61735017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, A., Li, Y., Liu, D. et al. Axial scanning in lensless microscopy to achieve high resolution. Appl. Phys. B 125, 43 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-019-7146-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-019-7146-7