Abstract
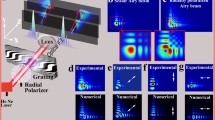
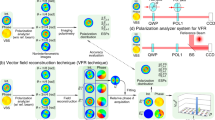
We investigate the focusing property and the polarization evolution characteristics of hybridly polarized vector fields in the focal region. Three types of hybridly polarized vector fields, namely azimuthal-variant hybridly polarized vector field, radial-variant hybridly polarized vector field, and spatial-variant hybridly polarized vector field, are experimentally generated. The intensity distributions and the polarization evolution of these hybridly polarized vector fields focused under low numerical aperture (NA) are experimentally studied and good agreements with the numerical simulations are obtained. The three-dimensional (3D) state of polarization and the field distribution within the focal volume of these hybridly polarized vector fields under high-NA focusing are studied numerically. The optical curl force on Rayleigh particles induced by tightly focused hybridly polarized vector fields, which results in the orbital motion of trapped particles, is analyzed. Simulation results demonstrate that polarization-only modulation provided by the hybridly polarized vector field allows one to control both the intensity distribution and 3D elliptical polarization in the focal region, which may find interesting applications in particle trapping, manipulation, and orientation analysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. Zhan, Trapping metallic Rayleigh particles with radial polarization. Opt. Express 12, 3377–3382 (2004)
C. Hnatovsky, V. Shvedov, W. Krolikowski, A. Rode, Revealing local field structure of focused ultrafast pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 123901 (2011)
G. Bautista, M.J. Huttunen, J. Mäkitalo, J.M. Kontio, J. Simonen, M. Kauranen, Second-harmonic generation imaging of metal nano-objects with cylindrical vector beams. Nano Lett. 12, 3207–3212 (2012)
S.M. Li, Y. Li, X.L. Wang, L.J. Kong, K. Lou, C. Tu, Y. Tian, H.T. Wang, Taming the collapse of optical fields. Sci. Rep. 2, 1007 (2012)
J.T. Barreiro, T.C. Wei, P.G. Kwiat, Remote preparation of single-photon “hybrid” entangled and vector-polarization states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 030407 (2010)
L. Novotny, M.R. Beversluis, K.S. Youngworth, T.G. Brown, Longitudinal field modes probed by single molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5251–5254 (2001)
K.G. Lee, H.W. Kihm, J.E. Kihm, W.J. Choi, H. Kim, C. Ropers, D.J. Park, Y.C. Yoon, S.B. Choi, D.H. Woo, J. Kim, B. Lee, Q.H. Park, C. Lienau, D.S. Kim, Vector field microscopic imaging of light. Nat. Photon. 1, 53–56 (2007)
X. Li, T.H. Lan, C.H. Tien, M. Gu, Three-dimensional orientation-unlimited polarization encryption by a single optically configured vectorial beam. Nat. Commun. 3, 998 (2012)
K.S. Youngworth, T.G. Brown, Focusing of high numerical aperture cylindrical-vector beams. Opt. Express 7, 77–87 (2000)
Q.W. Zhan, Cylindrical vector beams: from mathematical concepts to applications. Adv. Opt. Photon. 1, 1–57 (2009)
B. Gu, J.L. Wu, Y. Pan, Y. Cui, Controllable vector bottle-shaped fields generated by focused spatial-variant linearly polarized vector beams. Appl. Phys. B 113, 165–170 (2013)
J. Arlt, M.J. Padgett, Generation of a beam with a dark focus surrounded by regions of higher intensity: the optical bottle beam. Opt. Lett. 25, 191–193 (2000)
Y. Kozawa, S. Sato, Focusing property of a double-ring-shaped radially polarized beam. Opt. Lett. 31, 820–822 (2006)
X.L. Wang, J. Ding, J.Q. Qin, J. Chen, Y.X. Fan, H.T. Wang, Configurable three-dimensional optical cage generated from cylindrical vector beams. Opt. Commun. 282, 3421–3425 (2009)
Y. Zhao, Q. Zhan, Y. Zhang, Y.P. Li, Creation of a three-dimensional optical chain for controllable particle delivery. Opt. Lett. 30, 848–850 (2005)
H.F. Wang, L.P. Shi, B. Lukyanchuk, C. Sheppard, C.T. Chong, Creation of a needle of longitudinally polarized light in vacuum using binary optics. Nat. Photon. 2, 501–505 (2008)
K. Hu, Z. Chen, J. Pu, Generation of super-length optical needle by focusing hybridly polarized vector beams through a dielectric interface. Opt. Lett. 37, 3303–3305 (2012)
B. Gu, J.L. Wu, Y. Pan, Y. Cui, Achievement of needle-like focus by engineering radial-variant vector fields. Opt. Express 21, 30444–30452 (2013)
B. Gu, Y. Pan, J.L. Wu, Y. Cui, Manipulation of radial-variant polarization for creating tunable bifocusing spots. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 31, 253–257 (2014)
G.M. Lerman, L. Stern, U. Levy, Generation and tight focusing of hybridly polarized vector beams. Opt. Express 18, 27650–27657 (2010)
X.L. Wang, Y.N. Li, J. Chen, C.S. Guo, J.P. Ding, H.T. Wang, A new type of vector fields with hybrid states of polarization. Opt. Express 18, 10786–10795 (2010)
W. Han, W. Cheng, Q. Zhan, Flattop focusing with full Poincare beams under low numerical aperture illumination. Opt. Lett. 36, 1605–1607 (2011)
X.L. Wang, J. Chen, Y.N. Li, J.P. Ding, C.S. Guo, H.T. Wang, Optical orbital angular momentum from the curl of polarization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 253602 (2010)
L.G. Wang, Optical forces on submicron particles induced by full Poincaré beams. Opt. Express 20, 20814–20826 (2012)
K. Hu, Z. Chen, J. Pu, Tight focusing properties of hybridly polarized vector beams. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 29, 1099–1104 (2012)
H. Hu, P. Xiao, The tight focusing properties of spatial hybrid polarization vector beam. Optik 124, 2406–2410 (2013)
X.L. Wang, J.P. Ding, W.J. Ni, C.S. Guo, H.T. Wang, Generation of arbitrary vector beams with a spatial light modulator and a common path interferometric arrangement. Opt. Lett. 32, 3549–3551 (2007)
B. Richards, E. Wolf, Electromagnetic diffraction in optical systems II. Structure of the image field in an aplanatic system. Proc. R. Soc. A 253, 358–379 (1959)
M. Rashid, O.M. Maragò, P.H. Jones, Focusing of high order cylindrical vector beams. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 11, 065204 (2009)
H. Chen, Z. Zheng, B.F. Zhang, J. Ding, H.T. Wang, Polarization structuring of focused field through polarization-only modulation of incident beam. Opt. Lett. 35, 2825–2827 (2010)
A.F. Abouraddy, K.C. Toussaint Jr, Three-dimensional polarization control in microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 153901 (2006)
W. Chen, Q. Zhan, Diffraction limited focusing with controllable arbitrary three-dimensional polarzation. J. Opt. 12, 045707 (2010)
A. Ashkin, J.M. Dziedzic, J.E. Bjorkholm, S. Chu, Observation of a single-beam gradient force optical trap for dielectric particles. Opt. Lett. 11, 288–290 (1986)
Z. Liu, D. Zhao, Optical trapping Rayleigh dielectric spheres with focused anomalous hollow beams. Appl. Opt. 52, 1310–1316 (2013)
S. Albaladejo, M.I. Marqués, M. Laroche, J.J. Sáenz, Scattering forces from the curl of the spin angular momentum of a light field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 113602 (2009)
B.T. Draine, The discrete-dipole approximation and its application to interstellar graphite grains. Astrophys. J. 333, 848–872 (1988)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant: 11174160) and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-10-0503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, B., Pan, Y., Rui, G. et al. Polarization evolution characteristics of focused hybridly polarized vector fields. Appl. Phys. B 117, 915–926 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-014-5909-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-014-5909-8