Abstract
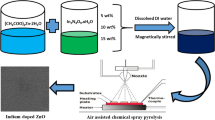
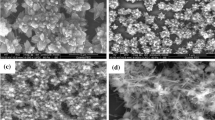
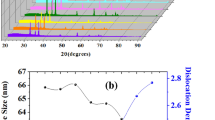
In the present study, we report the synthesis of undoped and Cr-doped ZnO thin films via spray pyrolysis for ammonia gas detection. The importance of work lies in addressing the need for ultrasensitive and selective gas sensors, particularly for ammonia detection, owing to their significance in various industrial and environmental applications. The utilization of Cr-doped ZnO thin films offers a promising approach, given their unique properties and potential for enhanced sensing performance. The prepared Cr-doped ZnO thin films exhibit remarkable response, selectivity, sensitivity and long-term stability towards 50 ppm of ammonia gas at room temperature. Also, 4% Cr-doped ZnO films show fast response (14 s) and recovery time (38 s). These findings emphasize the practical relevance and potential impact of Cr-doped ZnO thin films as efficient gas sensing materials.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data code and availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
W. de Vries, Impacts of nitrogen emissions on ecosystems and human health: a mini review. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Heal. 21, 100249 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2021.100249
I. Manisalidis, E. Stavropoulou, A. Stavropoulos, E. Bezirtzoglou, Environmental and health impacts of air pollution: a review. Front. Public Heal. 8, 14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/FPUBH.2020.00014
V. Kumar, D.R. Roy, Single-layer stanane as potential gas sensor for NO2, SO2, CO2 and NH3 under DFT investigation. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 110, 100–106 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2019.02.001
H. Rahman, M. Bråtveit, B.E. Moen, Exposure to ammonia and acute respiratory effects in a urea fertilizer factory. Int. J. Occup. Environ. HealthOccup. Environ. Health 13, 153–159 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1179/OEH.2007.13.2.153
Z. Li, J. Yi, Drastically enhanced ammonia sensing of Pt/ZnO ordered porous ultra-thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 317, 128217 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2020.128217
W. Liu, Y.Y. Liu, J.S. Do, J. Li, Highly sensitive room temperature ammonia gas sensor based on Ir-doped Pt porous ceramic electrodes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 390, 929–935 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.08.121
K.E. Wyer, D.B. Kelleghan, V. Blanes-Vidal, G. Schauberger, T.P. Curran, Ammonia emissions from agriculture and their contribution to fine particulate matter: a review of implications for human health. J. Environ. Manage. 323, 116285 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2022.116285
S. Büyükköse, Highly selective and sensitive WO3 nanoflakes based ammonia sensor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process.Semicond. Process. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.104969
Y. Kang, F. Yu, L. Zhang, W. Wang, L. Chen, Y. Li, Review of ZnO-based nanomaterials in gas sensors. Solid State Ionics 360, 115544 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2020.115544
H. Fu, Q. Wang, J. Ding, Y. Zhu, M. Zhang, C. Yang, S. Wang, Fe2O3 nanotube coating micro-fiber interferometer for ammonia detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 303, 127186 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127186
N.X. Thai, N. Van Duy, N. Van Toan, C.M. Hung, N. Van Hieu, N.D. Hoa, Effective monitoring and classification of hydrogen and ammonia gases with a bilayer Pt/SnO2 thin film sensor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 45, 2418–2428 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.11.072
G. Chaloeipote, R. Prathumwan, K. Subannajui, A. Wisitsoraat, C. Wongchoosuk, 3D printed CuO semiconducting gas sensor for ammonia detection at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 123, 105546 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105546
M.M. Gomaa, G. RezaYazdi, M. Rodner, G. Greczynski, M. Boshta, M.B.S. Osman, V. Khranovskyy, J. Eriksson, R. Yakimova, Exploring NiO nanosize structures for ammonia sensing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 11870–11877 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9287-6
V.L. Patil, S.A. Vanalakar, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Fabrication of nanostructured ZnO thin films based NO2 gas sensor via SILAR technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 239, 1185–1193 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.130
Y. Wang, X. NingMeng, J. Liang Cao, Rapid detection of low concentration CO using Pt-loaded ZnO nanosheets. J. Hazard. Mater. 381, 120944 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120944
F. Gong, L. Peng, Y. Zhang, Y. Cao, D. Jia, F. Li, Selectively sensing H2S and acetone through tailoring the facets exposed on the surfaces of ZnO supercrystals. Mater. Lett. 218, 106–109 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.01.116
L. Zhu, W. Zeng, H. Ye, Y. Li, Volatile organic compound sensing based on coral rock-like ZnO. Mater. Res. Bull. 100, 259–264 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.12.043
J. Ding, S. Chen, N. Han, Y. Shi, P. Hu, H. Li, J. Wang, Aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition of nanostructured ZnO thin films for NO2 and ethanol monitoring. Ceram. Int. 46, 15152–15158 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.051
B. Altun, I. KaradumanEr, A.O. Çağırtekin, A. Ajjaq, F. Sarf, S. Acar, Effect of Cd dopant on structural, optical and CO2 gas sensing properties of ZnO thin film sensors fabricated by chemical bath deposition method. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 127, 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04843-9
D. Mendil, F. Challali, T. Touam, A. Chelouche, A.H. Souici, S. Ouhenia, D. Djouadi, Influence of growth time and substrate type on the microstructure and luminescence properties of ZnO thin films deposited by RF sputtering. J. Lumin. 215, 116631 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.116631
Y.H. Navale, S.R. Patil, I.A. Dhole, D.K. Bandgar, Y.M. Jadhav, P.S. Kulkarni, V.B. Patil, Prominent NO2 gas sensor based on ZnO nanowires grown by thermal evaporation. AIP Conf. Proc. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5047709
M. Rabeel, S. Javed, R. Khan, M.A. Akram, S. Rehman, D.K. Kim, M.F. Khan, Controlling the wettability of ZnO thin films by spray pyrolysis for photocatalytic applications. Materials (Basel) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093364
R.R. Kumar, M.R. Habib, A. Khan, P.C. Chen, T. Murugesan, S. Gupta, A. Kumar Anbalagan, N.H. Tai, C.H. Lee, H.N. Lin, Sulfur monovacancies in liquid-exfoliated MoS2 nanosheets for NO2 gas sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4, 9459–9470 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSANM.1C01929/SUPPL_FILE/AN1C01929_SI_001.PDF
P. Nakarungsee, S. Srirattanapibul, C. Issro, I.M. Tang, S. Thongmee, High performance Cr doped ZnO by UV for NH3 gas sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 314, 112230 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.112230
M.M. Hassan, W. Khan, P. Mishra, S.S. Islam, A.H. Naqvi, Enhancement of the alcohol gas sensitivity in Cr doped ZnO gas sensor. Mater. Res. Bull. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.05.019
A. Khan, C. Jacob, Random and self-aligned growth of 3C-SiC nanorods via VLS–VS mechanism on the same silicon substrate. Mater. Lett. 135, 103–106 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATLET.2014.07.129
L. Zhu, Y. Li, W. Zeng, Enhnaced ethanol sensing and mechanism of Cr-doped ZnO nanorods: Experimental and computational study. Ceram. Int. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.003
G. Madhaiyan, T.W. Tung, H.W. Zan, H.F. Meng, C.J. Lu, A. Ansari, W.T. Chuang, H.C. Lin, UV-enhanced room-temperature ultrasensitive NO gas sensor with vertical channel nano-porous organic diodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 320, 128392 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2020.128392
I.Y. Habib, A.A. Tajuddin, H.A. Noor, C.M. Lim, A.H. Mahadi, N.T.R.N. Kumara, Enhanced Carbon monoxide-sensing properties of Chromium-doped ZnO nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45313-w
A. Khan, J. Cong, R. Ranjan Kumar, S. Ahmed, D. Yang, X. Yu, Chemical vapor deposition of graphene on self-limited SiC interfacial layers formed on silicon substrates for heterojunction devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 5, 17544–17555 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c03006
Z. Zang, Efficiency enhancement of ZnO/Cu2O solar cells with well oriented and micrometer grain sized Cu2O films, Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5017002.
C. Li, Z. Zang, C. Han, Z. Hu, X. Tang, J. Du, Y. Leng, K. Sun, Enhanced random lasing emission from highly compact CsPbBr 3 perovskite thin films decorated by ZnO nanoparticles. Nano Energy 40, 195–202 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.08.013
H. Wang, S. Cao, B. Yang, H. Li, M. Wang, X. Hu, K. Sun, Z. Zang, NH4Cl-modified ZnO for high-performance CsPbIBr 2 perovskite solar cells via low-temperature process. Sol. RRL. 4, 1–8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/solr.201900363
W. Cai, H. Li, Z. Zang, One-volt, solution-processed InZnO thin-film transistors. IEEE Electron Device Lett.Lett. 42, 525–528 (2021)
H. Wang, P. Zhang, Z. Zang, High performance CsPbBr 3 quantum dots photodetectors by using zinc oxide nanorods arrays as an electron-transport layer. Appl. Phys. Lett.Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0005464
N.M. Moussa, F.M. Ebrahim, K. Adly, M.Y. Hassaan, Chromium doped ZnO nanoparticles for energy storage, gas and humidity sensing and spin based electronic devices applications. Opt. Quantum Electron. 54, 1–20 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04075-y
M. Chinnasamy, K. Balasubramanian, Enhanced UV photodetection behavior of Cr doped wurtzite ZnO crystalline nanorods. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 110, 110492 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110492
J.K. Rajput, T.K. Pathak, V. Kumar, L.P. Purohit, Influence of sol concentration on CdO nanostructure with gas sensing application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 409, 8–16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.019
A. JansiSanthosam, K. Ravichandran, T. Ahamad, Donated free electrons induced enhancement in the NH3 sensing ability of ZnO thin films—effect of terbium loading. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 316, 112376 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.112376
L.H. Kathwate, G. Umadevi, P.M. Kulal, P. Nagaraju, D.P. Dubal, A.K. Nanjundan, V.D. Mote, Ammonia gas sensing properties of Al doped ZnO thin films. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 313, 112193 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.112193
A. Manivasaham, K. Ravichandran, K. Subha, Light intensity effects on the sensitivity of ZnO: Cr gas sensor. Surf. Eng. 33, 866–876 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/02670844.2017.1331724
M. Iqbal, A. Ali, W. Bux, M. Tayyab, A. Hussain, I. Shah, Facile synthesis of Cr doped hierarchical ZnO nano-structures for enhanced photovoltaic performance. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 116, 107902 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2020.107902
U.T. Nakate, P. Patil, B. Ghule, Y.T. Nakate, S. Ekar, R.C. Ambare, R.S. Mane, Room temperature LPG sensing properties using spray pyrolysis deposited nano-crystalline CdO thin films. Surfaces and Interfaces. 17, 100339 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SURFIN.2019.100339
A. Mirzaei, J.H. Lee, S.M. Majhi, M. Weber, M. Bechelany, H.W. Kim, S.S. Kim, Resistive gas sensors based on metal-oxide nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5118805
K.J. Shailja, R.C. Singh, Singh, Enhanced toluene sensing performance of nanostructured aluminium-doped nickel oxide gas sensor. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 129, 1–14 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/S00339-023-06473-9/METRICS
R. Aydın, A. Akkaya, O. Kahveci, B. Şahin, Nanostructured CuO thin-film-based conductometric sensors for real-time tracking of sweat loss. ACS Omega 8, 20009–20019 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.3c02232
Y. Zhang, C. Wang, L. Zhao, F. Liu, X. Sun, X. Hu, G. Lu, Microwave-assisted synthesis of La/ZnO hollow spheres for trace-level H2S detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 334, 129514 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129514
A.P. Rambu, L. Ursu, N. Iftimie, V. Nica, M. Dobromir, F. Iacomi, Study on Ni-doped ZnO films as gas sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 280, 598–604 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.05.033
H. Bian, S. Ma, A. Sun, X. Xu, G. Yang, S. Yan, J. Gao, Z. Zhang, H. Zhu, Improvement of acetone gas sensing performance of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 658, 629–635 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.217
R. Naji, F. Rahman, K.M. Batoo, Effect of grain size and grain boundary defects on electrical and magnetic properties of Cr doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 1065–1066, 199–204 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.02.056
A. Koo, R. Yoo, S.P. Woo, H.S. Lee, W. Lee, Enhanced acetone-sensing properties of pt-decorated al-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 280, 109–119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.049
X.L. Xu, Y. Chen, S.Y. Ma, W.Q. Li, Y.Z. Mao, Excellent acetone sensor of La-doped ZnO nanofibers with unique bead-like structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 213, 222–233 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2015.02.073
G.H. Zhang, X.Y. Deng, P.Y. Wang, X.L. Wang, Y. Chen, H.L. Ma, D.J. Gengzang, Morphology controlled syntheses of Cr doped ZnO single-crystal nanorods for acetone gas sensor 2 Theta (degree ). Mater. Lett.Lett. 165, 83–86 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.11.112
C. Belkhaoui, N. Mzabi, H. Smaoui, P. Daniel, Enhancing the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO nanopowders through (Al + Mn) doping. Results Phys. 12, 1686–1696 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.01.085
M. Shaheera, K.G. Girija, M. Kaur, V. Geetha, A.K. Debnath, R.K. Vatsa, K.P. Muthe, S.C. Gadkari, Characterization and device application of indium doped ZnO homojunction prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 101, 109723 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.109723
N. Üzar, Investigation of detailed physical properties and solar cell performances of various type rare earth elements doped ZnO thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 10471–10479 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10854-018-9111-3/TABLES/5
A. Renitta, K. Vijayalakshmi, Highly sensitive hydrogen safety sensor based on Cr incorporated ZnO nano-whiskers array fabricated on ITO substrate. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 237, 912–923 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.07.017
M.M.A. Ahmed, W.Z. Tawfik, M.A.K. Elfayoumi, M. Abdel-Hafiez, S.I. El-Dek, Tailoring the optical and physical properties of La doped ZnO nanostructured thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 791, 586–592 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.03.340
A. Maache, A. Chergui, D. Djouadi, B. Benhaoua, A. Chelouche, M. Boudissa, Effect of La doping on ZnO thin films physical properties: correlation between strain and morphology. Optik (Stuttg). 180, 1018–1026 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.11.002
R. Ghomri, M.N. Shaikh, M.I. Ahmed, M. Bououdina, M. Ghers, (Al, Er) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles for photodegradation of rhodamine blue. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 122, 1–9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0417-9
M.A. Moiz, A. Mumtaz, M. Salman, S.W. Husain, A.H. Baluch, M. Ramzan, Band gap Engineering of ZnO via transition metal Doping: an ab initio study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 781, 138979 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138979
A. Marikutsa, M. Rumyantseva, E.A. Konstantinova, A. Gaskov, The key role of active sites in the development of selective metal oxide sensor materials. Sensors. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072554
J. Wang, S. Fan, Y. Xia, C. Yang, S. Komarneni, Room-temperature gas sensors based on ZnO nanorod/Au hybrids: visible-light-modulated dual selectivity to NO2 and NH3. J. Hazard. Mater. 381, 120919 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120919
R.S. Ganesh, M. Navaneethan, V.L. Patil, S. Ponnusamy, C. Muthamizhchelvan, S. Kawasaki, P.S. Patil, Y. Hayakawa, Sensitivity enhancement of ammonia gas sensor based on Ag/ZnO flower and nanoellipsoids at low temperature. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.015
B. Himabindu, N.S.M.P. Latha Devi, P. Nagaraju, B. RajiniKanth, A nanostructured Al-doped ZnO as an ultra-sensitive room-temperature ammonia gas sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 1–18 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10337-6
F. Sarf, I. KaradumanEr, E. Yakar, S. Acar, The role of rare-earth metal (Y, Ru and Cs)-doped ZnO thin films in NH3 gas sensing performances at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 10084–10095 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03554-w
G.K. Mani, J.B.B. Rayappan, A highly selective and wide range ammonia sensor—nanostructured ZnO: Co thin film. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 191, 41–50 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2014.10.007
K. Ravichandran, A.J. Santhosam, M. Sridharan, Effect of tungsten doping on the ammonia vapour sensing ability of ZnO thin films prepared by a cost effective simplified spray technique. Surf. Interfaces 18, 100412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2019.100412
G.H. Mhlongo, D.E. Motaung, F.R. Cummings, H.C. Swart, S.S. Ray, A highly responsive NH 3 sensor based on Pd-loaded ZnO nanoparticles prepared via a chemical precipitation approach. Sci. Rep. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46247-z
K.D. Arun Kumar, S. Valanarasu, J.S. Ponraj, B.J. Fernandes, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, P. Murahari, K. Ramesh, Effect of Er doping on the ammonia sensing properties of ZnO thin films prepared by a nebulizer spray technique. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 144, 109513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109513
H. Song, L. Ma, S. Pei, C. Dong, E. Zhu, B. Zhang, Quantitative detection of formaldehyde and ammonia using a yttrium-doped ZnO sensor array combined with a back-propagation neural network model. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 331, 112940 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNA.2021.112940
K.R. Devi, G. Selvan, M. Karunakaran, I.L.P. Raj, A.F.A. El-Rehim, H.Y. Zahran, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, Enhanced room temperature ammonia gas sensing properties of Al-doped ZnO nanostructured thin films. Opt. Quantum Electron. 52, 1–19 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02621-0
S. Kanaparthi, S.S. Govind, Highly sensitive and ultra-fast responsive ammonia gas sensor based on 2D ZnO nanoflakes. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 3, 91–96 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2019.10.010
K. Kasirajan, L. Bruno Chandrasekar, S. Maheswari, M. Karunakaran, P. ShunmugaSundaram, A comparative study of different rare-earth (Gd, Nd, and Sm) metals doped ZnO thin films and its room temperature ammonia gas sensor activity: Synthesis, characterization, and investigation on the impact of dopant. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 121, 111554 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OPTMAT.2021.111554
A.J. Kulandaisamy, J.R. Reddy, P. Srinivasan, K.J. Babu, G.K. Mani, P. Shankar, J.B.B. Rayappan, Room temperature ammonia sensing properties of ZnO thin films grown by spray pyrolysis: Effect of Mg doping. J. Alloys Compd. 688, 422–429 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.050
V. Adimule, M.G. Revaigh, H.J. Adarsha, Synthesis and fabrication of Y-doped ZnO nanoparticles and their application as a gas sensor for the detection of ammonia. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020(29), 4586–4596 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11665-020-04979-4
Acknowledgements
VSC is thankful to the Department of Science and Technology for women Scientist-A project (WoS-A-PM-18/2021). JLG is thankful to the Science and Technology Research Board, a statutory body of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, for awarding the Ramanujan Fellowship (SB/S2/RJN-090/2017) and CORE research grant (CRG/2019/006059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VSC: Methodology, data curation, formal analysis, writing original draft. MBK: formal analysis. SVT: software. JLG: supervision, review and editing. PMK: conceptualization, supervision, writing-review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chandak, V.S., Kumbhar, M.B., Talekar, S.V. et al. Ultrasensitive and selective Cr-doped ZnO thin films synthesized via spray pyrolysis technique for detection of ammonia gas. Appl. Phys. A 130, 285 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07425-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07425-7