Abstract
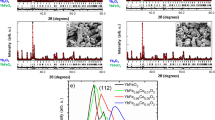
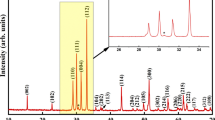
The solid-state reaction technique was employed to synthesize compounds of YMnO3 (YMO) and YMn1-xCoxO3 (YMCO) with various Co doping levels (x = 0.01, 0.10, 0.20, and 0.40), where Co atoms partially substituted Mn sites. XRD studies confirmed the presence of two phases, YMO and Y0.98CoO3 (YCO), for doping ratios above x = 0.10. Additionally, an increase in crystalline size was observed with cobalt substitution. Surface characteristics of synthesized pellets were examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), revealing a less porous structure with cobalt doping. XPS analysis elucidated valence states, showing the presence of both Mn3+ and Mn4+, as well as Co2+ and Co3+. The x = 0.20 and 0.40 Co-doped samples exhibited lower grain and grain boundary energies compared to other samples, such as a decrease from 0.556 eV (undoped) to 0.195 eV (x = 0.20). Moreover, the dielectric constants of x = 0.20 and 0.40 cobalt-doped samples (around 320) significantly surpassed the undoped sample (around 22) at 106 Hz and 100 °C. The x = 0.20 cobalt-doped sample demonstrated the highest conductivity at 100 °C and 106 Hz (31 × 10–4 S/cm). FT-IR analysis provided insights into vibration and bending modes, and frequency- and temperature-dependent electrical features were investigated. It was observed that a single conduction model is insufficient to fully explain the conduction mechanism in these samples.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
R. Von Helmolt, B. Holzapfel, L. Schulz, K. Samwer, Phys. Rev. 71, 2331 (1993)
K. Chahara, T. Ohno, M. Kasai, Y. Kozono, Appl. Phys. Lett. 63, 1993 (1990)
S. Jin, T. H. Tiefel, M.Mc. Cormack, R. A. Fastnachat, R. Ramesh, L. H. Chen, Chem. Sci. 264, 413, (1994)
P. Murugavel, P. Padhan, W. Prellier, Enhanced magnetoresistance in ferromagnetic Pr0.85Ca0.15MnO3∕ferroelectricPr0.85Ca0.15MnO3∕ferroelectricBa0.6Sr0.4TiO3Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 superlattice films, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 4992–4994 (2004)
T. Lottermoser, T. Lonkai, U. Amann, D. Hohlwein, J. Ihringer, M. Fiebig, Magnetic phase control by an electric field. Nature 430, 541–544 (2004)
H. Zheng, J. Wang, S.E. Lofland, Z. Ma, L. Mohaddes-Ardabili, T. Zhao, L. Salamanca-Riba, S.R. Shinde, S.B. Ogale, F. Bai, D. Viehland, Y. Jia, D.G. Schlom, M. Wuttig, A. Roytburd, R. Ramesh, Multiferroic BaTiO3-CoFe2O4 nanostructures. Science 303, 661 (2004)
N.A. Spaldin, M. Fiebig, The renaissance of magnetoelectric multiferroics. Science 309, 391–392 (2005)
M.P. Singh, W. Prellier, C. Simon, B. Raveau, Magnetocapacitance effect in perovskite-superlattice based multiferroics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 022505–022513 (2005)
S.X. Dong, J.Y. Zhai, N.G. Wang, F.M. Bai, J.F. Li, D. Vieland, T.A. Lograsso, Fe–Ga/Pb(Mg1∕3Nb2∕3)O3–PbTiO3Fe–Ga∕Pb(Mg1∕3Nb2∕3)O3–PbTiO3 magnetoelectric laminate composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 222504–222513 (2005)
N.G. Wang, J. Cheng, A. Pyatakov, A.K. Zvezdin, J.F. Li, L.E. Cross, D. Vieland, Multiferroic properties of modified BiFeO3−PbTiO3-based ceramics: random-field induced release of latent magnetization and polarization. Phys. Rev. B 72, 104434–104435 (2005)
C.W. Nan, G. Liu, Y.H. Lin, H.D. Chen, Magnetic-field-induced electric polarization in multiferroic nanostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 197203 (2005)
J. Slutsker, I. Levin, J.H. Li, A. Artemev, A.L. Royburd, Effect of elastic interactions on the self-assembly of multiferroic nanostructures in epitaxial films. Phys. Rev. B 73, 184127 (2006)
T. Wu, M.A. Zurbuchen, S. Saha, R.V. Wang, S.K. Streiffer, J.F. Mitchell, Observation of magnetoelectric effect in epitaxial ferroelectric film/manganite crystal heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 73, 134416 (2006)
Y. Yamasaki, S. Miyasaka, Y. Kaneko, J.P. He, T. Arima, Y. Tokura, Magnetic reversal of the ferroelectric polarization in a multiferroic spinel oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 249902 (2006)
X. Qi, J. Dho, R. Tomov, M.G. Blamire, J.L. MacManus-Driscoll, Greatly reduced leakage current and conduction mechanism in aliovalent-ion-doped BiFeO3, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 062903(1)–062903(3), (2005)
R. K. Thakur, R. Thakur, S. Samatham, N. Kaurav, V. Ganesan, and N. K. Gaur. Dielectric, magnetic, and thermodynamic properties of Y1¡xSrxMnO3 (x = 0.1 and 0.2). J. Appl. Phys., 112, 104115, (2012)
H. Satoh, J.-I. Iwasaki, K. Kawase, N. Kamegashira, High temperature enthalpies and heat capacities of YbMnO3 and YMnO3. J. Alloys Compd. 268, 42–46 (1998)
J.A. Alonso, M.J. Martínez-Lope, M.T. Casais, M.T. Fernández-Díaz, Evolution of the Jahn-Teller distortion of MnO6 octahedra in RMnO3 perovskites (R = Pr, Nd, Dy, Tb, Ho, Er, Y): a neutron diffraction study. Inorg. Chem. 39, 917–923 (2000)
J.A. Alonso, M.J. Martínez-Lope, M.T. Casa, M.T. Ferna, Evolution of the magnetic structure of hexagonal HoMnO3 from neutron powder diffraction data. Chem. Mater. 13, 1497–1505 (2001)
K. Uusi-Esko, M. Karppinen, Extensive series of hexagonal and orthorhombic RMnO3 (R = Y, La, Sm, Tb, Yb, Lu) thin films by atomic layer deposition. Chem. Mater. 23, 1835–1840 (2011)
D. Gutiérrez, O. Peña, P. Durán, C. Moure, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 22 (2002), p. 567 [11] O. Peña, M. Bahout, D. Gutierrez, J. F. Fernandez, P. Duran, C. Moure, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 61, 2019 (2000)
C. Moure, D. Gutierrez, O. Pena, P. Duran, Structural characterization of YMexMn1−xO3 (Me=Cu, Ni, Co) perovskites. J. Solid State Chem. 163, 377–384 (2002)
S.L. Samal, W. Green, S.E. Lofland, K.V. Ramanujachary, D. Das, A.K. Ganguli, Study on the solid solution of YMn1−xFexO3: Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties. J. Solid State Chem. 181, 61–66 (2008)
L. P. Yang, A. M. Zhang, K. Wang, X. S. Wu, and Z. Y. Zhai, The magnetic transition temperature tuned by strain in YMn0.9Ru0.1O3 thin films, AIP Adv. 8(5), 055805 (2017)
J. Y. Cui1, A. M. Zhang, J. Y. Shi, H. F. Cao, X. S. Wu, Y. M. Zhang, Competition of magnetic ordering and spin-phonon coupling in multiferroic hexagonal YMn1−xCrxO3. J. Appl. Phys. 126,114103 (2019)
T. Asaka, K. Nemoto, K. Kimoto, T. Arima, Y. Matsui, Crystallographic superstructure of Ti-doped hexagonal YMnO3. Phys. Rev. B 71, 014114 (2005)
K. Asokan, Y.S. Chen, C.W. Pao, H.M. Tsai, C.W.O. Lee, C.H. Lin, Effect of Co, Ni, and Cu substitution on the electronic structure of hexagonal YMnO3 studied by x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 131901 (2009)
O. Polat, M. Coskun, F.M. Coskun, Z. Durmus, Y. Caglar, M. Caglar, A. Turut, Tailoring the band gap of ferroelectric YMnO3 through tuning the Os doping level. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 3443 (2019)
O. Polat, M. Coskun, F.M. Coskun, Z. Durmus, M. Caglar, A. Turut, Os doped YMnO3 multiferroic: a study investigating the electrical properties through tuning the doping level. J. Alloy. Compd. 752, 274–288 (2018)
F. Wan, X. Bai, Y. Wang, Z. Hao, L. Gao, J. Li, N.S. Perov, C. Cao, Effect of Zr-doping on the structure and magnetic properties of YMnO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 926 (2023)
J. Shukla, P. Saxena, P. Joshi et al., Impact of aliovalent ions doping on structural and electrical characteristics of YMnO3 ceramic. Appl. Phys. A 129, 731 (2023)
P.K. Sharma, M. Pramanik, M.V. Limaye, S.B. Singh, J. Phys. Chem. C 127(33), 16259–16266 (2023)
B. Munisha, B. Mishra, J. Nanda, N.K. Sahoo, D. Ghosh, K.J. Sankaran et al., Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol using polyacrylamide assisted Ce-doped YMnO3 nanoparticles. J. Rare Earths 41(10), 1541 (2023)
D. Gutiérrez, O. Peña, K. Ghanimi, P. Durán, C. Moure. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 63, 1975–1982 (2002)
I.G. Ismailzade, S.A. Kizhaev, Determination of the Curie point in ferroelectric YMnO3 and YbMnO3. Sov. Phys. Solid State 7, 236–238 (1965)
G.A. Smolnskii, I.E. Chupis, Ferroelectromagnets. Sov. Phys. Usp. 25, 475–493 (1982)
A. Munoz, J.A. Alonso, M.J. Martinez-Lope, M.T. Casais, J.L. Martinez, M.T. Fernandez-Diaz, Magnetic structure of hexagonal RMnO3 (R=Y, Sc): thermal evolution from neutron powder diffraction data. Phys. Rev. B 62, 9498–9510 (2000)
G. Catalan, J.F. Scott, Physics and applications of bismuth ferrite. Adv. Mater. 21, 2463–2485 (2009)
T. Kimura, S. Kawamoto, I. Yamada, M. Azuma, M. Takano, Y. Tokura, Magnetocapacitance effect in multiferroic BiMnO3. Phys. Rev. B 67, 180401(R) (2003)
K.F. Wang, J.M. Liu, Z.F. Ren, Multiferroicity: the coupling between magnetic and polarization orders. Adv. Phys. 58, 321–448 (2009)
F. Wan, L. Li, X. Bai et al., Structure and dielectric relaxation behaviors of Co-doped YMnO3 multiferroic ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 17361–17371 (2022)
O. Polat, M. Coskun, Y. Yildirim, P. Roupcova, D. Sobola, C. Sen, Z. Durmus, M. Caglar, A. Turut, Variation in the dielectric and magnetic characteristics of multiferroic LuFeO3 as a result of cobalt substitution at Fe sites. J. Alloy. Compd. 963, 170939 (2023)
M. Coskun, O. Polat, F.M. Coskun, Z. Durmus, M. Caglar, A. Turut, The influence of cobalt (Co) doping on the electrical and dielectric properties of LaCr1-xCoxO3 perovskite-oxide compounds. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 109, 104923 (2020)
O. Polat, M. Caglar, F.M. Coskun, M. Coskun, Y. Caglar, A. Turut, An experimental investigation: the impact of cobalt doping on optical properties of YbFeO3-ẟ thin film. Mater. Res. Bull. 119, 110567 (2019)
O. Polat, M. Coskun, F.M. Coskun et al., Co doped YbFeO3: exploring the electrical properties via tuning the doping level. Ionics 25, 4013–4029 (2019)
M. Coskun, O. Polat, F.M. Coskun, Z. Durmus, M. Caglar, A. Turut Synthesis, characterization and wide range frequency and temperature dependent electrical modulus study of LaCrO3 and cobalt (Co) doped LaCrO3 perovskite compounds Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 248,114410 (2019)
F. Mukhtar, T. Munawar, M.S. Nadeem, M.N. ur Rehman, M. Riaz, F. Iqbal, Dual S-scheme heterojunction ZnO–V2O5–WO3 nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity, Mater. Chem. Phys. 263, 124372 (2021)
S. Aktas, I.S. Hasanli, A. Demiroglu, M. Caglar, Band gap tunability and optical properties of sol-gel derived Fe-doped CeO2 films. Physica B 675, 415621 (2024)
F. Wan, X. Lin, X. Bai, X. Han, K. Song, J. Zheng, C. Cao, Crystalline structure and dielectric properties of multiferroics Cr-doped YMnO3. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 3082–3087 (2016)
P.R. Mandal, T.K. Nath, Oxygen-vacancy and charge hopping related dielectric relaxation and conduction process in orthorhombic Gd doped YFe0.6Mn0.4O3 multiferroics. J. Alloys Comp. 628, 379–389 (2015)
J. Hua, L. Wang, L. Shi, H. Huang, Oxygen reduction reaction activity of LaMn1-xCoxO3-graphene nanocomposite for zinc-air battery. Electrochim. Acta 161, 115–123 (2015)
F. Hao, J. Du, X.P. Han, F.Y. Cheng, Sol-gel synthesis of perovekite La1-xCaxMnO3(X = 0–0.4) nanoparticles for eletrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Chinese journal of inorganic chemistry. J. Chen, Chinese J. Inor. Chem. 29,1617, (2013)
C. Zhanga, J. Su, X. Wang, F. Huang, J. Zhang, Y. Liu, L. Zhang, K. Min, Z. Wang, X. Lua, F. Yanc, J. Zhu, Study on magnetic and dielectric properties of YMnO3 ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 7738–7741 (2011)
F. Wan, X. Lin, X. Bai, X. Han, K. Song, J. Zheng, C. Cao, Crystalline structure and dielectric properties of multiferroic Cr-doped YMnO3. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 3082–3087 (2016)
P.R. Ren, H.Q. Fan, X. Wang, Bulk conduction and nonlinear behaviour in multiferroic YMnO3 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 152905 (2013)
A.G. Kochura, A.T. Kozakov, K.A. Googlev, A.V. Nikolskii, X-ray photoelectron study of temperature effect on the valence state of Mn in single crystal YMnO3. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 195, 1–7 (2014)
A.G. Kochura, A.T. Kozakov, A.V. Nikolskii, K.A. Googlev, A.V. Pavlenko, I.A. Verbenko, L.A. Reznichenko, T.I. Krasnenko, Valence state of the manganese ions in mixed-valence La1−αBiβMn1+δO3±γ ceramics by Mn 2p and Mn 3s X-ray photoelectron spectra. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 185, 175–183 (2012)
V.A. Khomchenko, I.O. Troyanchuk, O.S. Mantytskaya, M. Tovar, H. Szymczak, Crystalline and magnetic structures of La1−xBixMnO3+δ manganites. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 103, 54–59 (2006)
J. Li, Lu. Guanzhong, Wu. Guisheng, D. Mao, Y. Guo, Y. Wang, Y. Guo, Effect of TiO2 crystal structure on the catalytic performance of Co3O4/TiO2 catalyst for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 4, 1268 (2014)
J. Liu, C.G. Duan, W.G. Yin, W.N. Mei, R.W. Smith, J.R. Hardy, Dielectric permittivity and electric modulus in Bi2Ti4O11. J. Chem. Phys. 119, 2812–2819 (2003)
C.A. Angell, Dynamic processes in ionic glasses. Chem. Rev. 90, 523–542 (1990)
A. Rouahi, A. Kahouli, F. Challali, M.P. Besland, C. Vallee, B. Yangui, S. Salimy, A. Goullet, A. Sylvestre, Impedance and electric modulus study of amorphous TiTaO thin films: highlight of the interphase effect. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 46, 065308 (2013)
H. Hammami, M. Arous, M. Lagache, A. Kallel, Study of the interfacial MWS relaxation by dielectric spectroscopy in unidirectional PZT fibres/epoxy resin composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 430, 1–8 (2007)
G.V. Rao, B.M. Wanklyn, C.N.R. Rao, Electrical transport in rare earth ortho-chromites, -manganites and -ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 32, 345 (1971)
M. Tomczyk, P.M. Vilarinho, A. Moreira, A. Almeida, High temperature dielectric properties of YMnO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 064116 (2011)
U. Adem, N. Mufti, A.A. Nugroho, G. Catalan, B. Noheda, T.T.M. Palstra, Dielectric relaxation in YMnO3 single crystals. J. Alloy. Compd. 638, 228–232 (2015)
C. Moure, J.F. Fernandez, M. Villegas, P. Duran, Non-Ohmic behaviour and switching phenomena in YMnO3-based ceramic materials. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19(1), 131–137 (1999)
F.G. Chang, G.L. Song, K. Fang, Q.J. Zeng, Effect of gadolinium substitution on dielectric properties of bismuth ferrite. J. Rare Earths 24, 273–276 (2006)
A.K. Jonscher, The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267, 673–679 (1977)
G.H. Jonker, Analysis of the semiconducting properties of cobalt ferrite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 9, 165–175 (1959)
A.K. Jonscher, Universal Relaxation Law (Chelsea Dielectric Press, London, 1996)
A. Dhahri, F. I. H. Rhou, J. Dhahri, E. Dhahri, M. A. Valente Structural and electrical characteristics of rare earth simple perovskite oxide La0.57Nd0.1Pb0.33Mn0.8Ti0.2O3. Solid State Commun. 151, 738–742 (2011)
W.H. Jung, AC conduction mechanisms of Gd1/3Sr2/3FeO3 ceramic. Physica B 403, 636–638 (2008)
K. Wang, H. Chen, W.Z. Shen, AC electrical properties of nanocrystalline silicon thin films. Physica B 336, 369–378 (2003)
H.M. Abdelmoneim, Dielectric and AC conductivity οf potassium perchlorate, KCLO4. Acta Phisica Polonica A 117, 936–940 (2010)
S. R. Elliott, A theory of A.C. conduction in chalcogenide glasses, Philos. Mag. B. 36, 1291–1304 (1977)
S. Tan, S. Yue, Y.H. Zhang, Phys. Lett. A 319, 530 (2003)
P. Jayabal, V. Sasirekha, J. Mayandi, K. Jeganathan, V. Ramakrishnan, J. Alloys Compd. 586, 456 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) through Grant No: 116F025. We acknowledge Istanbul Medeniyet University Science and Advanced Technology Research Center (IMU-BILTAM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OP: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Funding acquisition, Supervision. MC: Validation, Investigation. YY: Validation, Investigation. FMC: Validation, Investigation. ZD: Validation, Investigation. CS: Validation, Investigation. YC: Validation, Investigation. MC: Review & Editing, Investigation, Validation, Supervision. AT: Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest in any form for this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Polat, O., Coskun, M., Yildirim, Y. et al. A comprehensive investigation of the structural, chemical, and dielectric properties of co-doped YMnO3 multiferroic component. Appl. Phys. A 130, 166 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07335-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07335-8