Abstract
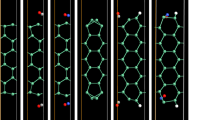
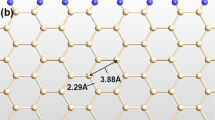
First-principles calculations, using density functional theory, have been studied to investigate the sensing of NO2, NO, N2, CO2, CO, O2, NH3 and SO2 gases on bare and Fe-doped antimonene armchair nanoribbons (Fe-doped ASbNRs). The sensing behaviors of these gases on bare and Fe-doped ASbNRs have been analyzed in terms of band structure, the density of states, adsorption energy, charge transfer, magnetic moments and I–V characteristics. We showed that doping the magnetic Fe atom increases the sensing ability of antimonene nanoribbon where the gas molecules are chemisorption on Fe-doped ASbNR. This chemisorption induces dramatic change in the adsorption energy and electronic structures, and injects magnetic moments into the nanoribbon system. The NO molecule depicts the tightest binding in the Fe-doped ASbNRs. Charge transfer analysis of adsorbates demonstrates that all gas molecules, except NO, NH3 and CO are electron donors to nanoribbon. Transport properties of Fe-doped ASbNRs transistor, display desirable I–V characteristics and spin filter efficiency for the NO2, N2, and NH3 gases. These two-dimensional systems may possess the potential in the promising application of gas sensing.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the analysis of current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
B. Adhikari, S. Majumdar, Polymers in sensor applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 29, 699 (2004)
K.R. Nemade, Gas sensors based on inorganic materials: an overview. Sens. Transducers Int. Freq. Sens. Assoc. 132, 1 (2011)
A. Dey, Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 229, 206 (2018)
S.S. Varghese, S.H. Varghese, S. Swaminathan, K. Singh, V. Mittal, Two dimensional materials for sensing: graphene and beyond. Electronics 4, 651 (2015)
G.F. Fine, L.M. Cavanagh, A. Afonja, R. Binions, Metal oxide semi-conductor gas sensors in environmental monitoring. Sensors 10, 5469 (2010)
K. Rajkumar, R.T.R. Kumar, Fundamentals and sensing applications of 2D materials (Elsevier, 2019), p.205
S. Yang, C. Jiang, Gas sensing in 2D materials. Appl. Phys. Rev. 4, 021304 (2017)
Y. Zeng, S. Lin, D. Gu, X. Li, Two-dimensional nanomaterials for gas sensing applications: the role of theoretical calculations. Nanomaterials 8(10), 851 (2018)
F. Schedin, A. Geim, S.V. Morozov, E. Hill, P. Blake, M. Katsnelson, K. Novoselov, Detection of individual gas molecules adsorbed on graphene. Nat. Mater. 6, 652 (2007)
A. Saffarzadeh, Modeling of gas adsorption on graphene nanoribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 114309 (2010)
D. Sun, Y. Luo, M. Debliquy, C. Zhang, Graphene-enhanced metal oxide gas sensors at room temperature: a review. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 9, 2832 (2018)
J.T. Robinson, F.K. Perkins, E.S. Snow, Z. Wei, P. Sheehan, Reduced graphene oxide molecular sensors. Nano Lett. 8, 3137 (2008)
Y.H. Zhang, Y.B. Chen, K.G. Zhou, C.H. Liu, J. Zeng, H.L. Zhang, Y. Peng, Improving gas sensing properties of graphene by introducing dopants and defects: a first-principles study. Nanotechnology 20(18), 185504 (2009)
J. Dai, J. Yuan, Adsorption of molecular oxygen on doped graphene: atomic, electronic, and magnetic properties. Phys. Rev. B 81, 165414 (2010)
S. Zhang, Z. Yan, Y. Li, Z. Chen, H. Zeng, Atomically thin arsenene and antimonene: Semimetal-semiconductor and indirect-direct band-gap transitions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 3155 (2015)
S. Zhang, M. Xie, F. Li, Z. Yan, Y. Li, E. Kan, W. Liu, Z. Chen, H. Zeng, Semiconducting group 15 monolayers: a broad range of band gaps and high carrier mobilities. Angew. Chem. 128, 1698 (2016)
P. Ares, F. Aguilar-Galindo, D. Rodriguez-San-Miguel, D.A. Aldave, S. DiazTendero, M. Alcami, F. Martin, J. Gomez-Herrero, F. Zamora, Mechanical isolation of highly stable antimonene under ambient conditions. Adv. Mater. 28, 6332 (2016)
C. Gibaja, D. Rodriguez-San-Miguel, P. Ares, J. Gómez-Herrero, M. Varela, R. Gillen, J. Maultzsch, F. Hauke, A. Hirsch, G. Abellán, F. Zamora, Few-layer antimonene by liquid-phase exfoliation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 14345 (2016)
O.Ü. Aktürk, V.O. Özçelik, S. Ciraci, Single-layer crystalline phases of antimony: antimonenes. Phys. Rev. B 91, 235446 (2015)
Y. Wang, Y. Ding, Electronic structure and carrier mobilities of arsenene and antimonene nanoribbons: a first-principle study. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10, 254 (2015)
V. Nagarajan, R. Chandiramouli, Sensing studies of DDT and Toxaphene molecules using chemi-resistive β-antimonene nanotubes based on first-principles insights. Chem. Phys. Lett. 757, 137895 (2020)
Y. Song, X. Wang, W. Mi, Spin splitting and electric field modulated electron-hole pockets in antimonene nanoribbons. NPJ Quantum Mater 2, 15 (2017)
A.C.R. Souzal, M.J.S. Matos, M.S.C. Mazzoni, Oxidation-driven formation of precisely ordered antimonene nanoribbons. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter. 32, 165302–888 (2019)
A.J.S. Impeng, P. Maitarad, N. Kungwan, D. Zhang, L. Shi, S. Namuangruk, A MnN4 moiety embedded graphene as a magnetic gas sensor for CO detection: a first principle study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 473, 820 (2018)
E. Salih, A.I. Ayesh, Enhancing the sensing performance of zigzag graphene nanoribbon to detect NO, NO2, and NH3 Gases. Sensors 20, 3932 (2020)
M. Ali, S. Khan, F. Awwad, N. Tit, High gas-sensing selectivity of bilaterally edge-doped graphene nanoribbons towards detecting NO2, O2 and SO3 gas molecules: Ab-initio investigation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 514, 145866 (2020)
R. Deji, A. Verma, B.C. Choudhary, R.K. Sharma, New insights into NO adsorption on alkali metal and transition metal doped graphene nanoribbon surface: a DFT approach. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 111, 108109 (2022)
R. Deji, B.C. Choudhary, R.K. Sharma, Hydrogen sulfide gas sensor using osmium doped graphene nanoribbon: an insights from DFT study. Mater. Lett. 306, 130986 (2022)
G.K. Walia, D.K.K. Randhawa, First-principles investigation on defect-induced silicene nanoribbons—a superior media for sensing NH3, NO2 and NO gas molecules. Surf. Sci. 670, 33–43 (2018)
S. Su, J. Gong, Z.-Q. Fan, Selective adsorption of harmful molecules on zigzag phosphorene nanoribbon for sensing applications. Physica E 117, 113838 (2020)
P. Sirvastava, Abhishek, V. Sharma, N.K. Jaiswal, First principle insights of CO and NO detection via antimonene nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. A 126, 668 (2020)
W. Hui, G. Chang, W. Gao, Exploring the electronic and magnetic properties of noble metal (Pd, Pt, Au) adsorbed MoSe2 monolayers and their performance towards sensing gas molecules. Physica E 122, 114167 (2020)
P. Sirvastava, Abhishek, V. Sharma, N.K. Jaiswal, First-principles investigation of CO2 and NH3 adsorption on antimonene nanoribbons. Mater. Today Proc. 28, 65 (2020)
G.-X. Chen, R.-Y. Du, D.-D. Wan, Z. Chen, S. Liu, J.-M. Zhang, Adsorption of NO gas molecule on the vacancy defected and transition metal doped antimonene: a first-principles study. Vacuum 207, 111654 (2023)
M.I. Khan, M. Hassan, A. Majid, M. Shakil, M. Rafique, DFT perspective of gas sensing properties of Fe-decorated monolayer antimonene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 616, 156520 (2023)
F. Safari, M. Moradinasab, M. Fathipour, H. Kosina, Adsorption of the NH3, NO, NO2, CO2, and CO gas molecules on blue phosphorene: a first-principles study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 464, 153 (2019)
C. Jin, X. Tang, X. Tan, S.C. Smith, Y. Dai, L. Kou, A Janus MoSSe monolayer: a superior and strain sensitive gas sensing material. J. Mater. Chem. A 496, 1099 (2019)
“Atomistix ToolKit, version 2016.04, Quantum Wise A/S. http://www.quantumwise.com”. Accessed 2016
J. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996)
S.B. Touski, M.P. López-Sancho, Effects of vertical electric field and charged impurities on the spin-polarized transport of β-antimonene armchair nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B 103, 115433 (2021)
R. Deji, A. Verma, N. Kaur, B.C. Choudhary, R.K. Sharma, Density functional theory study of carbon monoxide adsorption on transition metal doped armchair graphene nanoribbon. Mater. Today Proc. 54, 771 (2022)
D. Zhang, M. Long, X. Zhang, F. Ouyang, M. Li, H. Xu, Designing of spin-filtering devices in zigzag graphene nanoribbons heterojunctions by asymmetric hydrogenation and B-N doping. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 014311 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection was performed by SHK, and analysis were performed by Jamal Barvestani and Bahar Meshginqalam. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kashani, S.H., Barvestani, J. & Meshginqalam, B. Sensing behavior of various gas molecules adsorbed on Fe-doped and bare antimonene armchair nanoribbon. Appl. Phys. A 130, 63 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07234-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07234-4