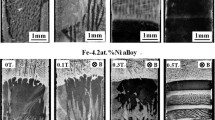
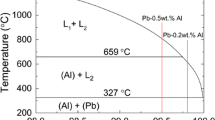
Abstract
Pb–Zn alloy is an ideal anode material for zinc electrodeposition. In this work, the microstructure of Pb–Zn alloy is controlled by composite electro-magnetic fields (CEMFs), and the mechanism is investigated. The results show that electric current pulses (ECPs) can significantly enhance the nucleation driving force for the second phase, thereby promoting the refinement of the second phase. Static magnetic field (SMF) can substantially suppress melt convection and increase the melt cooling rate around the center axis of the sample. Therefore, it is favorable for the formation of a homogeneous dispersed microstructure along the radial direction. CEMFs not only can inhibit melt convection, but also enhance the nucleation rates of Minority Phase Droplets (MPDs). This promotes the formation of a solidification microstructure in which the fine Minority Phase Particles (MPPs) are homogeneously distributed in the matrix. This work indicates that the application of CEMFs is an effective method for controlling the microstructure of monotectic alloys and it has an important industrial value.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding authors.
References
T.B. Singh, K. Lal, R.K. Mohanty, C.S. Shivaramakrisnan, Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Bv 1, (1998)
G.J. May, A. Davidson, B. Monahov, J. Energy Storage 15, 145–157 (2018)
S.V. Trukhanov, A.V. Trukhanov, V.A. Turchenko, A.V. Trukhanov, E.L. Trukhanova, D.I. Tishkevich, V.M. Ivanov, T.I. Zubar, M. Salem, V.G. Kostishyn, L.V. Panina, D.A. Vinnik, S.A. Gudkova, Ceram. Int. 44, 1 (2018)
T.I. Zubar, V.M. Fedosyuk, S.V. Trukhanov, D.I. Tishkevich, D. Michels, D. Lyakhov, A.V. Trukhanov, Sci. Rep. 10, 1 (2020)
M.V. Zdorovets, A.L. Kozlovskiy, D.I. Shlimas, D.B. Borgekov, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 32, 12 (2021)
A.L. Kozlovskiy, M.V. Zdorovets, J. Mater. Sci-Mater. El. 30, 12 (2019)
M.T. Wall, Y. Ren, T. Hesterberg, T. Ellis, M.L. Young, J Energy Storage 55, 105569 (2022)
S.L. Wang, C.C. Li, J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 30, 2 (2012)
S.C. Liu, S.S. Xu, J.C. Jie, J.J. Zhang, Y. Dong, X.Z. Li, T.J. Li, J. Alloys Compd. Alloys Compd. 888, 161627 (2021)
L. Bo, S.S. Li, L. Wang, D. Wu, M. Zuo, D.G. Zhao, Results Phys. 8, 1086–1091 (2018)
Q. Sun, H.X. Jiang, J.Z. Zhao, J. He, Acta Mater. Mater. 129, 321–330 (2017)
Y.H. Wu, W.L. Wang, J. Chang, B. Wei, J. Alloys Compd. Alloys Compd. 763, 808–814 (2018)
W.L. Wang, Y.H. Wu, L.H. Li, W. Zhai, X.M. Zhang, B. Wei, Sci. Rep. Rep. 5, 16335 (2015)
W.L. Wang, Y.H. Wu, L.H. Li, D.L. Geng, B. Wei, Phys. Rev. E 93, 3 (2016)
S.C. Liu, J.C. Jie, B.W. Dong, Z.K. Guo, T.M. Wang, T.J. Li, Mater. Des.. Des. 156, 71–81 (2018)
J.Z. Zhao, H. Sun, L.L. Zhang, H.X. Jiang, L.J. Yang, J. He, Natl. Sci. Rev. 10, 2 (2023)
H.X. Jiang, J.Z. Zhao, Acta Metall. Sin-Engl. 31, 12 (2018)
H. Friedman, S. Reich, R. Popovitz-Biro, P. von Huth, I. Halevy, Y. Koltypin, A. Gedanken, Z. Porat, Ultrason. Sonochem.. Sonochem. 20, 1 (2013)
J. Zhu, T.M. Wang, F. Cao, H.W. Fu, Y.N. Fu, H.L. Xie, T.Q. Xiao, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 22, 5 (2013)
Y.B. Zhong, T.X. Zheng, L.C. Dong, B.F. Zhou, W.L. Ren, J. Wang, Z.M. Ren, F. Debray, E. Beaugnon, H. Wang, Q.L. Wang, Y.M. Dai, Mater. Des.. Des. 100, 168–174 (2016)
Y.B. Zhong, J. Wang, T.X. Zheng, Y. Fautrelle, Z.M. Ren, Mater. Today: Proc. 2, S364–S372 (2015)
H.L. Li, J.Z. Zhao, Comput. Mater. Sci.. Mater. Sci. 46, 4 (2009)
Z.Q. Kang, E.G. Wang, L. Zhang, J.C. He, Chin. J. Mater. Res. 25, 2 (2011)
J. Wang, Y.B. Zhong, Y. Fautrelle, T.X. Zheng, F. Li, Z.M. Ren, F. Debray, Appl. Phys. A 112, 4 (2013)
B.F. Zhou, W.H. Lin, Y. Liu, T.X. Zheng, Y.B. Zhong, H. Wang, Q.L. Wang, J. Alloys Compd. 889, 161670 (2021)
H.X. Jiang, J.Z. Zhao, J. He, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30, 10 (2014)
H.X. Jiang, J. He, J.Z. Zhao, Sci. Rep. 5, 13825 (2015)
T. Ma, X.S. Sun, Y.N. Ning, W.X. Hao, High Temp. Mater. Process. 40, 382–388 (2021)
L. Ratke, D. Uffelmann, Coarsening processes in liquid dispersions. In: International Conf on Solidification and Microgravity, Trans Tech Publications Ltd, Miskolc, Hungary, pp. 69–84 (1991)
J. Wang, Y.B. Zhong, C. Wang, Z.Q. Wang, Z.M. Ren, K.D. Xu, Acta Phys. Sin. 60, 7 (2011)
N. David, J. Hertz, J.M. Fiorani, Zeitschrift fur Metallkunde 94, 1 (2003)
W.L. Ren, L. Lu, G.Z. Yuan, W.D. Xuan, Y.B. Zhong, J.B. Yu, Z.M. Ren, Mater. Lett.. Lett. 100, 223–226 (2013)
J.R. Rogers, R.H. Davis, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 21, 59–68 (1990)
W. Chester, J. Fluid Mech. 3, 3 (1957)
M.H. Wu, A. Ludwig, L. Ratke, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Mater. Trans. A 34, 755 (2003)
J.Z. Zhao, H.L. Li, X.F. Zhang, J. He, L. Ratke, Int. J. Mater. Res. 100, 1 (2009)
H.L. Li, J.Z. Zhao, Appl. Phys. Lett. Phys. Lett. 92, 241902 (2008)
A.T. Dinsdale, Calphad 15, 4 (1991)
A.I. Pommrich, A. Meyer, D. Holland-Moritz, T. Unruh, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 24 (2008)
D.C. Ghosh, R. Biswas, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 3, 2 (2002)
T. Iida, R.I.L. Guthrie, The thermophysical properties of metallic liquids: fundamentals (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2015)
J. Smithells, Metal reference book (Butterworths, London & Boston, 1976)
Y.Q. Li, J.Z. Zhao, H.X. Jiang, J. He, Acta Metall. Sin. Sin 58, 8 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China [Grant Number 2021YFA0716303], the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 51971227, 51974288, 52174380), China's Manned Space Station Project, and the Space Utilization System of China Manned Space Engineering (Grant Number KJZ-YY-NCL06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HJ, JZ, and JH conceived the idea and designed the experiments. BH, YL, HJ and LZ conducted the experiments. BH performed the numerical simulations. BH and YL prepared the samples and conducted materials characterization. BH, YL and HJ drafted the manuscript. HJ, JZ and JH interpreted, discussed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article.
Ethical approval
This research does not include experiments involving human tissue and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, B., Li, Y., Jiang, H. et al. The influence of composite pulse current and static magnetic fields on the solidification structure formation in Pb–Zn alloys. Appl. Phys. A 130, 15 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07165-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07165-0