Abstract
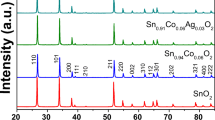
We conducted a comprehensive study on Sn0.94-yAg0.06SbyO2 (with y ranging from 0 to 0.10) compounds to investigate its crystal structure, morphology, optical, magnetic and transport properties. The creation of the tetragonal rutile phase of SnO2 and the successful insertion of Ag/Sb ions into the SnO2 lattice were confirmed by analysis of X-ray diffraction data and Raman spectroscopy. Elemental color mapping using EDS revealed a uniform distribution of the elements. The oxidation states of Sn, Sb, and Ag were observed to be + 4, + 3, and + 1, respectively. The optical property study showed a reduction in the bandgap as the doping level increased. All prepared samples tend to exhibit p-type behavior, and the total charge density decreased with an increase in the percentage of Ag/Sb co-doping. Magnetic property measurements indicated that these compounds displayed room temperature ferromagnetism up to 4 at % Ag–Sb co-doping level, beyond which they became diamagnetic.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
H. Ohno, Making nonmagnetic semiconductors ferromagnetic. Science 281, 951 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.281.5379.951
L. Chouhan, S.K. Srivastava, A comprehensive review on recent advancements in d0 ferromagnetic oxide materials for spintronics application. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 147, 106768 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.106768
N. Jiang, B. Yang, Y. Bai, Y. Jiang, S. Zhao, The sign reversal of anomalous Hall effect derived from the transformation of scattering effect in cluster-assembled Ni 0.8 Fe 0.2 nanostructural films. Nanoscale. 13(27), 11817–11826 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR02313F
M. Först, A. Caviglia, R. Scherwitzl et al., Spatially resolved ultrafast magnetic dynamics initiated at a complex oxide heterointerface. Nature Mater 14, 883–888 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4341
Y. Tsai, Z. Li, S. Hu, Recent progress of atomic layer technology in spintronics: mechanism materials and prospects. Nanomaterials 12, 661 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040661
J.K. Furdyna, Diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 64, R29 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.341700
S.B. Ogale, R.J. Choudhary, J.P. Buban, S.E. Lofland, S.R. Shinde, S.N. Kale, V.N. Kulkarni, J. Higgins, C. Lanci, J.R. Simpson et al., High temperature ferromagnetism with a giant magnetic moment in transparent Co-doped SnO2−δ. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 077205 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.077205
X.L. Wang, Z.X. Dai, Z. Zeng, Search for ferromagnetism in SnO2 doped with transition metals (V, Mn, Fe, and Co). J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 20, 045214 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/20/04/045214
S.K. Srivastava, P. Lejay, B. Barbara, O. Boisron, S. Pailhès, G. Bouzerar, Absence of ferromagnetism in Mn-doped tetragonal zirconia. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 043929 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3626788
S.K. Srivastava, Magnetic property of Mn-doped monoclinic ZrO2 compounds. J Supercond Nov Magn. 33, 2501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05522-1
P. Sharma, A. Gupta, K.V. Rao, F.J. Owens, R. Sharma, R. Ahuja, J.M.O. Guillen, B. Johansson, G.A. Gehring, Ferromagnetism above room temperature in bulk and transparent thin films of Mn-doped ZnO. Nat. Mater. 2, 673 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat984
M. Subramanian, P. Thakur, M. Tanemura, T. Hihara, V. Ganesan, T. Soga, K.H. Chae, R. Jayavel, T. Jimbo, Intrinsic ferromagnetism and magnetic anisotropy in Gd-doped ZnO thin films synthesized by pulsed spray pyrolysis method. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 053904 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3475992
J.D. Bryan, S.M. Heald, S.A. Chambers, D.R. Gamelin, Strong room-temperature ferromagnetism in Co2+- doped TiO2 made from colloidal nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 11640 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja047381r
S.K. Srivastava, R. Brahma, S. Datta, S. Guha, S.S. Baro, B. Aakansha, D.R. Narzary, M. Basumatary, S.R. Kar, Effect of (Ni-Ag) co-doping on crystal structure and magnetic property of SnO2. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 126107 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab58b1
S.K. Srivastava, S.S. Aakansha, B. Baro, D.R. Narzary, R. Basumatary, S..R. Brahma, Crystal structure and magnetic properties of (Co-Ag) co-doped SnO2 compounds. J Supercond Nov Magn. 34, 461 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05676-y
T. Dietl, A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides. Nat. Mater 9, 965 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2898
G. Bouzerar, T. Ziman, Model for vacancy-induced d0 ferromagnetism in oxide compounds. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 207602 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.207602
F. Máca, J. Kudrnovský, V. Drchal, G. Bouzerar, Magnetism without magnetic impurities in oxides ZrO2 and TiO2. Philos. Mag. 88, 2755 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/14786430802342584
K. Yang, Y. Dai, B. Huang, M.-H. Whangbo, On the possibility of ferromagnetism in carbon-doped anatase TiO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 132507 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2996024
H. Luitel, D. Sanyal, Ab initio calculation of magnetic properties in B, Al, C, Si, N, P and As-doped rutile TiO2. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 31, 1750227 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979217502277
F. Máca, J. Kudrnovský, V. Drchal, G. Bouzerar, Magnetism without magnetic impurities in ZrO2 oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 212503 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2936858
X. Guan, N. Cai, C. Yang, J. Chen, P. Lu, Magnetic properties of ZnO nanowires with Li dopants and Zn vacancies. Thin Solid Films 605, 273 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2015.04.077
W.-Z. Xiao, L.-L. Wang, L. Xu, X.-F. Li, H.-Q. Deng, First-principles study of magnetic properties in Ag-doped SnO2: first-principles study on magnetic properties in Ag-doped SnO2. Phys. Status Solidi B 248, 1961 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201046567
W. Wei, Y. Dai, M. Guo, K. Lai, B. Huang, Density functional study of magnetic properties in Zn-doped SnO2. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 093901 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3503224
Hou D.L., Meng H.J., Jia L.Y., Ye X.J., Zhou H.J., Li, X.L. (2007) Impurity concentration study on ferromagnetism in Cu-doped TiO2 thin films, Europhys. Lett. 78 67001. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/78/67001
S. Duhalde, M.F. Vignolo, F. Golmar, C. Chiliotte, C.E.R. Torres, L.A. Errico, A.F. Cabrera, M. Rentería, F.H. Sánchez, M. Weissmann, Appearance of room-temperature ferromagnetism in Cu-doped TiO2−δ films. Phys. Rev. B 72, 161313 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.161313
J.V. Pinto, M.M. Cruz, R.C. da Silva, E. Alves, M. Godinho, Magnetic properties of TiO2 rutile implanted with Ni and Co. J Magn Magn Mater. 294, e73 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.03.057
L. Chouhan, G. Bouzerar, S.K. Srivastava, Effect of Mg-doping in tailoring d0 ferromagnetism of rutile TiO2 compounds for spintronics application. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 32, 11193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05784-y
L. Chouhan, R. Narzary, B. Dey, S.K. Panda, M.K. Manglam, L. Roy, R. Brahma, A. Mondal, M. Kar, S. Ravi, S.K. Srivastava, Tailoring room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, dielectric, optical, and transport properties in Ag-doped rutile TiO2 compounds for spintronics applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 32, 28163 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07194-6
S. Song, J. Wei, X. He, G. Yan, M. Jiao, W. Zeng, F. Daiab, M. Shi, Oxygen vacancies generated by Sn-doped ZrO2 promoting the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from methanol and CO2. RSC Adv. 11, 35361 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA07060F
M.C. Dimri, H. Khanduri, H. Kooskora, M. Kodu, R. Jaaniso, I. Heinmaa, A. Mere, J. Krustok, R. Stern, Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Ca and Mg stabilized cubic zirconia bulk samples and thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 45, 475003 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/45/47/475003
N.H. Hong, N. Poirot, J. Sakai, Ferromagnetism observed in pristine SnO2 thin films. Phys. Rev. B 77, 033205 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.77.033205
G.S. Chang, J. Forrest, E.Z. Kurmaev, A.N. Morozovska, M.D. Glinchuk, J.A. McLeod, A. Moewes, T.P. Surkova, N.H. Hong, Oxygen-vacancy-induced ferromagnetism in undoped SnO2 thin films. Phys. Rev. B 85, 165319 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.85.165319
S.K. Srivastava, P. Lejay, B. Barbara, S. Pailhès, V. Madigou, G. Bouzerar, Possible room-temperature ferromagnetism in K-doped SnO2: X-ray diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy study. Phys. Rev. B. 82, 193203 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.82.193203
S.K. Srivastava, P. Lejay, A. Hadj-Azzem, G. Bouzerar, Non-magnetic impurity induced magnetism in Li-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 487 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-013-2287-0
L. Chouhan, S.K. Panda, S. Bhattacharjee, B. Das, A. Mondal, B.N. Parida, R. Brahma, M.K. Manglam, M. Kar, G. Bouzerar, S.K. Srivastava, Room temperature d0 ferromagnetism, zero dielectric loss and ac-conductivity enhancement in p-type Ag-doped SnO2 compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 870, 159515 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159515
J. Wang, D. Zhou, Y. Li, P. Wu, Experimental and first-principle studies of ferromagnetism in Na-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Vacuum 141, 62 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.03.024
S. Chawla, K. Jayanthi, R.K. Kotnala, High temperature carrier controlled ferromagnetism in alkali doped ZnO nanorods. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 113923 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3261722
R. Narzary, B. Dey, L. Chouhan, S. Kumar, S. Ravi, S.K. Srivastava, Optical band gap tuning, zero dielectric loss and room temperature ferromagnetism in (Ag/Mg) co-doped SnO2 compounds for spintronics applications. Materi Sci Semicond Process 142, 106477 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.106477
J. Rodriguez-Carvajal, Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys. B Condens. Matter 192, 55 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-4526(93)90108-I
R.A. Young, first ed., Oxford University Press, New York, 1993 https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/S0885715600019497.
P. Scherrer, GöttingerNachrichten Gesell, 2 (1918) 98. https://eudml.org/doc/59018
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.83.121
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, A. Vancu, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi 15, 627 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.19660150224
S. Picozzi, P. Santini, A.J. Freeman, Doping-dependent magnetism and band gap in Sn1−xSbxO2 from first principles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(16), 3410–3412 (2004)
R. Schmidt, A. Faghaninia, G. Kresse, E.S. Aydil, Doping and disorder in SnO2. Phys. Rev. B 89(19), 195205 (2014)
J.W. Xie, Y.M. Shi, X.H. Wang, H.F. Yang, Z.H. Cao, Z.D. Zhang, Ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism in Sb-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 111(7), 07A906 (2012)
A. Singh, R.J. Choudhary, Room temperature ferromagnetism in undoped and Sb doped SnOs2 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 397–402 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This present research work is not supported by any kind of research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RN: investigation, methodology, formal analysis, writing manuscript; SR: conceptualization, visualization, writing—review and editing, supervision; SKS: conceptualization, methodology, visualization, writing—review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Narzary, R., Ravi, S. & Srivastava, S.K. Crystal structure, micro-structure, Raman spectroscopy, optical, magnetic, and electrical property of Sn0.94-yAg0.06SbyO2 compounds. Appl. Phys. A 129, 630 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06910-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06910-9