Abstract
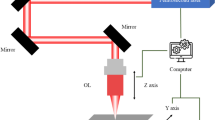
Recently, the need for enhanced cutting tools to fabricate next-generation multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) and batteries has been identified. This is because existing cutting tools cause problems such as defects, burrs, and breaking of MLCCs when the MLCCs are cut using the existing cutting tools. Furthermore, the productivity of MLCCs should be improved. To overcome these problems, enhanced cutting tools should have sharper blade angles and thinner widths. Currently, a cutting tool with a thickness of tens of micrometers is used in the industry. Also, cutting tools made of cemented tungsten carbide are difficult to machine. Therefore, fine ablation technology is required for their application. Machining technology using femtosecond lasers has been studied to realize fine ablation. However, studies on the subject are limited. Therefore, we studied fine ablation using the beam-shaping technology. In this study, a femtosecond laser with a wavelength of 1030 nm, a maximum repetition rate of 200 kHz, and a maximum pulse energy of 1 mJ was used. Additionally, a slit-optic system was used to transform the laser beam with Gaussian energy distribution into the laser beam with a quasi-flat top energy distribution. We demonstrated a machining depth resolution of 25 nm for cemented tungsten carbides using a femtosecond laser with a fluence of 0.32 J/cm2.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
L. Chen, H. Wang, P. Zhao, C. Zhu, Z. Cai, Z. Cen, L. Li, X. Wang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 4178 (2019)
R. Muhammad, Y. Iqbal, I.M. Reaney, C. Randall, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 2089 (2016)
L. Chen, H. Wang, P. Zhao, Z. Shen, C. Zhu, Z. Cen, L. Li, X. Wang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 2781 (2019)
K. Hong, T.H. Lee, J.M. Suh, S.H. Yoon, H.W. Jang, J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 9782 (2019)
T. Im, J. Pyo, J. Sung Lee, C.S. Lee, Powder Technol. 382, 118 (2021)
E.M. Trent, P.K. Wright, Chapter 7: cutting tool materials II: Cemented carbides, in Metal Cutting, 4th edn. (Elsevier, 2000), pp.175–226
A. Abdullah, M.R. Shabgard, A. Ivanov, M.T. Shervanyi-Tabar, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 41, 268 (2009)
K. Bonny, P. De Baets, W. Ost, S. Huang, J. Vleugels, W. Liu, B. Lauwers, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 27, 350 (2009)
A. Rizzo, S. Goel, M.L. Grilli, R. Iglesias, L. Jaworska, V. Lapkovskis, P. Novak, B.O. Postolnyi, D. Valerini, Materials (Basel) 13, 1377 (2020)
G. Eberle, K. Wegener, Phys. Procedia 56, 951 (2014)
B. Ali, I.V. Litvinyuk, M. Rybachuk, Carbon N. Y. 179, 209 (2021)
Y. Xie, D.J. Heath, J.A. Grant-Jacob, B.S. Mackay, M.D.T. McDonnell, M. Praeger, R.W. Eason, B. Mills, J. Phys. Photonics 1, 035002 (2019)
S.-J. Xu, Y.-Z. Duan, Y.-H. Yu, Z.-N. Tian, Q.-D. Chen, Opt. Express 29, 30952 (2021)
Q. Zhu, P. Fan, N. Li, T. Carlson, B. Cui, J.F. Silvain, J.L. Hudgins, Y.F. Lu, Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 3, 045001 (2021)
Z.H. Li, E.S. Cho, S.J. Kwon, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 9843 (2009)
K. Sugioka, Y. Cheng, Appl. Phys. Rev. 1, 041303 (2014)
K. Sugioka, Y. Cheng, Light Sci. Appl. 3, 1 (2014)
W. Zhao, H. Liu, X. Shen, L. Wang, X. Mei, Materials (Basel) 13, 31 (2020)
H. Wang, H. Lin, C. Wang, L. Zheng, X. Hu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37, 1157 (2017)
H. Wu, P. Zou, J. Cao, K.F. Ehmann, J. Manuf. Process. 55, 389 (2020)
H.-Y. Kim, W.-S. Choi, S.-Y. Ji, Y.-G. Shin, J.-W. Jeon, S. Ahn, S.-H. Cho, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1553-1
H. Legall, C. Schwanke, S. Pentzien, G. Dittmar, J. Bonse, J. Krüger, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 124, 407 (2018)
J.M. Liu, Opt. Lett. 7, 196 (1982)
W. Zhao, W. Wang, G. Jiang, B.Q. Li, X. Mei, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 80, 1713 (2015)
T. Viertel, L. Pabst, R. Ebert, H. Exner, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 125, 1 (2019)
N.M. Bulgakova, A.V. Bulgakov, V.P. Zhukov, W. Marine, A.Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, High-Power Laser Ablation VII 7005, 70050C (2008)
R.R. Phiri, O.P. Oladijo, E.T. Akinlabi, Procedia Manuf. 35, 522 (2019)
F. Di Niso, C. Gaudiuso, T. Sibillano, F.P. Mezzapesa, A. Ancona, P.M. Lugarà, Opt. Express 22, 12200 (2014)
W. Wang, G. Jiang, X. Mei, K. Wang, J. Shao, C. Yang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 3612 (2010)
M.D. Perry, B.C. Stuart, P.S. Banks, M.D. Feit, V. Yanovsky, A.M. Rubenchik, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 6803 (1999)
G. Tani, L. Orazi, A. Fortunato, G. Cuccolini, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 130, 0311111 (2008)
B. Rethfeld, A. Kaiser, M. Vicanek, G. Simon, Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 65, 2143031 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This study did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, YG., Choi, J. & Cho, SH. Fine ablation with depth control of 25-nm resolution and morphologies irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses via beam shaping. Appl. Phys. A 129, 534 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06799-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06799-4