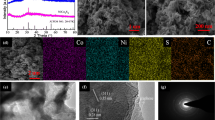
Abstract
SnSe with layered structure, as a member of 2D materials and transition metal chalcogenides, is a promising candidate of electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Reduced graphene oxide (RGO) is an excellent substrate of electrocatalyst. In this work, SnSe nanosheets (NSs) had been prepared via liquid exfoliation, and the as-prepared SnSe NSs had been hybridized with RGO by a simple hydrothermal method. The SnSe/RGO hybrid shows superior hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) performance and charge transfer capability than SnSe NSs. In addition, it exhibits a superior HER performance in 1.0 M H2SO4 with overpotential of − 298.79 mV (vs. RHE) at a current density of 10 mA/cm2 and a Tafel slope determined to be only 97.56 mV/dec. Moreover, the SnSe/RGO hybrid as working electrode is provided with excellent durability, which is capable of maintaining working current for 10 h. As demonstrated above, relative high activity and stability and low price make the SnSe/RGO hybrid a promising electrocatalyst.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All relevant data supporting the discoveries of this study are contained in this article or its supplementary information files.
References
W. Zhang, K. Zhou, Ultrathin two-dimensional nanostructured materials for highly efficient water oxidation. Small 13, 1700806 (2017)
H. Liu, W. Lei, Z. Tong, X. Li, Z. Wu, Q. Jia, S. Zhang, H. Zhang, Defect engineering of 2D materials for electrochemical energy storage. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 7, 2000494 (2020)
L.S.L. Huijuan, F. Qingliang, Research and application progress of electrochemical sensors based on two-dimensional layered semiconductor materials. Mater. Rep. 36, 20080298–20080210 (2022)
H. Qiao, Z. Huang, X. Ren, S. Liu, Y. Zhang, X. Qi, H. Zhang, Self-powered photodetectors based on 2D materials. Adv. Opt. Mater. 8, 1900765 (2020)
C. Huo, Z. Yan, X. Song, H. Zeng, 2D materials via liquid exfoliation: a review on fabrication and applications. Sci. Bull. 60, 1994–2008 (2015)
H. Qiao, H. Liu, Z. Huang, R. Hu, Q. Ma, J. Zhong, X. Qi, Tunable electronic and optical properties of 2D monoelemental materials beyond graphene for promising applications. Energy Environ. Mater. 4, 522–543 (2021)
G.F.Y. Chen, T. Xiaolong, Y.I. Honghong, M. Leilei, Y. Qingjun, Z. Shunzheng, Review on the synthesis techniques of two-dimensional materials and their application in the field of catalysis. Mater. Rep. 34, 13005–13016 (2020)
Q. Zhou, M. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Chen, Q. Wu, S. Wang, Fabrication of highly textured 2D SnSe layers with tunable electronic properties for hydrogen evolution. Molecules 26, 3319 (2021)
H. Qiao, H. Liu, Z. Huang, Q. Ma, S. Luo, J. Li, Y. Liu, J. Zhong, X. Qi, Black phosphorus nanosheets modified with au nanoparticles as high conductivity and high activity electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Energy Mater. 10, 2002424 (2020)
H. Qiao, Z. Li, F. Liu, Q. Ma, X. Ren, Z. Huang, H. Liu, J. Deng, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, X. Qi, H. Zhang, Au Nanoparticle modification induces charge-transfer channels to enhance the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction of InSe nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 2908–2917 (2022)
J. Zhao, J. Wang, Z. Chen, J. Ju, X. Han, Y. Deng, Metal chalcogenides: an emerging material for electrocatalysis. APL Mater. 9, 050902 (2021)
J. Yin, J. Jin, H. Lin, Z. Yin, J. Li, M. Lu, L. Guo, P. Xi, Y. Tang, C.-H. Yan, Optimized metal chalcogenides for boosting water splitting. Adv. Sci. 7, 1903070 (2020)
S.A. Shah, X. Shen, M. Xie, G. Zhu, Z. Ji, H. Zhou, K. Xu, X. Yue, A. Yuan, J. Zhu, Y. Chen, Nickel@nitrogen-doped carbon@MoS2 nanosheets: an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Small 15, e1804545 (2019)
Q. Yang, Y. He, Y. Fan, F. Li, X. Chen, Exfoliation of the defect-rich MoS2 nanosheets to obtain nanodots modified MoS2 thin nanosheets for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 7413–7418 (2017)
Z. Wu, B. Fang, A. Bonakdarpour, A. Sun, D.P. Wilkinson, D. Wang, WS2 nanosheets as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Catal. B 125, 59–66 (2012)
L. Cheng, W. Huang, Q. Gong, C. Liu, Z. Liu, Y. Li, H. Dai, Ultrathin WS2 Nanoflakes as a High-Performance Electrocatalyst for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 7860–7863 (2014)
D. Damien, A. Anil, D. Chatterjee, M.M. Shaijumon, Direct deposition of MoSe2 nanocrystals onto conducting substrates: towards ultra-efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 13364–13372 (2017)
H. Shi, H. Zhang, M. Li, Y. Wang, D. Wang, Nanoflower-like 1T/2H mixed-phase MoSe2 as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. J. Alloy. Compd. 878, 160381 (2021)
S. Li, Z. Zhao, J. Li, H. Liu, M. Liu, Y. Zhang, L. Su, A.I. Pérez-Jiménez, Y. Guo, F. Yang, Y. Liu, J. Zhao, J. Zhang, L.-D. Zhao, Y. Lin, Mechanically induced highly efficient hydrogen evolution from water over piezoelectric SnSe nanosheets. Small 18, 2202507 (2022)
Z. Feng, C.D. Jadhav, G.P. Patil, Y. Wang, C. Zhang, V.S. Baviskar, Z. Jia, R. Minnes, Solution processed 2D SnSe nanosheets catalysts: temperature dependent oxygen reduction reaction performance in alkaline media. J. Electroanal. Chem. 916, 116381 (2022)
W.-H. Hu, X. Shang, G.-Q. Han, B. Dong, Y.-R. Liu, X. Li, Y.-M. Chai, Y.-Q. Liu, C.-G. Liu, MoSx supported graphene oxides with different degree of oxidation as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Carbon 100, 236–242 (2016)
K. Wang, S. Wang, K.S. Hui, H. Gao, D.A. Dinh, C. Yuan, C. Zha, Z. Shao, Z. Tang, K.N. Hui, Synergistically boosting the elementary reactions over multiheterogeneous ordered macroporous Mo2C/NC-Ru for highly efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution, carbon. Energy 4, 856–866 (2022)
K. Wang, S. Wang, K.S. Hui, J. Li, C. Zha, D.A. Dinh, Z. Shao, B. Yan, Z. Tang, K.N. Hui, Dense platinum/nickel oxide heterointerfaces with abundant oxygen vacancies enable ampere-level current density ultrastable hydrogen evolution in alkaline. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2211273 (2023)
R. Hou, S. Zhang, Y. Zhang, N. Li, S. Wang, B. Ding, G. Shao, P. Zhang, A “three-region” configuration for enhanced electrochemical kinetics and high-areal capacity lithium-sulfur batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2200302 (2022)
Y. Zhang, Z. Wu, S. Wang, N. Li, S.R.P. Silva, G. Shao, P. Zhang, Complex permittivity-dependent plasma confinement-assisted growth of asymmetric vertical graphene nanofiber membrane for high-performance Li-S full cells. InfoMat 4, e12294 (2022)
L. Luo, C. Liu, Z. Li, L. Zhang, W. Xie, T. Zhang, Z. Chen, Anchoring ultrafine molybdenum phosphide on hierarchical three-dimensional CNTs/rGO framework as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 3175–3185 (2022)
L. Ye, Z. Wen, Reduced graphene oxide supporting hollow bimetallic phosphide nanoparticle hybrids for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Electrochem. Commun. 83, 85–89 (2017)
A. Sebastian, V. Deepthi, I. Sheebha, B. Vidhya, V. Maheskumar, A. Sakunthala, A comparative study on the electrocatalytic and photocatalytic activity of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and doped rGO based Cu5FeS4 composite. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 47, 27541–27554 (2022)
X. Cai, Q. Song, D. Jiao, H. Yu, X. Tan, R. Wang, S. Luo, Bifunctional electrocatalysts of CoFeP/rGO heterostructure for water splitting. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 47, 39499–39508 (2022)
D. Mukherjee, P.M. Austeria, S. Sampath, Two-dimensional, few-layer phosphochalcogenide, FePS3: a new catalyst for electrochemical hydrogen evolution over wide pH range. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 367–372 (2016)
C. Gong, G. Lee, B. Shan, E.M. Vogel, R.M. Wallace, K. Cho, First-principles study of metal–graphene interfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 123711 (2010)
H. Qiao, Z. Huang, X. Ren, H. Yao, S. Luo, P. Tang, X. Qi, J. Zhong, Photoresponse improvement in liquid-exfoliated SnSe nanosheets by reduced graphene oxide hybridization. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 4371–4377 (2017)
K.N. Kudin, B. Ozbas, H.C. Schniepp, R.K. Prud’homme, I.A. Aksay, R. Car, Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 8, 36–41 (2008)
S. Stankovich, D.A. Dikin, R.D. Piner, K.A. Kohlhaas, A. Kleinhammes, Y. Jia, Y. Wu, S.T. Nguyen, R.S. Ruoff, Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45, 1558–1565 (2007)
Y. Li, H. Wang, L. Xie, Y. Liang, G. Hong, H. Dai, MoS2 nanoparticles grown on graphene: an advanced catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 7296–7299 (2011)
A. Lasia, Mechanism and kinetics of the hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44, 19484–19518 (2019)
C.-Z. Yuan, K.S. Hui, H. Yin, S. Zhu, J. Zhang, X.-L. Wu, X. Hong, W. Zhou, X. Fan, F. Bin, F. Chen, K.N. Hui, Regulating intrinsic electronic structures of transition-metal-based catalysts and the potential applications for electrocatalytic water splitting. ACS Mater. Lett. 3, 752–780 (2021)
W. Shen, L. Ge, Y. Sun, F. Liao, L. Xu, Q. Dang, Z. Kang, M. Shao, Rhodium nanoparticles/F-doped graphene composites as multifunctional electrocatalyst superior to Pt/C for hydrogen evolution and formic acid oxidation reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 33153–33161 (2018)
D. Han, N. Gao, J. Ge, C. Liu, W. Xing, Activating MoS2 via electronic structure modulation and phase engineering for hydrogen evolution reaction. Catal. Commun. 164, 1046 (2022)
X. Zhang, H. Fei, Z. Wu, D. Wang, A facile preparation of WS2 nanosheets as a highly effective HER catalyst. Tungsten 1, 101–109 (2019)
N. Sen, A. Das, S. Maity, S. Ghosh, M. Samanta, K.K. Chattopadhyay, Tailoring the Sb2Se3/rGO heterointerfaces for modulation of electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution performances in acidic media. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 6, 58–67 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Grants from Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Hunan (No. 2022JJ30553, 2021JJ40524), Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (Nos. 21A0080, 19C1746), Suzhou key industrial technology innovation project (SYG201921), Hunan Key Laboratory of Two-Dimensional Materials (No. 2018TP1010), and Program of Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT-17R91).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed to this study. CL contributed to original draft writing, material preparation and electrochemical test. HQ contributed to investigation and writing editing. YL contributed to formal analysis and methodology. ZH contributed to writing—review and administration, SL contributed to characterization test. ZW contributed to investigation. XQ contributed to investigation and writing editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate that there is no conflict of interest in all aspects of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Qiao, H., Liu, Y. et al. SnSe nanosheet hybridized with reduced graphene oxide for enhanced hydrogen revolution reaction. Appl. Phys. A 129, 426 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06690-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06690-2