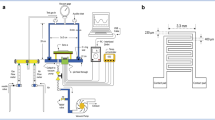
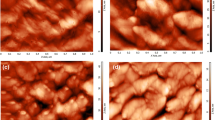
Abstract
ZnO thin films were made to grow on soda lime glass substrate through a two-step technique. The successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method (SILAR) at room temperature was employed by varying the number of SILAR cycles from 50 to 125 in steps of 25 on a ZnO seed layer deposited through nebulizer assisted spray pyrolysis technique (NSP). The characteristics of the two-step deposited films were studied with a quest for improvement when compared to ZnO thin films prepared through single step chemical processing techniques. All the prepared films are observed to be polycrystalline, with hexagonal crystal structure and preferential orientation of grains along (002) direction as per XRD analysis. The size of the crystallites grown along the (002) plane seems to increase with the number of dip cycles, reaching a maximum at 100 dip cycles. Furthermore increase in the film thickness causes the crystallite size to decrease. The 940 nm thick film had the lowest strain and dislocation density values, affirmed through structural characteristics. The surface morphology of the two-step processed ZnO thin films is observed to change with the film thickness as evidenced from HRSEM observations. The average elemental percentage ratio of Zn and O atoms in the deposited ZnO films was estimated using EDAX. Optical tests show a decrement in the band gap energy from 3.30 to 2.80 eV as the dip cycle is varied. The film with better characteristic properties is used to detect the presence of ammonia gas. This study shows that there is a definite variation in the ammonia detecting capability of the gas sensor when the active layer is produced through suggested two-step process. According to the impedance spectroscopy investigation, the grain boundary resistance reduces as ammonia concentration rises up to 250 ppm, with a maximum response observed for the film deposited with 100 dip cycles.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the authors on reasonable request
References
K. Liu, M. Sakurai, M. Aono, ZnO-based ultraviolet photo detectors. Sensors 10(9), 8604–8634 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3390/s100908604
K. Ravichandran, A. Manivasaham, K. Subha, A. Chandrabose, R. Mariappan, Cost effective nebulizer sprayed ZnO thin films for enhanced ammonia gas sensing-effect of deposition temperature. Surf. Interfaces 1–3, 13–20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2016.06.004
N.K. Sidhu, A.C. Rastogi, Vertically aligned ZnO nanorod core-polypyrrole conducting polymer sheath and nanotube arrays for electrochemical supercapacitor energy storage. Nano Scale Res. Lett. 9(1), 453 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-453
B. Timmer, W. Olthuis, A. Van Den Berg, Ammonia sensors and their applications—a review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 107, 666–677 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.11.054
S.G. Sazhin, E.I. Soborover, S.V. Tokarev, Sensor methods of ammonia inspection. Russ. J. Non Destruct. Test 39, 791–806 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUNT.0000020251.56686.a5
J.W. Erisman, M.A. Sutton, J. Galloway, Z. Klimont, W. Winiwarter, How a century of ammonia synthesis changed the world. Nat. Geosci. 1, 636–639 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo325
Y. Alarie, Dose–response analysis in animal studies: prediction of human responses. Environ. Health Perspect. 42, 9–13 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.81429
K. Wetchakun, T. Samerjai, N. Tamaekong, C. Liewhiran, C. Siriwong, V. Kruefu, A. Wisitsoraat, A. Tuantranontb, S. Phanichphant, Semiconducting metal oxides as sensors for environmentally hazardous gases. Sens. Actuators B 160, 580–591 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2011.08.032
Y.-F. Sun, S.-B. Liu, F.-L. Meng, J.-Y. Liu, Z. Jin, L.-T. Kong, Metal oxide nano structures and their gas sensing properties: a review. Sensors 12, 2610–2631 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3390/s120302610
C. Cachoncinlle, C. Hebert, J. Perriere, M. Nistor, A. Petit, E. Millon, Random lasing of ZnO thin films grown by pulsed-laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 336, 103–119 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.09.186
F.H. Wang, C.L. Chang, Effect of substrate temperature on transparent conducting Al and F co-doped ZnO thin films prepared by rf magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 370, 83–91 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.161
P. Samadipakchin, H.R. Mortaheb, A. Zolfaghari, ZnO nanotubes: preparation and photocatalytic performance evaluation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 337, 91–99 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.01.018
Y. Qu, T.A. Gessert, T.J. Coutts, R. Naufi, Study of ion beam-sputtered, ZnO films as a function of deposition temperature. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 12, 1507–1512 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.579346
Y. Dali, H. Ming, L. Shenyu, L. Jiran, W. Yaqiao, M. Shangyun, Electrochemical deposition of ZnO nanostructures onto porous silicon and their enhanced gas sensing to NO2 at room temperature. Electrochim. Acta 115, 297–305 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.10.007
Y.H. Navale, S.T. Navale, F.J. Stadler, N.S. Ramgir, V.B. Patil, Thermally evaporated copper oxide films: a view of annealing effect on physical and gas sensing properties. Ceram. Int. 43, 7057–7064 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.02.135
J. Hu, R.G. Gordon, Textured aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films from atmospheric pressure chemical-vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 71, 880–890 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.351309
K. Muthukrishnan, M. Vanaraja, S. Boomadevi, R.K. Karn, K. Pandiya, Studies on acetone sensing characteristics of ZnO thin film prepared by sol–gel dip coating. J. Alloys Compd. 673, 138–143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.02.222
V.G. Krishnan, P. Elango, Influence of Ba doping concentration on the physical properties and gas sensing performance of ZnO nanocrystalline films: automated nebulizer spray pyrolysis (ANSP) method. Optik 141, 83–89 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.05.045
I. Muniyandi, G.K. Mani, P. Shankar, J.B.B. Rayappann, Effect of nickel doping on structural, optical, electrical and ethanol sensing properties of spray deposited nano structured ZnO thin films. Ceram. Int. 40, 7993–8001 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.150
R. Mariappan, V. Ponnuswamy, R. Suresh, P. Suresh, A. Chandra Bose, M. Ragavendar, Role of substrate temperature on the properties of Na-doped ZnO thin film nanorods and performance of ammonia gas sensors using nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 387–391 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.048
V.L. Patil, S.A. Vanalakar, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Fabrication of nano structured ZnO thin films based NO2 gas sensor via SILAR technique. Sens. Actuators B 239, 1185–1193 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.130
A.C. Nwanya, P.R. Deshmukh, R.U. Osuji, M. Maaza, C.D. Lokhande, F.I. Ezema, Synthesis, characterization and gas-sensing properties of SILAR deposited ZnO–CdO nano-composite thin film. Sens. Actuators B 206, 671–678 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.111
T. Çorlu, I. Karaduman, S. Galioglu, B. Akata, M.A. Yıldırım, A. Ateş, S. Acar, Low level no gas sensing properties Of Cu doped Zno thin films prepared by Silar method. Mater. Lett. 212, 292–295 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.10.121
M.P. Suryawanshi, S.W. Shin, U.V. Ghorpade, K.V. Gurav, C.W. Hong, G.L. Agawane, S.A. Vanalakar, J.H. Moon, J.H. Yun, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, A.V. Moholkar, Improved photoelectrochemical performance of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films prepared using modified successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) sequence. Electrochim. Acta 150, 136–145 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.10.124
A. Tricoli, M. Righettoni, A. Teleki, Semiconductor gas sensors: dry synthesis and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 7632–7659 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200903801
X. Wang, F. Sun, Y. Duan, Z. Yin, W. Luo, Y.A. Huang, J. Chen, Highly sensitive, temperature-dependent gas sensor based on hierarchical ZnO nanorod arrays. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 11397–21140 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TC02187A
Y. Morinaga, K. Sakuragi, N. Fujimura, T. Ito, Effect of Ce doping on the growth of ZnO thin films. J. Cryst. Growth 174, 691–695 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(97)00045-6
A. Raidou, F. Benmalek, T. Sall, M. Aggour, A. Qachaou, L. Laanab, M. Fahoume, The influence of rinsing period on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films. Opt. Quant Electron. 46, 171–178 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-013-9737-6
K.P. Misra, R.K. Shukla, A. Srivastava, A. Srivastava, Blue shift in optical band gap in nano crystalline Zn1xCaxO films deposited by sol-gel method. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 31901 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3184789
S.B. Jambure, S.J. Patil, A.R. Deshpande, C.D. Lokhande, A comparative study of physico-chemical properties of CBD and SILAR grown ZnO thin films. Mater. Res. Bull. 49, 420–425 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.09.007
R. Mariappan, M. Ragavendar, V. Ponnuswamy, Growth and characterization of chemical bath deposited Cd1-xZnxS thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 7337–7343 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.04.088
M. Balaji, J. Chandrasekaran, M. Raja, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 43, 104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.12.009
D. Iskenderoglu, H. Guney, M.E. Gulduren, A comprehensive study on SILAR grown on cobalt doped CdO. Optik 254, 168658 (2022)
G. Yergaliuly, B. Soltabayev, S. Kalybekkyzy, Z. Bakenov, A. Mentbayeva, Effect of thickness and reaction media on properties of ZnO thin films by SILAR. Sci Rep 12, 851 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-04782-2
B.C. Ghos, S.F.U. Farhad, M.A.M. Patwary, S. Majumder, M.A. Hossain, N.I. Tanvir, M.A. Rahman, T. Tanaka, Q. Guo, Influence of the substrate, process conditions, and postannealing temperature on the properties of ZnO thin films grown by the successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method. ACS Omega 6(4), 2665–2674 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c04837
R. Bhargava, P.K. Sharma, S. Kumar, A.C. Pandey, N. Kumar, Consequence of doping mediated strain and the activation energy on the structural and optical properties of ZnO: Cr nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 183, 1400–1408 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2010.04.014
R. Nisha, K.N. Madhusoodanan, T.V. Vimalkumar, K.P. Vijayakumar, Gas sensing application of nanocrystalline zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Bull. Mater. Sci. 38(3), 583–591 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-015-0911-2
M. Heshmat, H. Abdizadeh, M.R. Golobostanfard, Sonochemical assisted synthesis of ZnO nanostructured thin films prepared by sol-gel method. Procedia Mater. Sci. 11, 486–490 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2015.11.070
C. Jayachandraiah, G. Krishnaiah, Erbium induced Raman studies and dielectric properties of Er-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Lett. 6(8), 743–748 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5185/amlett.2015.5801
S. Bouhouche, F. Bensouici, M. Toubane, A. Azizi, A. Otmani, K. Chebout, F. Kezzoula, R. Tala-Ighil, M. Bououdina, Effect of Er3þ doping on structural, morphological and photocatalytical properties of ZnO thin films. Mater. Res. Express 5, 056407 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aac4e8
A. Hastir, N. Kohli, R.C. Singh, Comparative study on gas sensing properties of rare earth (Tb, Dy and Er) doped ZnO sensor. J. Phys. Chem. Solid. 105, 23–34 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2017.02.004
M. Dehimi, T. Touam, A. Chelouche, F. Boudjouan, D. Djouadi, J. Solard, A. Fischer, A. Boudrioua, A. Doghmane, Effects of low Ag doping on physical and optical waveguide properties of highly oriented sol-gel ZnO thin films. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2015(74028), 1–10 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/740208
K. Ravichandran, R. Mohan, N.J. Begum, S. Snega, K. Swaminathan, C. Ravidhas, B. Sakthivel, S. Varadharajaperumal, Impact of spray flux density and vacuum annealing on the transparent conducting properties of doubly doped (Sn þ F) zinc oxide films deposited using a simplified spray technique. Vacuum 107, 68–76 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2014.03.029
K. Deva, A. Kumar, S. Valanarasu, J.S. Ponraj, B.J. Fernandes, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, P. Murahari, K. Ramesh, Effect of Er doping on the ammonia sensing properties of ZnO thin films prepared by a nebulizer spray technique. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 144, 109513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109513
K. Shingange, Z.P. Tshabalala, O.M. Ntwaeaborwa, D.E. Motaung, G.H. Mhlongo, Highly selective NH3 gas sensor based on Au loaded ZnO nanostructures prepared using microwave-as sisted method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 479, 127–138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.06.046
M.R. Alenezi, A.S. Alshammari, K.D.G.I. Jayawardena, M.J. Beliatis, S.J. Henley, S.R.P. Silva, Role of the exposed polar facets in the performance of thermally and UV activated ZnO nanostructured gas sensors. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 17850–17858 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4061895
K.R. Devi, G. Selvan, M. Karunakaran, K. Kasirajan, L.B. Chandrasekar, M. Shkir, AlFaify S SILAR-coated Mg-doped ZnO thin films for ammonia vapor sensing applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 10186–10195 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03564-8
J. Huang, D. Jiang, J. Zhou, J. Ye, Y. Sun, X. Li, Y. Geng, J. Wang, Y. Du, Z. Qian, Visible light-activated room temperature NH3 sensor base on CuPc-loaded ZnO nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 327, 128911 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128911
L.H. Kathwate, G. Umadevi, P.M. Kulal, P. Nagaraju, D.P. Dubal, A.K. Nanjundan, V.D. Mote, Ammonia gas sensing properties of Al doped ZnO thin films. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 313, 112193 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.112193
G.K. Mani, J.B.B. Rayappan, Selective detection of ammonia using spray pyrolysis deposited pure and nickel doped ZnO thin film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 311, 405–412 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.05.075
G.K. Mani, J.B.B. Rayappan, A highly selective room temperature ammonia sensor using spray deposited zinc oxide thin film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 183, 459–466 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.03.132
G.K. Mani, J.B.B. Rayappan, Novel and facile synthesis of randomly interconnected ZnO nano platelets using spray pyrolysis and their room temperature sensing characteristics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 198, 125–133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.02.101
I.L. Poul Raj, S. Gobalakrishnan, P.K. Praseetha, N. Chidhambaram, S. Saravanakumar, V. Ganesh, S. AlFaify, H. Algarni, I.S. Yahia, Improved ammonia vapor sensing properties of Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel process. Phys. Scr. 96, 85802 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/abfb22
N. Rajappan, K.N. Madhusoodanan, T. Vimalkumar, K. Vijayakumar, Gas sensing application of nano crystalline zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Bull. Mater. Sci. 38, 583–591 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-015-0911-2
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at KKU for funding to carry this work through the research groups program under Grant number R.G.P. 2/147/43.
Funding
.The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at KKU for funding to carry this work through the research groups program under Grant number R.G.P. 2/147/43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study, conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by KVG, PM, RB, VG, SR and RT. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Dr. AMSA and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The work described in the present article has not been published previously. It is not under consideration/submitted for publication elsewhere. Its publication is approved by all authors and tacitly or explicitly by the responsible authorities where the work was carried out. That, if accepted, it will not be published elsewhere including electronically in the same form, in English or in any other language, without the written consent of the copyright-holder. All authors have checked the manuscript and have agreed to the submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interests exist between the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arulanantham, A.M.S., Gunavathy, K.V., Mohan raj, P. et al. Noticeable gas sensing properties of ZnO nano-crystallites using two-step preparation technique. Appl. Phys. A 129, 290 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06556-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06556-7