Abstract
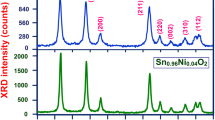
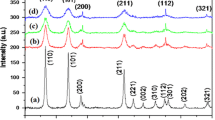
In this work, the un-doped, Cu-doped, and (Ni, Cu) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized using the sol–gel method with a fixed concentration of copper dopant while varying the nickel concentrations. The structural, optical and electrical properties, as well as the surface morphology, were investigated systematically by various characterization techniques. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) study confirmed that the prepared samples had a tetragonal rutile crystal structure for all single-doped/co-doped and un-doped SnO2 NPs. The XRD results further confirmed that the crystalline sizes varied from 16 to 10 nm with the concentrations of the dopants. The UV–Vis diffusion reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) analysis showed that the optical band gap was found to be decreased from 3.38 to 3.27 eV when the dopant concentrations were increased. The energy dispersive analysis of X-ray spectra (EDX) results confirmed the presence of the expected elements in the prepared samples. Three major photoluminescence (PL) emission peaks were observed in the visible region, with a small shift toward lower wavelengths with dopant and co-dopant concentrations. Chemical bonding and the position of the O–Sn–O bond at 600–660 cm−1 were confirmed by the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) study. The activation energies and conduction mechanisms of the prepared samples were investigated using the Hall Effect measurement method. The I–V studies confirmed that the prepared samples had a good ohmic contact behavior and the resistivity decreased significantly for co-doped sample.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Pascariu Dorneanu, A. Airinei, M. Grigoras, N. Fifere, L. Sacarescu, N. Lupu, L. Stoleriu, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Alloy Compd. 668, 65–72 (2016)
B. Venugopal, B. Nandan, A. Ayyachamy, V. Balaji, S. Amirthapandian, B.K. Panigrahi, T. Paramasivam, Influence of manganese ions in the band gap of tin oxide nanoparticles: structure, microstructure and optical studies. RSC Adv. 4, 6141–6150 (2014)
V. Kumar, K. Singh, J. Sharma, A. Kumar, A. Vij, A. Thakur, Zn-doped SnO2 nanostructures: structural, morphological and spectroscopic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. 28(24), 18849–18856 (2017)
M. Batzill, U. Diebold, the surface and materials science of tin oxide. Prog. Surf. Sci. 79, 47–154 (2005)
M.P. Subramaniam, G. Arunachalam, R. Kandasamy, P. Veluswamy, I. Hiroya, Effect of pH and annealing temperature on the properties of tin oxide nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel method. J. Mater. Sci-Mater. El. 29, 658–666 (2018)
E. Shanthi, V. Dutta, A.S. Banerjee, K.L. Chopra, Electrical and optical properties of undoped and antimony-doped tin oxide films. J. Appl. Phys. 51(12), 6243–6251 (1980)
C. Mrabet, A. Boukhachem, M. Amlouk, T. Manoubi, Improvement of the optoelectronic properties of tin oxide transparent conductive thin films through lanthanum doping. J. Alloy Compd. 666, 392–405 (2016)
E.J. López-Naranjo, L.J. González-Ortiz, L.M. Apátiga, E.M. Rivera-Muñoz, A. Manzano-Ramírez, Transparent electrodes: a review of the use of carbon-based nanomaterials. J Nanomater 2016, 1 (2016)
D. Haridas, V. Gupta, Enhanced response characteristics of SnO2 thin film based sensors loaded with Pd clusters for methane detection. Sens. Actuat. B:Chem 166, 156–164 (2012)
E.T.H. Tan, G.W. Ho, A.S.W. Wong, S. Kawi, A.T.S. Wee, Gas sensing properties of tin oxide nanostructures synthesized via a solid-state reaction method. Nanotechnology 19(25), 255706 (2008)
A. Papaderakis, I. Mintsouli, J. Georgieva, S. Sotiropoulos, Electrocatalysts prepared by galvanic replacement. Catalysts 7(3), 80 (2017)
A.M.A. Maisara, M.K. Khairudin, H. Lee, A.R. Sheikh, Synthesis of tin oxide nanostructures using hydrothermal method and optimization of its crystal size using statistical design of experiment. Procedia Chem. 19, 993–998 (2016)
P. Baraneedharan, S.I. Hussain, V.P. Dinesh, C. Siva, P. Biji, M. Sivakumar, Lattice doped Zn-SnO2 nanospheres: a systematic exploration of dopant ion effects on structural, optical, and enhanced gas sensing properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 1511–1521 (2015)
A.-M. Ungureanu, O. Oprea, B.S. Vasile, C. Andronescu, G. Voicu, I. Jitaru, Temperature effect over structure and photochemical properties of nanostructured SnO2 powders. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 12, 909–917 (2014)
M. Ivanovskaya, E. Ovodok, V. Golovanov, The nature of paramagnetic defects in tin (IV) oxide. Chem. Phys. 457, 98–105 (2015)
G. Singh, R.C. Singh, Synthesis and characterization of Gd-doped SnO2 nanostructures and their enhanced gas sensing properties. Ceram Int. 43, 2350–2360 (2017)
C. Fu, J. Wang, M. Yang, X. Su, J. Xu, B. Jiang, Effect of La doping on microstructure of SnO2 nanopowders prepared by co-precipitation method. J. Non-Cryst Solids. 357, 1172–1176 (2011)
M. Akram, A.T. Saleh, W.A.W. Ibrahim, A.S. Awan, R. Hussain, Continuous microwave flow synthesis (CMFS) of nano-sized tin oxide: Effect of precursor concentration. Ceram Int 42, 8613–8619 (2016)
S.M. Priya, A. Geetha, K. Ramamurthi, Structural, morphological and optical properties of tin oxide nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel method adding hydrochloric acid. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 78, 365–372 (2016)
A.G. Habte, F.G. Hone, F.B. Dejene, Effect of solution pH on structural, optical and morphological properties of SnO2 nanoparticles. Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 580, 411832 (2020)
A.K. Singh, V. Viswanath, V.C. Janu, Synthesis, effect of capping agents, structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 129(8), 874–878 (2009)
R. Adhikari, A.K. Das, D. Karmakar, T.C. Rao, J. Ghatak, Structure and magnetism of Fe-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B. 78(2), 02440 (2008)
H. Jin, Y. Xu, G. Pang, W. Dong, Q. Wan, F.S. SunY, Al-doped SnO2 nanocrystals from hydrothermal systems. Mater. Chem. Phys. 85(1), 58–62 (2004)
N. Salah, S. Habib, A. Azam, M.S. Ansari, W.M. Al-Shawafi, Formation of Mn-doped SnO2 nanoparticles via the microwave technique: structural, optical and electrical properties. Nanomater. Nanotech. 6, 17 (2016)
X. Xu, Y. Tong, J. Zhang, X. Fang, J. Xu, F. Liu, J. Liu, W. Zhong, O.E. Lebedeva, X. Wang, Investigation of lattice capacity effect on Cu2+doped SnO2 solid solution catalysts to promote reaction performance toward NOx-SCR with NH3. Chinese J. Catal. 41(5), 877–888 (2020)
M. Kuppan, S. Kaleemulla, N. MadhusudhanaRao, N. SaiKrishna, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped SnO2 thin films prepared by flash evaporation technique. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 6(3), 1933–1935 (2014)
A. Bouaine, N. Brihi, G. Schmerber, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, S. Colis, A. Dinia, Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Co-doped SnO2 powders synthesized by the coprecipitation technique. J. Phys. Chem. 111(7), 2924–2928 (2007)
J. Divya, A. Pramothkumar, S.J. Gnanamuthu, D.B. Victoria, Structural, optical, electrical and magnetic properties of Cu and Ni doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared via Co-precipitation approach. Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 588, 412169 (2020)
M.A. Basyooni, Y.R. Eker, M. Yilmaz, Structural, optical, electrical and room temperature gas sensing characterizations of spin coated multilayer cobalt-doped tin oxide thin films. Superlattice Micro 140, 106465 (2020)
S. Nilavazhagan, S. Muthukumaran, Investigation of optical and structural properties of Fe, Cu co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Superlattice Micro 83, 507–520 (2015)
S. Bhuvana, H.B. Ramalingam, G. Thilakavathi, K. Vadivel, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of (Ni-Mn) co-doped tin oxide nanoparticles. Mater Technol. 32, 305–309 (2017)
S. Mehraj, M. Shahnawaze Ansari, Alimuddin, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of (Fe, Co) co-doped SnO2 diluted magnetic semiconductor nanostructures. Phys. E. 65, 84–92 (2015)
P.V. Reddy, S.V. Reddy, B.S. Reddy, Synthesis and properties of (Fe, Al) codoped SnO2 nanoparticles. Mater Today: Proc. 3, 1752–1761 (2016)
N. Houaidji, M. Ajili, B. Chouial, N.T. Kamoun, First investigation of structural and optoelectronic properties of F and Ni co-doped SnO2 sprayed thin films. Optik 208, 164026 (2020)
N. Ahmad, S. Khan, Effect of (Mn-Co) co-doping on the structural, morphological, optical, photoluminescence and electrical properties of SnO2. J. Alloys Compd. 720, 502–509 (2017)
M. Duhan, N. Kumar, A. Gupta, A. Singh, H. Kaur, Enhanced room temperature ferromagnetism in Cr and Fe co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel method. Vacuum 181, 109635 (2020)
R. Ramarajan, M. Kovendhan, K. Thangaraju, D.P. Joseph, R.R. Babu, V. Elumalai, Enhanced optical transparency and electrical conductivity of Ba and Sb co-doped SnO2 thin films. J. Alloy Compd. 823, 153709 (2020)
J. Divya, A. Pramothkumar, H.J.L. Hilary, P.J. Jayanthi, P.C. Jobe brabakar, Impact of copper (Cu) and iron (Fe) co-doping on structural, optical, magnetic and electrical properties of tin oxide (SnO2) nanoparticles for optoelectronics applications. J Mater Sci: Mater. Electron. 32, 16755–16785 (2021)
N. Lavanya, C. Sekar, E. Fazio, F. Neri, S.G. Leonardi, G. Neri, Development of a selective hydrogen leak sensor based on chemically doped SnO2 for automotive applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 42(15), 10645–10655 (2017)
S. Zulfiqar, Z. Iqbal, J. Lü, Zn-Cu-codoped SnO2 nanoparticles: structural, optical, and ferromagnetic behaviors. Chin. Phys. B. 26, 126104 (2017)
M. Ashokkumar, S. Muthukumaran, Microstructure, optical and FTIR studies of Ni, Cu co-doped ZnO NPs by co-precipitation method. Opt. Mater. 37, 671–678 (2014)
B. Babu, A.N. Kadam, R.V.S.S.N. Ravikumar, C. Byon, Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of Cu-doped SnO2 quantum dots by solution combustion synthesis. J. Alloy Compd. 703, 330–336 (2017)
A. Abdelkrim, S. Rahmane, O. Abdelouahab, N. Abdelmalek, G. Brahim, Effect of solution concentration on the structural, optical and electrical properties of SnO2 thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Optik 127, 2653–2658 (2016)
P.K. Sharma, R.K. Dutta, A.C. Pandey, Effect of nickel doping concentration on structural and magnetic properties of ultrafine diluted magnetic semiconductor ZnO nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. 321(20), 3457–3461 (2009)
S. Thanikaikarasan, K. Sundaram, T. Mahalingam, S. Velumani, J.K. Rhee, Electrodeposition and characterization of Fe doped CdSe thin films from aqueous solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. 174(1–3), 242–248 (2010)
E.T. Seid, F.B. Dejene, Z.N. Urgessa, J.R. Botha, Refluxed sol–gel synthesized ZnO nanopowder with variable zinc precursor concentration. Appl. Phys. A 124(11), 738 (2018)
B. Rajesh Kumar, B. Hymavathi, X-ray peak profile analysis of solid-state sintered alumina doped zinc oxide ceramics by Williamson-Hall and size-strain plot methods. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 5(2), 94–103 (2017)
P.V. Reddy, S.V. Reddy, B.S. Reddy, Synthesis and properties of (Fe, Al) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Today: Proc. 3(6), 1752–1761 (2016). (Eram Soc .5: 94–103)
N. Sergent, P. Gélin, L. Périer-Camby, H. Praliaud, G. Thomas, Preparation and characterisation of high surface area stannic oxides: structural, textural and semiconducting properties. Sensor Actuat. B- Chem. 84, 176–188 (2002)
N. Ahmad, S. Khan, Effect of (Mn-Co) co-doping on the structural, morphological, optical, photoluminescence and electrical properties of SnO2. J. Alloy Compd. 720, 502–509 (2017)
M. Shu, X. Li, Electrospun MnxCo0.5−xSn0.5O2 and SnO2 porous nanofibers and nanoparticles as anode materials for lithium-ion battery. J Nanopart Res. 21, 179 (2019)
F.G. Hone, F.B. Dejene, L.F. Koao, Tailoring optical and electrical properties of ternary Pb1− xCoxS thin films synthesized from a combination of two complexing agents. Indian J. Phys 95(9), 1763–1773 (2021)
K.J. Kim, Y.R. Park, Spectroscopic ellipsometry study of optical transitions in Zn 1–x Cox O alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81(8), 1420–1422 (2002)
A.G. Habte, F.G. Hone, F.B. Dejene, Zn doping effect on the properties of SnO2 nanostructure by co-precipitation technique. Appl. Phys. A 125, 402 (2019)
P. Baraneedharan, S.I. Hussain, V.P. Dinesh, C. Siva, P. Biji, M. Sivakumar, Lattice doped Zn–SnO2 nanospheres: a systematic exploration of dopant ion effects on structural, optical, and enhanced gas sensing properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 1511–1521 (2015)
S. Suwanboon, T. Ratana, T. Ratana, Effects of Al and Mn dopant on structural and optical properties of ZnO thin film prepared by sol-gel route. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 4(1), 111–121 (2007)
S. Bansal, D.K. Pandya, S.C. Kashyap, D. Haranath, Growth ambient dependence of defects, structural disorder and photoluminescence in SnO2 films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. J. Alloys Compd. 583, 186–190 (2014)
A. Kar, A. Patra, Optical and electrical properties of Eu3+-doped SnO2 nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113(11), 4375–4380 (2009)
E.J. Lee, C. Ribeiro, T.R. Giraldi, E. Longo, E.R. Leite, J.A. Varela, Photoluminescence in quantum-confined SnO2 nanocrystals: evidence of free exciton decay. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(10), 1745–1747 (2004)
W.S.F. GuF, M.K. Lü, X.F. Cheng, S.W. Liu, G.J. Zhou, D.R. Yuan, Luminescence of SnO2 thin films prepared by spin-coating method. J. Cryst. Growth 262(1–4), 182–185 (2004)
F. Gu, S.F. Wang, M.K. Lü, G.J. Zhou, D. Xu, D.R. Yuan, Photoluminescence properties of SnO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol− gel method. J. Phys. Chem 108(24), 8119–8123 (2004)
A.S.H. Hameed, C. Karthikeyan, A.P. Ahamed, N. Thajuddin, N.S. Alharbi, S.A. Alharbi, G. Ravi, In vitro antibacterial activity of ZnO and Nd- doped ZnO nanoparticles against ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 1–11 (2016)
R.K. Mishra, A. Kushwaha, P.P. Sahay, Influence of Cu doping on the structural, photoluminescence and formaldehyde sensing properties of SnO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 4(8), 3904–3912 (2014)
C.T. Lee, Fabrication methods and luminescent properties of ZnO materials for light-emitting diodes. Mater. 3(4), 2218–2259 (2010)
I. AlivovY, M.V. Chukichev, V.A. Nikitenko, Green luminescence band of zinc oxide films copper-doped by thermal diffusion. J. Semicond. 38(1), 31–35 (2004)
F.H. Leiter, H.R. Alves, A. Hofstaetter, D.M. Hofmann, B.K. Meyer, Rapid research notes-the oxygen vacancy as the origin of a green emission in undoped ZnO. Phys. Status Solidi. 226(1), R4 (2001)
A. Rahmati, A.B. Sirgani, M. Molaei, M. Karimipour, Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by simple co-precipitation route. Eur Phys J Plus. 129, 250 (2014)
N. Shanmugam, T. Sathya, G. Viruthagiri, C. Kalyanasundaram, R. Gobi, S. Ragupathy, Photocatalytic degradation of brilliant green using undoped and Zn doped SnO2 nanoparticles under sunlight irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 360, 283–290 (2016)
D. Das, R. Banerjee, Properties of electron-beam-evaporated tin oxide films. Thin Solid Films 147(3), 321–331 (1987)
J. Bruneaux, H. Cachet, M. Froment, A. Messad, Correlation between structural and electrical properties of sprayed tin oxide films with and without fluorine doping. Thin Solid Films 197(1–2), 129–142 (1991)
H. Sefardjella, B. Boudjema, A. Kabir, G. Schmerber, Structural and photoluminescence properties of SnO2 obtained by thermal oxidation of evaporated Sn thin films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13(9), 1971–1974 (2013)
J.H. Bang, N. Lee, A. Mirzaei, M.S. Choi, H.G. Na, C. Jin, H.W. Kim, Effect of microwave irradiation on the electrical and optical properties of SnO2 thin films. Ceram Int. 45(6), 7723–7729 (2019)
F. Yakuphanoglu, Electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient and optical properties of SnO2 film deposited on ITO by dip coating. J. Alloys Compd. 470(1–2), 55–59 (2009)
J.L.G. Fierro, Metal oxides: chemistry and applications. Mater. Today. 8(12), 59 (2005)
L. Soussi, T. Garmim, O. Karzazi, A. Rmili, A. El Bachiri, A. Louardi, H. Erguig, Effect of (Co, Fe, Ni) doping on structural, optical and electrical properties of sprayed SnO2 thin film. Surf. Interfaces. 19, 100467 (2020)
F.G. Hone, N.A. Tegegne, F.B. Dejene, D.M. Andoshe, Nanofiber cadmium oxide thin films prepared from ethanolamine complexing agent by solution growth method. Optik 243, 167402 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author Dr Fekadu Gahsw is acknowledge the support from Addis Ababa University thematic research project (Grant Ref. LT/PY-242/2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lachore, W.L., Andoshe, D.M., Hone, F.G. et al. Structural, optical and electrical properties of copper (Cu) and [nickel (Ni), copper]: co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. Appl. Phys. A 128, 515 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05655-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05655-1