Abstract
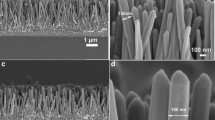
In this paper, we study, as a first part, the current density effect on ZnO nanosheets formed through electrochemical deposition. The films are elaborated galvanostatically in a nitrate solution that contain 80 mM \(\hbox {Zn}{(\hbox {NO}_3)}_2\) and 100 mM \((\hbox {KNO}_3)\), by applying current densities of range (\(-0.5\,\hbox {mA}\,\hbox {cm}^{-2}\) and \(-3\,\hbox {mA}\,\hbox {cm}^{-2}\)). The ZnO nanosheets elaborated under \(-2\,\hbox {mA}\,\hbox {cm}^{-2}\) reached a donor density charge of about \(5.36\times 10^{20}\,\hbox {cm}^{-2}\), and photoresponse around \(30\,\upmu \hbox {A}\,\hbox {cm}^{-2}\). As a second part, we study the mode effect onto the ZnO nanosheets and the ZnO nanowires. When the mode transformed from potentio to galvano, the crystallization, the optical transmittance were ameliorated, as well as, the donor carrier density significantly improved. However, under potentiostatic approach, the diameter and the length of the nanowires have been extended. The significant effects on the electrochemical proprieties are collected from Mott–Schottky measurement and photocurrent analyses. Whereas, the structural, optical, and morphological proprieties are obtained through X-ray diffraction, UV–Vis spectrophotometer, Atomic force microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy.
Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Klingshirn, ZnO: from basics towards applications. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 244(9), 3027–3073 (2007)
G. Malik, S. Mourya, J. Jaiswal, R. Chandra, Effect of annealing parameters on optoelectronic properties of highly ordered ZnO thin films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 100, 200–213 (2019)
A. Sarkar, A.K. Katiyar, A.K. Das, S.K. Ray, Si membrane-ZnO heterojunction-based broad band visible light emitting diode for flexible optoelectronic devices. Flex. Print. Electron. 3(2), 025004 (2018)
K. Li, R. Kondrotas, C. Chen, S. Lu, X. Wen, D. Li, J. Luo, Y. Zhao, J. Tang, Improved efficiency by insertion of Zn1–xMgxO through sol–gel method in ZnO/Sb2Se3 solar cell. Sol. Energy 167, 10–17 (2018)
S. Karuppuchamy, K. Nonomura, T. Yoshida, T. Sugiura, H. Minoura, Cathodic electrodeposition of oxide semiconductor thin films and their application to dye-sensitized solar cells. Solid State Ion. 151(1–4), 19–27 (2002)
F. Rahman, Zinc oxide light-emitting diodes: a review. Opt. Eng. 58(1), 010901 (2019)
G. Eda, G. Fanchini, M. Chhowalla, Large-area ultrathin films of reduced graphene oxide as a transparent and flexible electronic material. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3(5), 270–274 (2008)
X. Wang, L. Zhi, K. Müllen, Transparent, conductive graphene electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Lett. 8(1), 323–327 (2008)
Z. Yin, S. Wu, X. Zhou, X. Huang, Q. Zhang, F. Boey, H. Zhang, Electrochemical deposition of ZnO nanorods on transparent reduced graphene oxide electrodes for hybrid solar cells. Small 6(2), 307–312 (2010)
W.I. Park, C.-H. Lee, J.M. Lee, N.-J. Kim, G.-C. Yi, Inorganic nanostructures grown on graphene layers. Nanoscale 3(9), 3522–3533 (2011)
M. Izaki, T. Omi, Transparent zinc oxide films prepared by electrochemical reaction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68(17), 2439–2440 (1996)
S. Peulon, D. Lincot, Cathodic electrodeposition from aqueous solution of dense or open-structured zinc oxide films. Adv. Mater. 8(2), 166–170 (1996)
Y. Leprince-Wang, A. Yacoubi-Ouslim, G. Wang, Structure study of electrodeposited ZnO nanowires. Microelectron. J. 36(7), 625–628 (2005)
O. Lupan, T. Pauporté, B. Viana, I. Tiginyanu, V. Ursaki, R. Cortes, Epitaxial electrodeposition of ZnO nanowire arrays on p-GAN for efficient UV-light-emitting diode fabrication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2(7), 2083–2090 (2010)
M. Izaki, T. Shinagawa, K.-T. Mizuno, Y. Ida, M. Inaba, A. Tasaka, Electrochemically constructed p-Cu2O/n-ZnO heterojunction diode for photovoltaic device. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40(11), 3326 (2007)
D. Pradhan, K.T. Leung, Controlled growth of two-dimensional and one-dimensional ZnO nanostructures on indium tin oxide coated glass by direct electrodeposition. Langmuir 24(17), 9707–9716 (2008)
R. Liu, A.A. Vertegel, E.W. Bohannan, T.A. Sorenson, J.A. Switzer, Epitaxial electrodeposition of zinc oxide nanopillars on single-crystal gold. Chem. Mater. 13(2), 508–512 (2001)
V. Consonni, J. Briscoe, E. Kärber, X. Li, T. Cossuet, ZnO nanowires for solar cells: a comprehensive review. Nanotechnology 30(36), 362001 (2019)
R. Chen, C. Liu, K. Asare-Yeboah, Z. Zhang, Z. He, Y. Liu, Retracted article: Wavelength modulation of ZnO nanowire based organic light-emitting diodes with ultraviolet electroluminescence. RSC Adv. 10(40), 23775–23781 (2020)
S. Zhao, Y. Shen, P. Zhou, F. Hao, X. Xu, S. Gao, D. Wei, Y. Ao, Y. Shen, Enhanced NO2 sensing performance of ZnO nanowires functionalized with ultra-fine In2O3 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 308, 127729 (2020)
T. Yoshida, D. Komatsu, N. Shimokawa, H. Minoura, Mechanism of cathodic electrodeposition of zinc oxide thin films from aqueous zinc nitrate baths. Thin Solid Films 451, 166–169 (2004)
C. Gorla, N. Emanetoglu, S. Liang, W. Mayo, Y. Lu, M. Wraback, H. Shen, Structural, optical, and surface acoustic wave properties of epitaxial ZnO films grown on (0112) sapphire by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 85(5), 2595–2602 (1999)
M. Puchert, P. Timbrell, R. Lamb, Postdeposition annealing of radio frequency magnetron sputtered ZnO films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 14(4), 2220–2230 (1996)
S. Eisermann, A. Kronenberger, M. Dietrich, S. Petznick, A. Laufer, A. Polity, B. Meyer, Hydrogen and nitrogen incorporation in ZnO thin films grown by radio-frequency (RF) sputtering. Thin Solid Films 518(4), 1099–1102 (2009)
C.-W. Kung, H.-W. Chen, C.-Y. Lin, Y.-H. Lai, R. Vittal, K.-C. Ho, Electrochemical synthesis of a double-layer film of ZnO nanosheets/nanoparticles and its application for dye-sensitized solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 22(4), 440–451 (2014)
T. Pauporté, O. Lupan, V. Postica, M. Hoppe, L. Chow, R. Adelung, Al-doped ZnO nanowires by electrochemical deposition for selective VOC nanosensor and nanophotodetector. Phys. status solidi (a) 215(16), 1700824 (2018)
T. Yoshida, J. Zhang, D. Komatsu, S. Sawatani, H. Minoura, T. Pauporté, D. Lincot, T. Oekermann, D. Schlettwein, H. Tada et al., Electrodeposition of inorganic/organic hybrid thin films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19(1), 17–43 (2009)
L. Mentar, O. Baka, M. Khelladi, A. Azizi, S. Velumani, G. Schmerber, A. Dinia, Effect of nitrate concentration on the electrochemical growth and properties of ZnO nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(2), 1217–1224 (2015)
G.E. Timuda, K. Waki, Controlling zno nanosheet morphology by galvanostatic electrodeposition. In: ECS Meeting Abstracts, p. 2122 (2016). IOP Publishing
R. Salazar, C. Lévy-Clément, V. Ivanova, Galvanostatic deposition of ZnO thin films. Electrochim. Acta 78, 547–556 (2012)
G.E. Timuda, K. Waki, Galvanostatic electrodeposition of ZnO nanosheet: effect of different applied current densities and deposition times on the nanosheet morphology. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11(2), 025005 (2020)
M. Stumpp, T. Nguyen, C. Lupo, D. Schlettwein, Interplay of different reaction pathways in the pulsed galvanostatic deposition of zinc oxide. Electrochim. Acta 169, 367–375 (2015)
Y. Zhang, X. Zhong, D. Zhang, W. Duan, X. Li, S. Zheng, J. Wang, TiO2 nanorod arrays/ZnO nanosheets heterostructured photoanode for quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy 166, 371–378 (2018)
H. Yuan, S.A.A.A. Aljneibi, J. Yuan, Y. Wang, H. Liu, J. Fang, C. Tang, X. Yan, H. Cai, Y. Gu et al., ZnO nanosheets abundant in oxygen vacancies derived from metal-organic frameworks for ppb-level gas sensing. Adv. Mater. 31(11), 1807161 (2019)
S.P. Gupta, A.S. Pawbake, B.R. Sathe, D.J. Late, P.S. Walke, Superior humidity sensor and photodetector of mesoporous ZnO nanosheets at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 293, 83–92 (2019)
Z. Sun, T. Liao, Y. Dou, S.M. Hwang, M.-S. Park, L. Jiang, J.H. Kim, S.X. Dou, Generalized self-assembly of scalable two-dimensional transition metal oxide nanosheets. Nat. Commun. 5(1), 1–9 (2014)
R. Ivan, C. Popescu, Á.P. del Pino, C. Logofatu, E. György, Carbon-based nanomaterials and ZnO ternary compound layers grown by laser technique for environmental and energy storage applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 509, 145359 (2020)
Y. Manjula, R.R. Kumar, P.M.S. Raju, G.A. Kumar, T.V. Rao, A. Akshaykranth, P. Supraja, Piezoelectric flexible nanogenerator based on ZnO nanosheet networks for mechanical energy harvesting. Chem. Phys. 533, 110699 (2020)
M. Khelladi, L. Mentar, A. Beniaiche, L. Makhloufi, A. Azizi, A study on electrodeposited zinc oxide nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24(1), 153–159 (2013)
R. Tena-Zaera, J. Elias, G. Wang, C. Levy-Clement, Role of chloride ions on electrochemical deposition of ZnO nanowire arrays from O2 reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(45), 16706–16711 (2007)
J. Elias, R. Tena-Zaera, C. Lévy-Clément, Electrochemical deposition of ZnO nanowire arrays with tailored dimensions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 621(2), 171–177 (2008)
S.J. Limmer, E.A. Kulp, J.A. Switzer, Epitaxial electrodeposition of ZnO on Au (111) from alkaline solution: exploiting amphoterism in Zn(II). Langmuir 22(25), 10535–10539 (2006)
G. Gunawardena, G. Hills, I. Montenegro, B. Scharifker, Electrochemical nucleation part: I. General considerations. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 138(2), 225–239 (1982)
A. Paracchino, N. Mathews, T. Hisatomi, M. Stefik, S.D. Tilley, M. Grätzel, Ultrathin films on copper (I) oxide water splitting photocathodes: a study on performance and stability. Energy Environ. Sci. 5(9), 8673–8681 (2012)
B. Enright, D. Fitzmaurice, Spectroscopic determination of electron and hole effective masses in a nanocrystalline semiconductor film. J. Phys. Chem. 100(3), 1027–1035 (1996)
M. Izaki, T. Omi, Characterization of transparent zinc oxide films prepared by electrochemical reaction. J. Electrochem. Soc. 144(6), 1949 (1997)
T. Yamamoto, T. Shiosaki, A. Kawabata, Characterization of ZnO piezoelectric films prepared by RF planar-magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 51(6), 3113–3120 (1980)
J. Tauc, A. Menth, States in the gap. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 8, 569–585 (1972)
B. Scharifker, G. Hills, Theoretical and experimental studies of multiple nucleation. Electrochim. Acta 28(7), 879–889 (1983)
S. Strbac, R.R. Adžić, The influence of pH on reaction pathways for O2 reduction on the Au (100) face. Electrochim. Acta 41(18), 2903–2908 (1996)
S. Jiang, C. Cui, A. Tseung, Reactive deposition of cobalt electrodes: V. Mechanistic studies of oxygen reduction in unbuffered neutral solutions saturated with oxygen. J. Electrochem. Soc. 138(12), 3599 (1991)
S. Peulon, D. Lincot, Mechanistic study of cathodic electrodeposition of zinc oxide and zinc hydroxychloride films from oxygenated aqueous zinc chloride solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 145(3), 864 (1998)
T. Pauporté, E. Jouanno, F. Pellé, B. Viana, P. Aschehoug, Key growth parameters for the electrodeposition of ZnO films with an intense UV-light emission at room temperature. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(24), 10422–10431 (2009)
R. Könenkamp, K. Boedecker, M.C. Lux-Steiner, M. Poschenrieder, F. Zenia, C. Levy-Clement, S. Wagner, Thin film semiconductor deposition on free-standing ZnO columns. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77(16), 2575–2577 (2000)
H. Rudigier, E. Bergmann, J. Vogel, Properties of ion-plated tin coatings grown at low temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 36(3–4), 675–682 (1988)
W.-Y. Wu, T.-L. Chen, J.-M. Ting, Effects of seed layer precursor type on the synthesis of ZnO nanowires using chemical bath deposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157(8), 177 (2010)
Acknowledgements
Meriem Aloui is grateful to “Laboratoire de Chimie, Ingénierie Moléculaire et Nanostructures” for the technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aloui, M., Mentar, L., Beniaiche, A. et al. Electrochemical and physical properties of ZnO nanosheets and ZnO nanowires, under different applied current densities and deposition approaches. Appl. Phys. A 128, 278 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05389-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05389-0