Abstract
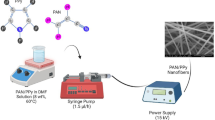
In this study, polyacrilonitrile (PAN) nanofibers obtained by electrospinning were directly coated on the surface of a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) and were investigated for their sensing characteristics against chloroform, dichloromethane and carbon tetrachloride as volatile organic compounds (VOCs). PAN nanofibers were characterized by SEM, DSC, Raman Spectroscopy, and FT-IR and the results indicated that beadless and regular nanofibers with the average diameter of 182.7 ± 32 nm were obtained. Kinetic measurements indicated that electrospun PAN nanofibers were sensitive to the VOCs and they were appropriate for sensing applications of chlorine compounds. The reproducibility of PAN nanofiber sensor was also shown in this study. The results revealed that the diffusion coefficients of VOCs increased with the order carbontetrachloride < dichloromethane < chloroform which was supported by the density functional theory (DFT) simulations that revealed the highest binding energy for chloroform.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Bhardwaj, S.C. Kundu, Electrospinning: a fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 28(3), 325–347 (2010)
M. Gorji, R. Bagherzadeh, H. Fashandi, Electrospun nanofibers in protective clothing. Electrospun. Nanofibers 571–598 (2017)
D. Bjorge, N. Daels, S. De Vrieze, P. Dejans, T. Van Camp, W. Audenaert, J. Hogie, P. Westbroek, K. De Clerck, S.W. Van Hulle, Performance assessment of electrospun nanofibers for filter applications. Desalination 249(3), 942–948 (2009)
R.S. Bhattarai, R.D. Bachu, S.H. Boddu, S. Bhaduri, Biomedical applications of electrospun nanofibers: drug and nanoparticle delivery. Pharmaceutics 11(1), 5 (2019)
A. Haider, S. Haider, I.K. Kang, A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 11(8), 1165–1188 (2018)
A. Ince Yardimci, O. Baskan, S. Yilmaz, G. Mese, E. Ozcivici, Y. Selamet, Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on random and aligned PAN/PPy nanofibrous scaffolds. J. Biomater. Appl. 34(5), 640–650 (2019)
A. Ince Yardimci, H. Aypek, O. Ozturk, S. Yilmaz, E. Ozcivici, G. Mese, Y. Selamet, CNT incorporated polyacrilonitrile/polypyrrole nanofibers as keratinocytes scaffold. J. Biomim. Biomater. Biomed. Eng. 41, 69–81 (2019)
E. Kivrak, A. Ince Yardimci, R. Ilhan, P.B. Kirmizibayrak, S. Yilmaz, P. Kara, Aptamer-based electrochemical biosensing strategy toward human non-small cell lung cancer using polyacrylonitrile/polypyrrole nanofibers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 412(28), 7851–7860 (2020)
Y. Luu, K. Kim, B. Hsiao, B. Chu, M. Hadjiargyrou, Development of a nanostructured DNA delivery scaffold via electrospinning of PLGA and PLA–PEG block copolymers. J. Control. Release 89(2), 341–353 (2003)
J. Doshi, D.H. Reneker, Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrostat. 35(2–3), 151–160 (1995)
K. Sada, K. Kokado, Y. Furukawa, Polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Encycl. Polym. Nanomater. 1745–1750 (2015)
R. Awad, A.H. Mamaghani, Y. Boluk, Z. Hashisho, Synthesis and characterization of electrospun PAN-based activated carbon nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals for adsorption of VOCs. Chem. Eng. J. 410, 128412 (2021)
M. Rahaman, T.K. Chaki, D. Khastgir, High-performance EMI shielding materials based on short carbon fiber-filled ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer, acrylonitrile butadiene copolymer, and their blends. Polym. Compos. 32(11), 1790–1805 (2011)
S. Nataraj, K. Yang, T. Aminabhavi, Polyacrylonitrile-based nanofibers—a state-of-the-art review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 37(3), 487–513 (2012)
A.C.C. Bortolassi, S. Nagarajan, B. de Araújo Lima, V.G. Guerra, M.L. Aguiar, V. Huon, L. Soussan, D. Cornu, P. Miele, M. Bechelany, Efficient nanoparticles removal and bactericidal action of electrospun nanofibers membranes for air filtration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 102, 718–729 (2019)
S. Gu, J. Ren, Q. Wu, Preparation and structures of electrospun PAN nanofibers as a precursor of carbon nanofibers. Synth. Met. 155(1), 157–161 (2005)
A. Mahapatra, N. Garg, B. Nayak, B. Mishra, G. Hota, Studies on the synthesis of electrospun PAN-Ag composite nanofibers for antibacterial application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 124(2), 1178–1185 (2012)
L. Zhang, A. Aboagye, A. Kelkar, C. Lai, H. Fong, A review: carbon nanofibers from electrospun polyacrylonitrile and their applications. J. Mater. Sci. 49(2), 463–480 (2014)
A. Rianjanu, T. Julian, S. Hidayat, E. Suyono, A. Kusumaatmaja, K. Triyana, Polyacrylonitrile nanofiber as polar solvent N, N-dimethyl formamide sensor based on quartz crystal microbalance technique. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1011 (2018)
A. Rianjanu, S. Hidayat, T. Julian, E. Suyono, A. Kusumaatmaja, K. Triyana, Swelling behavior in solvent vapor sensing based on Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) Coated Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofiber. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 367 (2018)
A. Rianjanu, R. Roto, T. Julian, S.N. Hidayat, A. Kusumaatmaja, E.A. Suyono, K. Triyana, Polyacrylonitrile nanofiber-based quartz crystal microbalance for sensitive detection of safrole. Sensors 18(4), 1150 (2018)
A. Rianjanu, K. Triyana, N. Nurbaiti, S.A. Hasanah, A. Kusumaatmaja, R. Roto, An enhanced safrole sensing performance of a polyacrylonitrile nanofiber-based-QCM sensor by overlaying with chitosan. Sains Malays. 48(9), 2041–2049 (2019)
B. Szulczyński, J. Gębicki, Currently commercially available chemical sensors employed for detection of volatile organic compounds in outdoor and indoor air. Environments 4(1), 21 (2017)
J. Wang, E. He, X. Liu, L. Yu, H. Wang, R. Zhang, H. Zhang, High performance hydrazine vapor sensor based on redox mechanism of twisted perylene diimide derivative with lower reduction potential. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 239, 898–905 (2017)
Y. Acikbas, G.D. Tetik, L. Noory, S. Bozkurt, R. Çapan, M. Erdogan, C. Ozkaya, Improvement of sensing properties for polymer based gas sensors via host–guest principles. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 96(3), 315–323 (2020)
S.N. Hidayat, K. Triyana, Optimized back-propagation combined with radial basic neural network for improving performance of the electronic nose: case study on the fermentation process of tempeh. AIP Conf. Proc. 1755, 20001 (2016)
K. He, X. Wang, X. Meng, H. Zheng, S. Suye, Amperometric determination of hydroquinone and catechol on gold electrode modified by direct electrodeposition of poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 193, 212–219 (2014)
N. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Jia, X. Li, J. Yu, B. Ding, Electrospun nanofibrous chitosan membranes modified with polyethyleneimine for formaldehyde detection. Carbohydr. Polym. 108, 192–199 (2014)
N. Horzum, D. Tascioglu, C. Özbek, S. Okur, M.M. Demir, VOC sensors based on a metal oxide nanofibrous membrane/QCM system prepared by electrospinning. New J. Chem. 38(12), 5761–5768 (2014)
H. Karimi-Maleh, O.A. Arotiba, Simultaneous determination of cholesterol, ascorbic acid and uric acid as three essential biological compounds at a carbon paste electrode modified with copper oxide decorated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite and ionic liquid. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 560, 208–212 (2020)
A. Erol, S. Okur, N. Yağmurcukardeş, M.Ç. Arıkan, Humidity-sensing properties of a ZnO nanowire film as measured with a QCM. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 152(1), 115–120 (2011)
Y.F. Sun, S.B. Liu, F.L. Meng, J.Y. Liu, Z. Jin, L.T. Kong, J.H. Liu, Metal oxide nanostructures and their gas sensing properties: a review. Sensors 12(3), 2610–2631 (2012)
K. Triyana, M.S. Mu’min, K. Faizah, Y. Yusuf, A. Kusumaatmaja, Electrospun nanofibers based on polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan and its stability in KOH solution. Mater. Sci. Forum 827, 321–325 (2015)
S. Okur, N. Üzar, N. Tekgüzel, A. Erol, M.Ç. Arıkan, Synthesis and humidity sensing analysis of ZnS nanowires. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 44(6), 1103–1107 (2012)
J. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Perdew, burke, and ernzerhof reply. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80(4), 89 (1998)
G. Kresse, J. Hafner, Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 47(1), 558 (1993)
N. Kaur, V. Kumar, S.R. Dhakate, Synthesis and characterization of multiwalled CNT–PAN based composite carbon nanofibers via electrospinning. Springerplus 5 (483) (2016)
H. Hou, J.J. Ge, J. Zeng, Q. Li, D.H. Reneker, A. Greiner, S.Z. Cheng, Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers containing a high concentration of well-aligned multiwall carbon nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 17(5), 967–973 (2005)
W.X. Zhang, Y.Z. Wang, C.F. Sun, Characterization on oxidative stabilization of polyacrylonitrile nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. J. Polym. Res. 14, 467–474 (2007)
H.S. Kim, Thermal behavior of polyacrylonitrile and Poly(vinylpyrro1idone-graft-acrylonitrile)Blend. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 34(7), 1181–1187 (1996)
C. Kim, Y.I. Jeong, B.T.N. Ngoc, K.S. Yang, M. Kojima, Y.A. Kim, M. Endo, J.W. Lee, Synthesis and characterization of porous carbon nanofibers with hollow cores through the thermal treatment of electrospun copolymeric nanofiber webs. Small 3(1), 91–95 (2007)
J. Li, S. Su, L. Zhou, V. Kundrat, A.M. Abbot, F. Mushtaq, D. Ouyang, D. James, D. Roberts, H. Ye, Carbon nanowalls grown by microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition during the carbonization of polyacrylonitrile fibers. J. Appl. Phys. 113 (2013)
J. Sutasinpromprae, S. Jitjaicham, M. Nithitanakul, C. Meechaisue, P. Supaphol, Preparation and characterization of ultrafine electrospun polyacrylonitrile fibers and their subsequent pyrolysis to carbon fibers. Polym. Int. 55(8), 825–833 (2006)
F. Pashalou, S. Bazigar, M. Tamizifar, S.M.A. Faghihi, S. Zakerifar, Preparation and characterization of carbon nanofibers via electrospun PAN nanofibers. Technol. Text. J. 3(4), 1–10 (2008)
G. Ma, D. Yang, J. Nie, Preparation of porous ultrafine polyacrylonitrile(PAN) fibers by electrospinning. Polym. Adv. Technol. 20(2), 147–150 (2009)
H. Zhang, H. Nie, S. Li, C.J.B. White, L. Zhu, Crosslinking of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/hydroxyethyl cellulose composite nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 63(13–14), 1199–1202 (2009)
Y. Wang, J. Liu, J.Y. Liang, Thermo-chemical reactions of modified PAN fibers during heat-treatment process. Adv. Mater. Res. 11–12, 73–76 (2006)
J. Crank, The mathematics of diffusion (Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 1975)
M. Durmaz, Y. Acikbas, S. Bozkurt, R. Capan, M. Erdogan, C. Ozkaya, A novel Calix[4]arene thiourea decorated with 2-(2- Aminophenyl)benzothiazole moiety as highly selective chemical gas sensor for dichloromethane vapor. Chem. Select. 6, 4670–4676 (2021)
K. Büyükkabasakal, S. Celik Acikbas, A. Deniz, Y. Acikbas, R. Capan, M. Erdogan, Chemical sensor properties and mathematical modeling of graphene oxide langmuir-blodgett thin films. IEEE Sens. J. 19(20), 9097–9104 (2019)
Y. Yua, Q. Maa, J.-b Zhangb, G.-b Liu, Electrospun SiO2 aerogel/polyacrylonitrile composited nanofibers with enhanced adsorption performance of volatile organic compounds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 512, 145697 (2020)
J.C. Ge, J.Y. Kim, S.K. Yoon, N.J. Choi, Fabrication of low-cost and high-performance coal fly ash nanofibrous membranes via electrospinning for the control of harmful substances. Fuel 237, 236–244 (2019)
M. Sajjad, E. Montes, N. Singh, U. Schwingenschlögl, Superior gas sensing properties of monolayer PtSe2. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 4, 1600911 (2017)
D.J. Late, Y.-K. Huang, B. Liu, J. Acharya, S.N. Shirodkar, J. Luo, A. Yan, D. Charles, U.V. Waghmare, V.P. Dravid, C.N.R. Rao, Sensing behavior of atomically thin-layered MoS2 transistors. ACS Nano 7, 4879 (2013)
Acknowledgments
We are very thankful to İzmir Institute of Technology Material Research Center for SEM pictures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ince Yardimci, A., Yagmurcukardes, N., Yagmurcukardes, M. et al. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofiber: preparation, experimental characterization, organic vapor sensing ability and theoretical simulations of binding energies. Appl. Phys. A 128, 173 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05314-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05314-5