Abstract
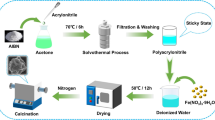
Owing to the urgent need of microwave absorbers in low-frequency range, herein, the core–shell nickel/nickel oxide@carbon nanocomposites with ideal low-frequency absorbing properties were fabricated via a simple solvothermal and pyrolysis approach. The Ni and NiO nanoparticles were wrapped by outer carbon shell, providing abundant defects and interfaces, which is helpful to the dipole and interfacial polarizations. Besides, the conduction loss of the carbon shell and Ni nanoparticles, magnetic losses induced by Ni nanoparticles, core–shell porous structure and proper impedance matching regulated by calcining process could accelerate the absorption of microwave. Importantly, these factors are all strongly influenced by the pyrolysis temperature, and the composite treated under 500 °C shows the maximum reflection loss of − 34.13 dB at 0.85 GHz when the thickness is 3.0 mm, also the broadest effective frequency bandwidth in low frequency range can reach 1.65 GHz at 2.0 mm. Thus, this calcination temperature depended core–shell nickel/nickel oxide@carbon composite provides a feasible way to design absorbers with high performance and thin thickness in low-frequency bands.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Zhang, Z. Jia, B. Wang, X. Wu, T. Sun, X. Liu, L. Bi, G. Wu, Construction of remarkable electromagnetic wave absorber from heterogeneous structure of Co-CoFe2O4@mesoporous hollow carbon spheres. Chem. Eng. J. 421, 129960 (2021)
T. Hou, Z. Jia, B. Wang, H. Li, X. Liu, L. Bi, G. Wu, MXene-based accordion 2D hybrid structure with Co9S8/C/Ti3C2Tx as efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 414, 128875 (2021)
X. Zhou, Z. Jia, X. Zhang, B. Wang, W. Wu, X. Liu, B. Xu, G. Wu, Controllable synthesis of Ni/NiO@porous carbon hybrid composites towards remarkable electromagnetic wave absorption and wide absorption bandwidth. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 87, 120–132 (2021)
Z. Gao, Z. Jia, K. Wang, X. Liu, L. Bi, G. Wu, Simultaneous enhancement of recoverable energy density and efficiency of lead-free relaxor-ferroelectric BNT-based ceramics. Chem. Eng. J. 402, 125951 (2020)
H. Wei, X. Yin, Z. Hou, F. Jiang, H. Xu, M. Li, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, A novel SiC-based microwave absorption ceramic with Sc2Si2O7 as transparent matrix. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(12), 4189–4197 (2018)
J. Yan, Y. Huang, X. Chen, C. Wei, Conducting polymers-NiFe2O4 coated on reduced graphene oxide sheets as electromagnetic (EM) wave absorption materials. Synth. Met. 221, 291–298 (2016)
P. Liu, S. Gao, G. Zhang, Y. Huang, W. You, R. Che, Hollow engineering to Co@N-doped carbon nanocages via synergistic protecting-etching strategy for ultrahigh microwave absorption. Adv. Func. Mater. 31(27), 2102812 (2021)
B. Lu, X. Dong, H. Huang, X. Zhang, X. Zhu, J. Lei, J. Sun, Microwave absorption properties of the core/shell-type iron and nickel nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320(6), 1106–1111 (2008)
D. Liu, R. Qiang, Y. Du, Y. Wang, C. Tian, X. Han, Prussian blue analogues derived magnetic FeCo alloy/carbon composites with tunable chemical composition and enhanced microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 514, 10–20 (2018)
J. Zhou, M. Wang, X. Shu, J. Ma, H. Ren, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, R. Shu, W. Oh, L.B. Kong, Facile synthesis of La-doped cobalt ferrite@glucose-based carbon composite as effective multiband microwave absorber. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 104(5), 2191–2200 (2020)
T. Hou, Z. Jia, A. Feng, Z. Zhou, X. Liu, H. Lv, G. Wu, Hierarchical composite of biomass derived magnetic carbon framework and phytic acid doped polyanilne with prominent electromagnetic wave absorption capacity. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 68, 61–69 (2021)
J. Wang, Z. Jia, X. Liu, J. Dou, B. Xu, B. Wang, G. Wu, Construction of 1D heterostructure NiCo@C/ZnO nanorod with enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Letters 13, 175 (2021)
X. Huang, X. Liu, Z. Jia, B. Wang, X. Wu, G. Wu, Synthesis of 3D cerium oxide/porous carbon for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 1–15 (2021)
F. Zhang, Z. Jia, Z. Wang, C. Zhang, B. Wang, B. Xu, X. Liu, G. Wu, Tailoring nanoparticles composites derived from metal-organic framework as electromagnetic wave absorber. Mater. Today Phys. 20, 100475 (2021)
T. Hou, Z. Jia, B. Wang, H. Li, X. Liu, Q. Chi, G. Wu, Metal-organic framework derived NiSe2-CoSe2@C/Ti3C2Tx composites as electromagnetic wave absorbers. Chem. Eng. J. 422, 130079 (2021)
H. Bai, P. Yin, X. Lu, L. Zhang, W. Wu, X. Feng, J. Wang, J. Dai, Recent advances of magnetism-based microwave absorbing composites: an insight from perspective of typical morphologies. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 46, 1–26 (2020)
Z. Liao, M. Ma, Z. Tong, Y. Bi, K.L. Chung, M. Qiao, Y. Ma, A. Ma, G. Wu, Z. Li, Y. Zhang, Fabrication of one-dimensional ZnFe2O4@carbon@MoS2/FeS2 composites as electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 599, 262–270 (2021)
Z. Liao, M. Ma, Z. Tong, R. Wang, Y. Bi, Y. Chen, K.L. Chung, Y. Ma, Fabrication of ZnFe2O4/C@PPy composites with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 602, 602–611 (2021)
W. Chu, Y. Wang, Y. Du, R. Qiang, C. Tian, X. Han, FeCo alloy nanoparticles supported on ordered mesoporous carbon for enhanced microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 13636–13649 (2017)
T. Liu, Y. Pang, M. Zhu, S. Kobayashi, Microporous Co@CoO nanoparticles with superior microwave absorption properties. Nanoscale 6, 2447–2454 (2014)
W. Liu, L. Liu, G. Ji, D. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Ma, Y. Du, Composition design and structural characterization of MOF-derived composites with controllable electromagnetic properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5(9), 7961–7971 (2017)
Y. Du, T. Liu, B. Yu, H. Gao, P. Xu, J. Wang, X. Wang, X. Han, The electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption of mesoporous carbon. Mater. Chem. Phys. 135(2–3), 884–891 (2012)
H. Zhao, Y. Cheng, H. Lv, G. Ji, Y. Du, A novel hierarchically porous magnetic carbon derived from biomass for strong lightweight microwave absorption. Carbon 142, 245–253 (2019)
P. Liu, C. Zhu, S. Gao, C. Guan, Y. Huang, W. He, N-doped porous carbon nanoplates embedded with CoS2 vertically anchored on carbon cloths for flexible and ultrahigh microwave absorption. Carbon 163, 348–359 (2020)
X. Xie, Y. Pang, H. Kikuchi, T. Liu, The synergistic effects of the carbon coating and micropore structure on the microwave absorption properties of the Co/CoO nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 30507–30514 (2016)
L. Wang, X. Yu, X. Li, J. Zhang, M. Wang, R. Che, MOF-derived yolk-shell Ni@C@ZnO Schottky contact structure for enhanced microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 383, 123099 (2019)
M. Yang, Y. Yuan, W. Yin, S. Yang, Q. Peng, J. Li, Y. Li, X. He, Co/CoO@C nanocomposites with a hierarchical bowknot-like nanostructure for high performance broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 469, 607–616 (2019)
X. Wang, P. Zhou, G. Qiu, X. Zhang, L. Wang, Q. Zhang, M. Wang, Z. Liu, Excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous core-shell Co/CoO@C nanocomposites derived from a needle-shaped Co(OH)2@ZIF-67 template. J. Alloys Compod. 842, 155807 (2020)
P. Yin, L. Zhang, Y. Tang, J. Liu, Earthworm-like (Co/CoO)@C composite derived from MOF for solving the problem of low-frequency microwave radiation. J. Alloys Compd. 881, 160556 (2021)
Z. Tong, Z. Liao, Y. Liu, M. Ma, Y. Bi, W. Huang, Y. Ma, M. Qiao, G. Wu, Hierarchical Fe3O4/Fe@C@MoS2 core-shell nanofibers for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 179, 646–654 (2021)
Y. Bi, M. Ma, Y. Liu, Z. Tong, R. Wang, K.L. Chung, A. Ma, G. Wu, Y. Ma, C. He, P. Liu, L. Hu, Microwave absorption enhancement of 2-dimensional CoZn/C@MoS2@PPy composites derived from metal organic framework. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 600, 209–218 (2021)
Y. Mi, D. Yuan, Y. Liu, J. Zhang, Y. Xiao, Synthesis of hexagonal close-packed nanocrystalline nickel by a thermal reduction process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 89, 359–361 (2005)
C. Li, J. Sui, Z. Zhang, X. Jiang, Z. Zhang, L. Yu, Microwave-assisted synthesis of tremella-like NiCo/C composites for efficient broadband electromagnetic wave absorption at 2–40 GHz. Chem. Eng. J. 375, 122017 (2019)
M. Kong, X. Liu, Z. Jia, B. Wang, X. Wu, G. Wu, Porous magnetic carbon CoFe alloys@ZnO@C composites based on Zn/Co-based bimetallic MOF with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 604, 39–51 (2021)
S. Gao, G. Zhang, Y. Wang, X. Han, Y. Huang, P. Liu, MOFs derived magnetic porous carbon microspheres constructed by core-shell Ni@C with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 88, 56–65 (2021)
X. Shu, H. Ren, Y. Jiang, J. Zhou, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, W. Oh, Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance of silane coupling agent KH55O@Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres/graphere composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 2913–2926 (2020)
J. Gu, W. Dong, S. Xu, Y. Tang, L. Ye, J. Kong, Development of wave-transparent, light-weight composites combined with superior dielectric performance and desirable thermal stabilities. Compos. Sci. Technol. 144, 185–192 (2017)
Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, X. Wu, Z. Deng, E. Zhou, Z. Yu, Nanolayered cobalt@carbon hybrids derived from metal-organic frameworks for microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2, 2325–2335 (2019)
R. Qiang, Y. Du, Y. Wang, N. Wang, C. Tian, J. Ma, P. Xu, X. Han, Rational design of yolk-shell C@C microspheres for the effective enhancement in microwave absorption. Carbon 98, 599–606 (2016)
H. Wei, Z. Zhang, G. Hussain, L. Zhou, Q. Li, K. Ostrikov, Techniques to enhance magnetic permeability in microwave absorbing materials. Appl. Mater. Today 19, 100596 (2020)
M. Qin, L. Zhang, X. Zhao, H. Wu, Lightweight Ni foam-based ultra-broadband electromagnetic wave absorber. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2103436 (2021)
M. Qin, L. Zhang, X. Zhao, H. Wu, Defect induced polarization loss in multi-shelled spinel hollow spheres for electromagnetic wave absorption application. Adv. Sci. 8(8), 2004640 (2021)
J. Ma, J. Shu, W. Cao, M. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Yuan, M. Cao, A green fabrication and variable temperature electromagnetic properties for thermal stable microwave absorption towards flower-like Co3O4@rGO/SiO2 composites. Compos. B Eng. 166, 187–195 (2019)
X. Di, Y. Wang, Y. Fu, X. Wu, P. Wang, Wheat flour-derived nanoporous carbon@ZnFe2O4 hierarchical composite as an outstanding microwave absorber. Carbon 173, 174–184 (2021)
Z. Jia, Z. Guo, A. Feng, Y. Zhang, C. Zhang, G. Nie, K. Wang, G. Wu, Laminated microwave absorbers of A-site cation deficiency perovskite La0.8FeO3 doped at hybrid RGO carbon. Compos. Part B Eng. 176, 107246 (2019)
Y. Wang, X. Di, X. Wu, X. Li, MOF-derived nanoporous carbon/Co/Co3O4/CNTs/RGO composite with hierarchical structure as a high efficiency electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Alloys Compd. 846, 156215 (2020)
X. Zhou, Z. Jia, X. Zhang, B. Wang, X. Liu, B. Xu, L. Bi, G. Wu, Electromagnetic wave absorption performance of NiCo2X4 (X=O, S, Se, Te) spinel structures. Chem. Eng. J. 420, 129907 (2021)
T. Hou, Z. Jia, B. Wang, H. Li, X. Liu, Q. Chi, G. Wu, Metal-organic frameworkderived NiSe2-CoSe2@C/Ti3C2Tx composites as electromagnetic wave absorbers. Chem. Eng. J. 422, 130079 (2021)
X. Gao, Z. Jia, B. Wang, X. Wu, T. Sun, X. Liu, Q. Chi, G. Wu, Synthesis of NiCo-LDH/MXene hybrids with abundant heterojunction surfaces as a lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 419, 130019 (2021)
Z. Mosleh, P. Kameli, A. Poorbaferani, M. Ranjbar, H. Salamati, Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Ce-doped barium hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 397, 101–107 (2016)
N. Li, G. Huang, Y. Li, H. Xiao, Q. Feng, N. Hu, S. Fu, Enhanced microwave absorption performance of coated carbon nanotubes by optimizing the Fe3O4 nanocoating structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(3), 2973–2983 (2017)
Y. Wang, X. Di, X. Gao, X. Wu, Design of MOF-derived hierarchical Co@C@RGO composite with controllable heterogeneous interfaces as a high-efficiency microwave absorber. Nanotechnology 31, 395710 (2020)
P. Liu, S. Gao, G. Zhang, Y. Huang, W. You, R. Che, Hollow engineering to Co@N-doped carbon nanocages via synergistic protecting-etching strategy for ultrahigh microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 2102812 (2021)
F. Xie, F. Jia, L. Zhuo, Z. Lu, L. Si, J. Huang, M. Zhang, Q. Ma, Ultrathin MXene/aramid nanofiber composite paper with excellent mechanical properties for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Nanoscale 11(48), 23382–23391 (2019)
L. Chai, Y. Wang, N. Zhou, Y. Du, X. Zeng, S. Zhou, Q. He, G. Wu, In-situ growth of core-shell ZnFe2O4@porous hollow carbon microspheres as an efficient microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 581, 475–484 (2021)
Y. Cui, Z. Liu, X. Li, J. Ren, Y. Wang, Q. Zhang, B. Zhang, MOF-derived yolk-shell Co@ZnO/Ni@NC nanocage: Structure control and electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 600, 99–110 (2021)
A. Feng, Z. Jia, Y. Zhao, H. Lv, Development of Fe/Fe3O4@C composite with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 745, 547–554 (2018)
X. Jian, X. Xiao, L. Deng, W. Tian, X. Wang, N. Mahmood, S. Dou, Heterostructured nanorings of Fe-Fe3O4@C hybrid with enhanced microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 9369–9378 (2018)
X. Zhu, Y. Dong, F. Pan, Z. Xiang, Z. Liu, B. Deng, X. Zhang, Z. Shi, W. Lu, Covalent organic framework-derived hollow core-shell Fe/Fe3O4@porous carbon composites with corrosion resistance for lightweight and efficient microwave absorption. Compos. Commun. 25, 100731 (2021)
F. Chen, H. Luo, Y. Cheng, J. Liu, X. Wang, R. Gong, Fe/Fe3O4@N-doped carbon hexagonal plates decorated with Ag nanoparticles for microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2, 7266–7278 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52074227), the Project of National Innovation Training Program (No. 202010626006) and Two-way Support Program of Sichuan Agricultural University (No. 2121993099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflict of interests in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, H., Yin, P., Zhang, L. et al. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on the low-frequency microwave absorption properties of carbon encapsulated nickel/nickel oxide composites. Appl. Phys. A 127, 875 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05032-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05032-4