Abstract
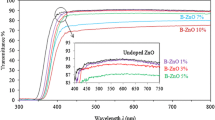
In the present paper, zinc oxide nanoflakes (ZnO NFs) have been prepared by a laser-assisted chemical bath deposition technique on a buffer metal layer of aluminum (Al). A continuous flow cavity design has been used, with a wavelength of 460 nm and a power output of 1 W, with a 30 min continuous laser irradiation period. The surface morphology and crystallinity have been investigated without/with post-annealing at 400 °C for 3 h, respectively. The field emission scanning electron microscope images show uniformly distributed, dense ZnO NFs and improved morphologies combined with EDX analysis. The XRD patterns showed that the synthesized ZnO NFs have a hexagonal wurtzite structure and exhibit a preferred orientation along the c-axis for all the samples. The crystallite size was found to be 8.72 nm and 18.70 nm, respectively. The Fourier Transform Infrared spectrum verifies the presence of vibrational modes of the Zn single bond O bond. UV–Visible spectroscopy (UV–Vis) absorbance spectra analysis indicated that the energy bandgap (Eg) for ZnO nanoparticles was found to be 3.25 eV and 3.4 eV, respectively. According to the results, the Al buffer layer plays an essential role in the growth orientation and growth rate of the ZnO NFs. However, the results showed that the post-annealing effectively modified the surface structures and topography properties of the polycrystalline ZnO thin films (TFs).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.G. Guillén, M.I.M. Palma, B. Krishnan, D. Avellaneda, G.A. Castillo, T.K.D. Roy, S. Shaji, Structure and morphologies of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in liquid: effects of temperature and energy fluence. Mater. Chem. Phys. 162, 561–570 (2015)
G.G. Guillén, S. Shaji, M.I.M. Palma, D. Avellaneda, G.A. Castillo, T.K.D. Roy, D.I.G. Gutiérrez, B. Krishnan, Effects of ablation energy and post-irradiation on the structure and properties of titanium dioxide nanomaterials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 405, 183–194 (2017)
Ü. Özgür, D. Hofstetter, H. Morkoc, ZnO devices and applications: a review of current status and future prospects. Proc. IEEE 98(7), 1255–1268 (2010)
R. Kumar, G. Kumar, O. Al-Dossary, A. Umar, ZnO nanostructured thin films: depositions, properties and applications-a review. Mater. Express 5(1), 3–23 (2015)
M. Laurenti, V. Cauda, Porous zinc oxide thin films: synthesis approaches and applications. Coatings 8(2), 67 (2018)
I.Y.Y. Bu, Novel all solution processed heterojunction using p-type cupric oxide and n-type zinc oxide nanowires for solar cell applications. Ceram. Int. 39(7), 8073–8078 (2013)
A. Naveed Ul Haq, A. Nadhman, I. Ullah, G. Mustafa, M. Yasinzai, I. Khan, Synthesis approaches of zinc oxide nanoparticles: the dilemma of ecotoxicity. J. Nanomater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8510342
Y. Zhang, M.K. Ram, E.K. Stefanakos, D. Yogi Goswami, Synthesis, characterization, and applications of ZnO nanowires. J. Nanomater. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/624520
A.B. Djurišić, X. Chen, Y.H. Leung, A.M.C. Ng, ZnO nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 22(14), 6526–6535 (2012)
E. Ferrone, R. Araneo, A. Notargiacomo, M. Pea, A. Rinaldi, ZnO nanostructures and electrospun ZnO–polymeric hybrid nanomaterials in biomedical, health, and sustainability applications. Nanomaterials 9(10), 1449 (2019)
H. Esfahani, R. Jose, S. Ramakrishna, Electrospun ceramic nanofiber mats today: synthesis, properties, and applications. Materials 10(11), 1238 (2017)
Y. Mao, Y. Li, Y. Zou, X. Shen, L. Zhu, G. Liao, Solvothermal synthesis and photocatalytic properties of ZnO micro/nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 45(2), 1724–1729 (2019)
M.A. Borysiewicz, ZnO as a functional material, a review. Crystals 9(10), 505 (2019)
M. Laurenti, V. Cauda, ZnO nanostructures for tissue engineering applications. Nanomaterials 7(11), 374 (2017)
M. Carofiglio, S. Barui, V. Cauda, M. Laurenti, Doped zinc oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and potential use in nanomedicine. Appl. Sci. 10(15), 5194 (2020)
J. Wojnarowicz, T. Chudoba, W. Lojkowski, A review of microwave synthesis of zinc oxide nanomaterials: reactants, process parameters and morphologies. Nanomaterials 10(6), 1086 (2020)
M. Sheikh, M. Pazirofteh, M. Dehghani, M. Asghari, M. Rezakazemi, C. Valderrama, J.-L. Cortina, Application of ZnO nanostructures in ceramic and polymeric membranes for water and wastewater technologies: a review. Chem. Eng. J. 391, 123475 (2020)
M.T. Noman, N. Amor, M. Petru, A. Mahmood, P. Kejzlar, Photocatalytic behaviour of zinc oxide nanostructures on surface activation of polymeric fibres. Polymers 13(8), 1227 (2021)
R.A. Gonçalves, R.P. Toledo, N. Joshi, O.M. Berengue, Green synthesis and applications of ZnO and TiO2 nanostructures. Molecules 26(8), 2236 (2021)
A.F. Abdulrahman, S.M. Ahmed, N.M. Ahmed, M.A. Almessiere, Enhancement of ZnO nanorods properties using modified chemical bath deposition method: effect of precursor concentration. Crystals 10(5), 386 (2020)
S. Shahzad, S. Javed, M. Usman, A review on synthesis and optoelectronic applications of nanostructured ZnO. Front. Mater. 8, 613825 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats
J. Villafuerte, F. Donatini, J. Kioseoglou, E. Sarigiannidou, O. Chaix-Pluchery, J. Pernot, V. Consonni, Zinc vacancy-hydrogen complexes as major defects in ZnO nanowires grown by chemical bath deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 124(30), 16652–16662 (2020)
J. Elias, R. Tena-Zaera, C. Lévy-Clément, Electrodeposition of ZnO nanowires with controlled dimensions for photovoltaic applications: role of buffer layer. Thin Solid Films 515(24), 8553–8557 (2007)
S.A.M. Tofail, E.P. Koumoulos, A. Bandyopadhyay, S. Bose, L. O’Donoghue, C. Charitidis, Additive manufacturing: scientific and technological challenges, market uptake and opportunities. Mater. Today 21(1), 22–37 (2018)
H. Palneedi, J.H. Park, D. Maurya, M. Peddigari, G.-T. Hwang, V. Annapureddy, J.-W. Kim et al., Laser processing of metal oxides: laser irradiation of metal oxide films and nanostructures: applications and advances (Adv. Mater. 14/2018). Adv. Mater. 30(14), 1870094 (2018)
H. Palneedi, J.H. Park, D. Maurya, M. Peddigari, G.-T. Hwang, V. Annapureddy, J.-W. Kim et al., Laser irradiation of metal oxide films and nanostructures: applications and advances. Adv. Mater. 30(14), 1705148 (2018)
S. Mourdikoudis, R.M. Pallares, N.T.K. Thanh, Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 10(27), 12871–12934 (2018)
F. Ruffino, M.G. Grimaldi, Nanostructuration of thin metal films by pulsed laser irradiations: a review. Nanomaterials 9(8), 1133 (2019)
J.J. Cheng, S.M. Nicaise, K.K. Berggren, S. Gradečak, Dimensional tailoring of hydrothermally grown zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Nano Lett. 16(1), 753–759 (2016)
H. Ghayour, H.R. Rezaie, S. Mirdamadi, A.A. Nourbakhsh, The effect of seed layer thickness on alignment and morphology of ZnO nanorods. Vacuum 86(1), 101–105 (2011)
G. Kenanakis, D. Vernardou, E. Koudoumas, N. Katsarakis, Growth of c-axis oriented ZnO nanowires from aqueous solution: the decisive role of a seed layer for controlling the wires’ diameter. J. Cryst. Growth 311(23–24), 4799–4804 (2009)
L.-W. Ji, S.-M. Peng, J.-S. Wu, W.-S. Shih, C.-Z. Wu, I.-T. Tang, Effect of seed layer on the growth of well-aligned ZnO nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 70(10), 1359–1362 (2009)
N.J. Ridha, F.K. Mohamad Alosfur, M.H.H. Jumali, S. Radiman, Effect of Al thickness on the structural and ethanol vapor sensing performance of ZnO porous nanostructures prepared by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. Nanotechnology 31(14), 145502 (2020)
R.T. Qu, M. Stoica, J. Eckert, Z.F. Zhang, Tensile fracture morphologies of bulk metallic glass. J. Appl. Phys. 108(6), 063509 (2010)
T.N. Otto, W. Habicht, E. Dinjus, M. Zimmerman, Catalyst Characterization with FESEM/EDX by the Example of Silver-Catalyzed Epoxidation of 1, 3-Butadiene (IntechOpen, London, 2012)
L.J. Allen, A.J. D’Alfonso, B. Freitag, D.O. Klenov, Chemical mapping at atomic resolution using energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy. MRS Bull. 37(1), 47–52 (2012)
A.S.Z. Lahewil, Y. Al-Douri, U. Hashim, N.M. Ahmed, Structural and optical investigations of cadmium sulfide nanostructures for optoelectronic applications. Sol. Energy 86(11), 3234–3240 (2012)
A.S.Z. Lahewil, Y. Al-Douri, U. Hashim, N.M. Ahmed, Structural, analysis and optical studies of cadmium sulfide nanostructured. Procedia Eng. 53, 217–224 (2013)
A.S.Z. Lahewil, Y. Al-Douri, U. Hashim, N.M. Ahmed, Structural and morphological studies of cadmium sulfide nanostructures. Adv. Mater. Res. 795, 228–232 (2013)
J.G. Lu, Z.Z. Ye, Y.J. Zeng, L.P. Zhu, L. Wang, J. Yuan, B.H. Zhao, Q.L. Liang, Structural, optical, and electrical properties of (Zn, Al) O films over a wide range of compositions. J. Appl. Phys. 100(7), 073714 (2006)
S.-F. Tseng, Investigation of post-annealing aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) thin films by a graphene-based heater. Appl. Surf. Sci. 448, 163–167 (2018)
Z. Ye, J. Li, M. Zhou, H. Wang, Y. Ma, P. Huo, Yu. Longbao, Y. Yan, Well-dispersed nebula-like ZnO/CeO2@ HNTs heterostructure for efficient photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 304, 917–933 (2016)
M.J. Kadhim, M.A. Mahdi, J.J. Hassan, A.S. Al-Asadi, Photocatalytic activity and photoelectrochemical properties of Ag/ZnO core/shell nanorods under low-intensity white light irradiation. Nanotechnology 32(19), 195706 (2021)
S. Paiman, T.H. Ling, M. Husham, S. Sagadevan, Significant effect on annealing temperature and enhancement on structural, optical and electrical properties of zinc oxide nanowires. Results Phys. 17, 103185 (2020)
P. Bindu, S. Thomas, Estimation of lattice strain in ZnO nanoparticles: X-ray peak profile analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 8(4), 123–134 (2014)
S.M. Mohammad, Z. Hassan, N.M. Ahmed, N.H. Al-Hardan, M. Bououdina, Fabrication of low-cost UV photo detector using ZnO nanorods grown onto nylon substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26(3), 1322–1331 (2015)
M.J. Chithra, M. Sathya, K. Pushpanathan, Effect of pH on crystal size and photoluminescence property of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by chemical precipitation method. Acta Metall. Sin. (English Letters) 28(3), 394–404 (2015)
P. Kumbhakar, D. Singh, C.S. Tiwary, A.K. Mitra, Chemical synthesis and visible photoluminescence emission from monodispersed ZnO nanoparticles. Chalcogenide Lett. 5(12), 387–394 (2008)
P. Bindu, S. Thomas, Optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesised from a polysaccharide and ZnCl2. Acta Phys. Pol. A 131(6), 1474–1478 (2017)
R.N. Moussawi, D. Patra, Modification of nanostructured ZnO surfaces with curcumin: fluorescence-based sensing for arsenic and improving arsenic removal by ZnO. RSC Adv. 6(21), 17256–17268 (2016)
J. Winiarski, W. Tylus, K. Winiarska, I. Szczygieł, B. Szczygieł, XPS and FT-IR characterization of selected synthetic corrosion products of zinc expected in neutral environment containing chloride ions. J. Spectrosc. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2079278
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the School of Physics Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for providing the research facilities and support. We appreciate the financial support from the RCMO USM through the Short-Term Grant (304/PFIZIK/6315514).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahewil, A.S.Z., Ahmed, N.M. & Azman, N.Z.N. Structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoflakes/Al/glass via laser-assisted chemical bath deposition (LACBD) technique. Appl. Phys. A 127, 836 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04996-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04996-7