Abstract
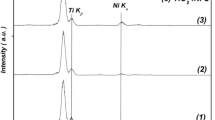
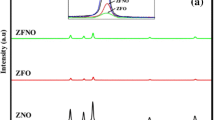
Fe/Ga- and Fe/Zn-codoped titanium oxide nanoparticles were prepared by co-precipitation technique. The samples were characterized by several methods: energy-dispersive X‐ray fluorescence, X‐Ray Diffraction, UV–visible absorption, and magnetization methods. The host Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles were co-doped either with Ga3+ or Zn2+ ions aiming to compare their effects on the possible creation of long-range (LR) interaction between Fe2+−Fe2+ dopant ions. The hydrogenation of the samples was necessary to fabricate the dilute magnetic semiconductor based on TiO2 by its creation of O-vacancies (VO). It was established that Zn/VO defects are energetically favourable for the LR Fe3+−Fe3+ ferromagnetic coupling in Fe/Zn-codoped anatase TiO2 by the superexchange interaction through Zn ions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Rahimi, R.A. Pax, E. Mac, A. Gray, Review of functional titanium oxides I: TiO2 and its modifications. Prog. Solid State Chem. 44(3), 86–105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2016.07.002
D. Reyes-Coronado, G. Rodrıguez-Gattorno, M.E. Espinosa-Pesqueira, C. Cab, R. de Coss, G. Oskam, Phase-pure TiO2 nanoparticles: anatase, brookite and rutile. Nanotechnology 19, 145605 (2008)
P.V. Kala, B.T. Rao, K. Srinivasarao, Structural, optical and gas sensing properties of TiO2-MoO3, thin films. Int. J. Thin. Fil. Sci. Tec. 8(3), 163–174 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18576/ijtfst/080309
V. Sivaranjani, P. Deepa, P. Philominathan, Thin Films of TiO2-MoO3 binary oxides obtained by an economically viable and simplified spray pyrolysis technique for gas sensing application. Int. J. Thin. Fil. Sci. Tec. 4, 125–131 (2015). https://doi.org/10.18576/ijtfst/080309
B. Qi, S. Olafsson, H.P. Gislason, Vacancy defect-induced d0 ferromagnetism in undoped ZnO nanostructures: controversial origin and challenges. Prog. Mater. Sci. 90, 45–74 (2017)
R. Marchand, L. Brohan, M. Tournoux, TiO2(B) a new form of titanium dioxide and the potassium octatitanate K2Ti8O17. Mater. Res. Bull. 15(8), 1129–1133 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5408(80)90076-8
J. Tian, H. Gao, H. Deng, L. Sun, H. Kong, P. Yang, J. Chu, Structural, magnetic and optical properties of Ni-doped TiO2 thin films deposited on silicon(100) substrates by sol-gel process. J. Alloy. Compds. 581, 318–323 (2013)
Lu. Xuefeng, Xu. Tingting Zhao, Junqiang Ren Gao, Xiaobin Yan, Peiqing La, Investigation of Mo-, Pt-, and Rh-doped rutile TiO2 based on first-principles calculations. AIP Adv. 8, 075014 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5038776
Y. Ma, X. Wang, Y. Jia, X. Chen, H. Han, C. Li, Titanium dioxide-based nanomaterials for photocatalytic fuel generations. Chem. Rev. 114, 9987–10043 (2014)
A. Di Paola, M. Bellardita, L. Palmisano, Brookite, the least known TiO2 photocatalyst. Catalysts 3, 36–7 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010036
R. Mukherji, V. Mathur, A. Samariys, M. Mukherji, Experimental and theoretical assessment of Fe-doped indium-oxide-based dilute magnetic semiconductors. Phil. Mag. 99, 2285–2302 (2019)
A. Gupta, R. Zhang, P. Kumar, V. Kumar, A. Kumar, Nano-structured dilute magnetic semiconductors for efficient spintronics at room temperature. Magnetochemistry 6(1), 15 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry6010015
A.C.M. Padilha, H. Raebiger, A.R. Rocha, G.M. Dalpian, Charge storage in oxygen deficient phases of TiO2: defect Physics without defects. Sci. Rep. 6–28871, 1–6 (2016)
Y. Xu, C. Zhang, L. Zhang, X. Zhang, H. Yao, J. Shi, Pd-catalyzed instant hydrogenation of TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic performance Energy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 9, 2410–2417 (2016)
A. Bouaine, N. Brihi, G. Schmerber, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, S. Colis, A. Dinia, Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of co-doped SnO2 Powders synthesized by the co-precipitation technique. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 2924–2928 (2007)
Md.K. Debashis Roy, S.M. Hossain, Milon Hasan, Md. AbdulHossain, F. Ahmed, Understanding the atomistic origin of the magnetic phases in Cobalt-TM (V, Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf, W) pair co-doped boron nitride monolayer and the hydrogenation effect. Physica E: Low-dimensional Syst Nanostructures 125, 114359 (2012)
A.A. Dakhel, M. El-Hilo, M. Bououdina, Ferromagnetic properties of Cu- and Fe-codoped nanocrystalline CdO powders: annealing in hydrogen promote long-range ferromagnetic order. Adv. Pow. Tech. 25, 1839–1844 (2014)
M. El-Hilo, A.A. Dakhel, Z.J. Yacoob, Magnetic interactions in Co2+ doped ZnO synthesized by co-precipitation method: efficient effect of hydrogenation on the long-range ferromagnetic order. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 482, 125–134 (2019)
A.A. Dakhel, Hydrogenation tuned the created ferromagnetic properties of Ni doped nano- ZnO. Appl. Phys. A 123(214), 2–8 (2017)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751–767 (1976)
C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, 7th edn. (Wiley, USA, 1996), p. 614
A.A. Dakhel, Structural, magnetic, and optical properties of degenerated Ni and (Ga/Zn) co-doped TiO2 nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. A 126(12), 1–9 (2020)
S.M. Gupta, M. Tripathi, A review of TiO2 nanoparticles. Chinese Sci. Bulletin 56, 1639–1657 (2011)
Yu. Yanlong, J. Wang, W. Li, W. Zheng, Y. Cao, Doping mechanism of Zn2+ ions in Zn-doped TiO2 prepared by a sol–gel method. CrystEngComm 17, 5074–5080 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CE00933B
L.B. McCusker, R.B. Von Dreele, D.E. Cox, D. Louer, P. Scardi, Rietveld refinement guidelines. J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 36 (1999)
K. Tanaka, Y. Akiniwa, diffraction measurements of residual macrostress and microstress using X-rays, synchrotron and neutrons, Jap. Soc. Mech. Eng. (JSME) Int. J. A 47(3), 252–263 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1299/jsmea.47.252
M. Pozzo, D. Alfe, Hydrogen dissociation and diffusion on transition metal (=Ti, Zr, V, Fe, Ru Co, Rh, Ni, Pd, Cu, Ag)-doped Mg (0001) surface. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 34, 1922–1930 (2009)
A.E. Morales, E.S. Mora, U. Pal, Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Revista Mexicana de Fisica S 53, 18–22 (2007)
J. Tauc, F. Abelesn (eds.), Optical Properties of Solids (North Holland, Springer, 1969), pp. 123–136
D. Sojic, V. Despotovic, B. Abramovic, N. Todorova, T. Giannakopoulou, C. Trapalis, Photocatalytic degradation of mecoprop and clopyralid in aqueous suspensions of nanostructured N-doped TiO2. Molecules 15, 2994–3009 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15052994
F.N.C. Anyaegbunam, C. Augustine, A study of optical gap associated urbach energy tail of chemically deposited metal oxides binary films. Dig. J. Nanomater. Bios. 13, 847–856 (2018)
N.J. Kim, Y.H. La, S.H. Im, B.K. Ryu, Optical and structural properties of Fe–TiO2 thin films prepared by sol–gel dip coating. Thin Solid Films 518, 156–160 (2010)
G. Wei, L. Wei, Y. Chen, S. Yan, Y. Tian, L. Mei, J. Jiao, Magnetic coupling and electric transport in Nb, Fe co-doped rutile TiO2 epitaxial films. J. Alloy. Compds. 695, 2261–2265 (2017)
J.I. Pankove, Optical Processes in Semiconductors (Dover, NY, 1975), p. 36
The web page of the University of the West Indies at Mona, Jamaica, The Dept. of Chemistry, http://wwwchem.uwimona.edu.jm/spectra/MagMom.html. accessed May. 2020.
J. Chen, P. Rulis, L. Ouyang, S. Satpathy, W.Y. Ching, Vacancy-enhanced ferromagnetism in Fe- doped rutile TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 74, 235207 (2006)
J.M.D. Coey, M. Venkatesan, C.B. Fitzgerald, Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nat. Mater. 4, 173–179 (2005)
M. Yeganeha, N. Shahtahmasebi, A. Kompany, M. Karimipour, F. Razavi, N.H.S. Nasralla, L. Šiller, The magnetic characterization of Fe doped TiO2 semiconducting oxide NPs synthesized by sol–gel method. Phys. B 511, 89–98 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dakhel, A.A. Microstructural, optical and magnetic properties of TiO2:Fe:M (M = Ga, Zn) dilute magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles: a comparative study. Appl. Phys. A 127, 440 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04588-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04588-5